Diseases
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
DIC syndrome (disseminated intravascular coagulation) is a pathological nonspecific process triggered by the entry into the bloodstream of factors that activate platelet aggregation (gluing) and blood coagulation. Thrombin is formed in the blood, activation and rapid depletion of plasma enzyme systems (fibrinolytic, kallikrein-kinin, coagulation)
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Demyelination is a pathological process in which the myelin sheath of nerve fibers is destroyed. The myelin sheath performs an insulating function: it ensures the propagation of an electrical impulse along the fiber without energy loss. Demyelination causes impairment of functional activity of structures involved in the pathological process
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Surprisingly, but true: almost everyone is a carrier of tiny, but very unpleasant mites - Demodexes. Usually they do not manifest themselves in any way, however, when a number of conditions coincide, domodexes are activated and lead to demodicosis
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
According to the definition of the World Health Organization, dementia is a syndrome of acquired memory impairment in combination with one of the following disorders: speech impairment, impaired ability to perform complex purposeful planned actions (praxis), or the ability to recognize objects and their characteristics based on sensations (gnosis), - noted on for at least six months and hindering work or limiting the patient's social activity
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Depersonalization is a mental disorder, a feature of which is the patient's perception of himself from the outside
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Derealization is a mental illness in which the patient's perception of the world is impaired
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
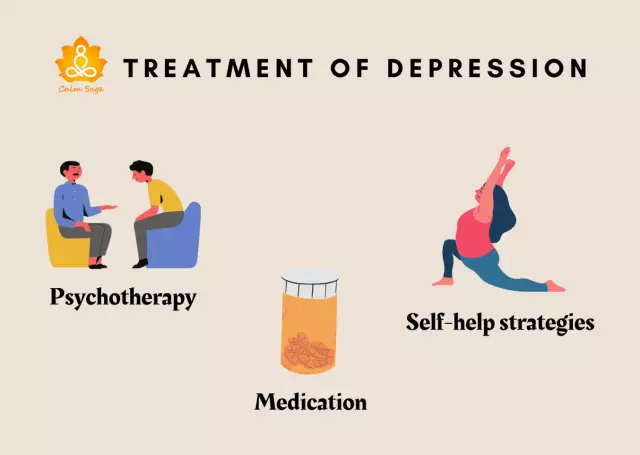
Depressive syndrome is manifested by mental and physical disorders: depressed mood, slowing down of mental processes, decreased general tone, indigestion, sleep
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Dermatofibroma - a disease characterized by a benign formation on the skin
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Dumping syndrome (from the English dumping - "dumping", "dropping") - a pathological condition characterized by accelerated evacuation of not properly processed stomach contents into the small intestine
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Bilateral pneumonia - acute inflammation of both lungs with a high risk of developing respiratory failure
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Dermatoses are an extensive group of heterogeneous diseases of the skin and its appendages of various origins (infectious, allergic, immune, etc.), caused by both external and internal (endogenous) causes. This group does not include transient changes in the skin that accompany many diseases and conditions
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
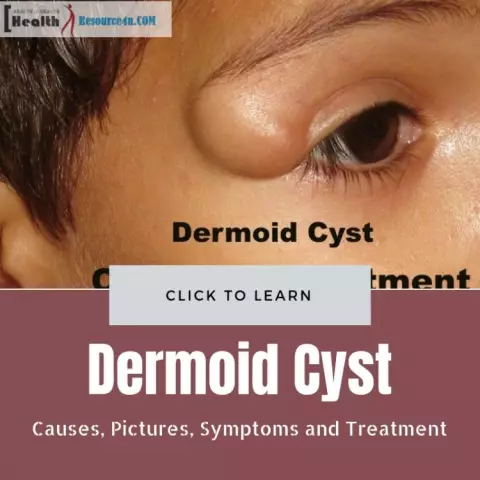
A dermoid cyst is a benign mass that consists of the epidermis, dermis, sebaceous glands, hair follicles and hair
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Dermographism (artificial urticaria) is an abnormal reaction of the skin that occurs as a result of minor mechanical stress and is characterized by the appearance of stripes of red or white
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Dermatomyositis (generalized fibromyositis, generalized myositis, angiomyositis, sclerodermatomyositis, poikilodermatomyositis, polymyositis) is a systemic inflammatory disease that affects muscle tissue, skin, capillaries and internal organs
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Roseola infantile is an infection that usually affects young children. There is no specific treatment for baby roseola. To alleviate the condition of the child during the rise in temperature, he is given antipyretic drugs
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Cerebral palsy is a congenital disease of the parts of the brain during intrauterine development. Treatment involves the use of drugs aimed at improving brain function
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
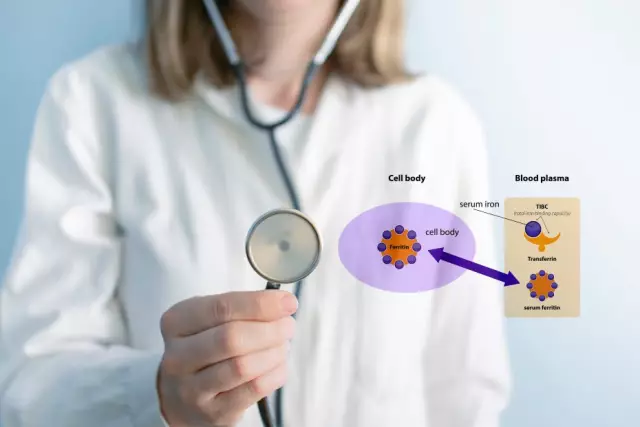
Iron deficiency is a pathological condition characterized by a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin and erythrocytes
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
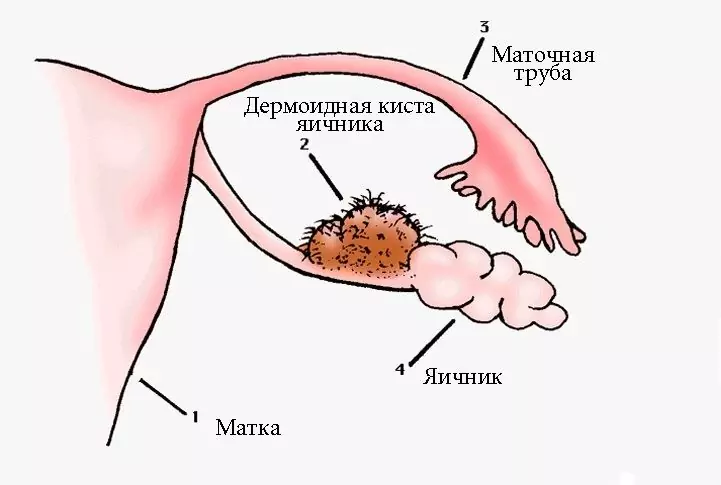
Dermoid ovarian cyst - a benign germ cell neoplasm that develops from germ cells atypically located in the ovaries
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Iodine deficiency is a dangerous condition of a person, the symptoms of which are drowsiness, lethargy, bad mood, impairment of attention and memory
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Injuries, bruises, pathological changes in muscles - all this can lead to the appearance of deformity of the foot, that is, to a change in its appearance and other serious complications
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Destruction of the vitreous humor is the partial or complete destruction of the vitreous humor of the eyeball
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
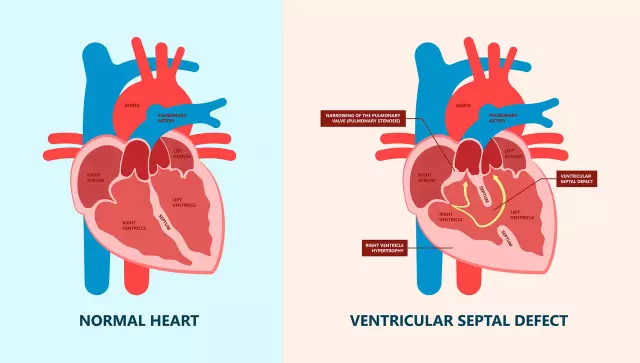
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital defect, which is a non-closure (of different area) of the inner wall of the heart that separates the right atrium from the left
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
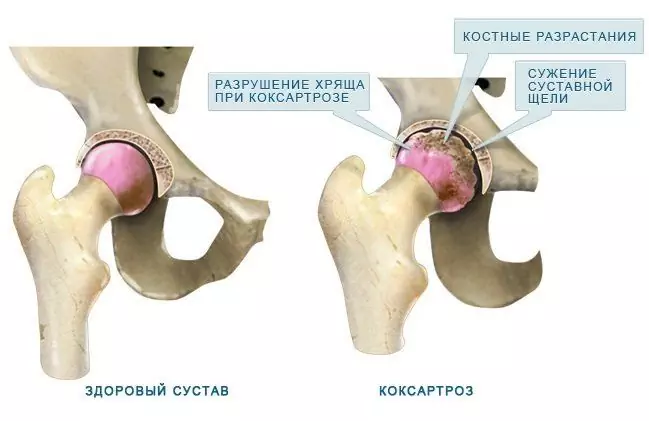
Deforming arthrosis is a widespread disease of the musculoskeletal system that most often affects the hip and knee joints
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Osteoarthritis deformans is a progressive non-inflammatory joint disease associated with an imbalance between the destruction and repair of cartilage tissue
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Jetlag (from the English jet - "jet", lag - "delay") is a sleep disorder that develops when changing 2 or more time zones in a limited period of time
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Diabetic retinopathy is one of the types of microangiopathy that develops against the background of long-term diabetes mellitus and affects the blood vessels of the retina. This pathology is the main cause of low vision and blindness in people with diabetes
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Diabetic nephropathy is kidney damage that is common in patients with diabetes. The basis of the disease is damage to the renal vessels and, as a consequence, developing functional organ failure
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Diabetic coma is a dangerous and serious condition caused by relative or absolute insufficiency of insulin and characterized by serious metabolic disorders. Unlike hypoglycemic coma, diabetic coma develops gradually and can last for a very long time. The medical literature describes a case when the patient was in a coma for over 40 years
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Diabetic neuropathy is a dystrophic lesion of peripheral nerves caused by metabolic disorders arising in the setting of diabetes mellitus. The disease is manifested by impaired sensitivity and autonomic dysfunction
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Diathesis is a predisposition of the body to the development of certain pathological reactions or diseases that usually manifest themselves in childhood
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Diverticulosis is a pathological process characterized by the formation of diverticulums (saccular protrusions) on the intestinal walls
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Diabetic polyneuropathy is one of the most severe complications of diabetes mellitus, characterized by degenerative processes in the nerve fibers
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Diathesis in children - a predisposition to certain diseases or an increased sensitivity of the body to common stimuli
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Diaphragmatic hernia is a common gastroenterological disease. It requires long-term treatment to prevent the development of complications
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Intestinal diverticulosis is a disease in which small, saccular protrusions of the walls of the large (less often small) intestine form outward
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon is a common pathology. It often proceeds without any symptoms and remains undiagnosed
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Diverticulitis is a disease characterized by inflammation of diverticulum that occurs on the intestinal wall during infection
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Dysarthria is a severe speech disorder as it is associated with malfunctions in the central nervous system. Dysarthria is most often diagnosed after five years
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Dysentery is an acute or chronic infection that proceeds with symptoms of general intoxication and affects the large intestine of a person. The disease can be either acute or chronic
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Dicroceliosis is an invasive disease that occurs when infected with a lanceolate fluke, a parasite in the body of both wild and domestic animals, and humans. This biohelminthiasis is accompanied by damage to the gallbladder and liver. Human dicroceliosis is a relatively rare pathology that occurs sporadically almost everywhere; the highest incidence rates are observed in the southern regions