Diseases
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Meniere's disease, a condition caused by an increase in fluid in the ear cavity due to a disorder of the inner ear
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
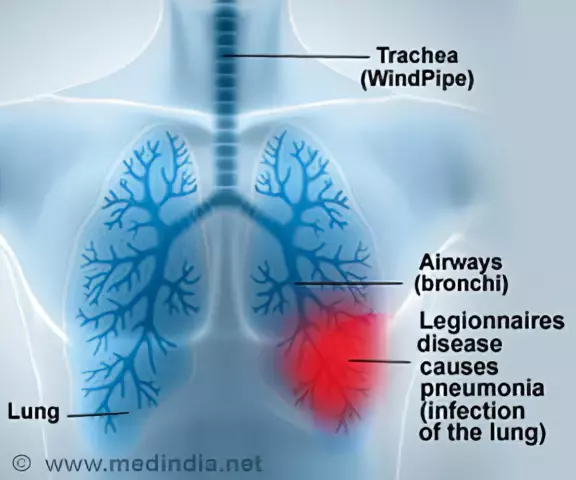
Legionnaires' disease is an infectious disease caused by a microorganism of the genus Legionella
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
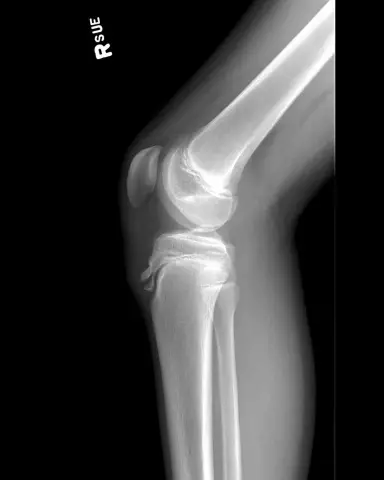
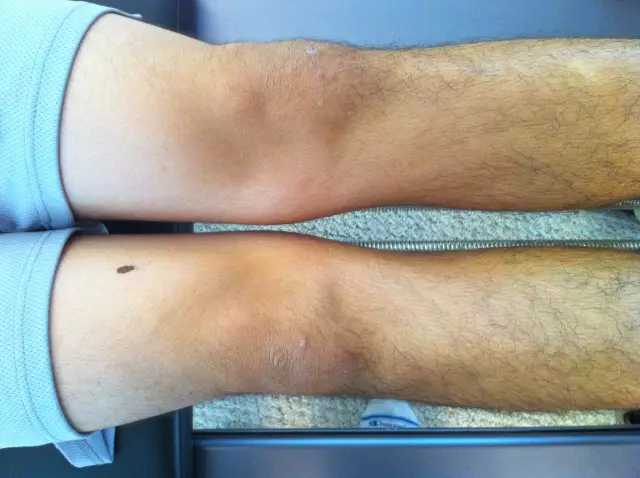
Osgood Schlatter's disease - a disease characterized by a pathological change in the tibia that occurs due to inflammatory processes in the cartilage structure and bone
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Huntington's disease is a severe, progressive neurodegenerative brain disease characterized by progressive dementia and choreic hyperkinesis. It occurs with a frequency of 10 cases per 100,000 population, in men and women equally. The first symptoms can appear at any age, but usually the onset of the disease occurs at 30-50 years
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Gunther's disease (congenital erythropoietic porphyria) is a rare hereditary disease in which pigment metabolism is impaired and a nitrogen-containing pigment (porphyrin) accumulates in the tissues. With this disease in the later stages, the appearance of patients is disfigured
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Peyronie's disease - curvature of the penis followed by fibrotic changes
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Raynaud's disease or Raynaud's phenomenon is one of the diseases of the arteries of the extremities. Treatment of the disease occurs in the relief of symptoms of the disease and prevention of the causes that cause attacks of the disease
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Whipple's disease is a systemic infectious disease characterized by damage to the small intestine
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Huntington's disease is a very rare disease characterized by hereditary brain pathology
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Schlatter's disease is a necrosis of the cartilaginous and bone tissues of the upper part of the tibia. Electrophoresis treatment is effective
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Perthes disease (Perthes-Legg-Calvet disease, osteochondropathy of the femoral head) is a disease of the hip joint, which is based on a violation of the blood supply to the femoral head, leading to its necrosis
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Parkinson's disease is a chronic, steadily progressive brain disease in which neurodegenerative changes are observed in the structures of the substantia nigra
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Pick's disease is a variant of senile dementia (senile acquired dementia), the development of which is associated with atrophy of the cerebral cortex in the region of the frontal and temporal lobes
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
This article will focus on botulism, an infectious disease that is caused by poor quality cooked food. The reader will learn about the causes, symptoms and treatments for botulism
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Still's disease is a systemic disease that manifests itself as polyarthritis, fever, transient skin rashes, and inflammatory damage to internal organs
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Delusional disorder is a psychological disease, the main difference of which is the presence of systematic delusions
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Warts in children are a viral skin disease in which small benign neoplasms form on the skin
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Brachydactyly (short-fingered) is a congenital pathology, the main manifestation of which is shortening of the toes or hands (from ancient Greek βραχύς - "short" and δάκτυλος - "finger") due to hypo- or aplasia of the distal phalanges or bones of the metacarpus (metatarsus)
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Bradycardia is a type of arrhythmia that is manifested by a low heart rate. Often this condition develops as a variant of the norm and does not require treatment
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Bronchiectasis is a disease characterized by the destruction of muscles and lung tissue
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Bronchiolitis is an inflammatory disease of the bronchioles, observed mainly in children under two years of age, which is characterized by seasonal epidemiological outbreaks
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (bronchopulmonary dysplasia) is a chronic lung disease that develops in children during the neonatal period during the treatment of respiratory disorders using artificial ventilation of the lungs with a high oxygen concentration
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
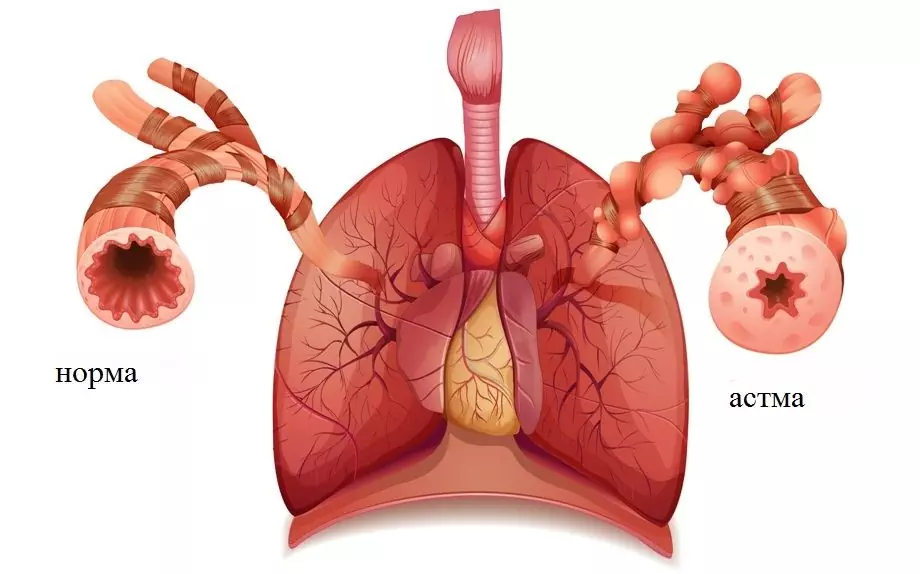
Bronchial asthma in children is a disease manifested by recurrent attacks of suffocation. Often disguised as other respiratory diseases
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Typhoid fever - an infectious disease characterized by damage to the intestinal lymphatic system
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Bruxism - recurrent grinding of teeth, manifestation of increased tonic tension of the chewing muscles, intense clenching of the jaws and (or) their movement relative to each other
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Bulimia is an eating disorder that results in bouts of uncontrolled overeating, usually followed by cleansing rituals such as vomiting or laxatives
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Bronchopneumonia is a type of pneumonia in which not only the lung tissue is affected, but also the adjacent structural elements of the bronchial tree. The inflammatory process in this case is focal in nature: it is common within a segment, lobule or acinus
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Bronchitis in children is a polyetiological inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane of the walls of the bronchi of various sizes, which is common in pediatric practice
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Bulbar syndrome is a dysfunction of the medulla oblongata or its individual formations. It manifests itself mainly in swallowing and speech disorders
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Disease bursitis is an acute or chronic periarticular inflammation of the mucous membranes of the synovial bag. Treatment is usually carried out in a hospital setting for 7-10 days
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Epidermolysis bullosa is a large group of hereditary diseases that are characterized by the formation of blisters on the mucous membranes and skin (spontaneous or under the influence of minor traumatic effects). The incidence rate of epidermolysis bullosa is 1 to 3 cases per 100,000 population
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Bulbit - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the duodenal bulb, a special case of duodenitis
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Bursitis of the elbow joint is an inflammatory disease in which the pathological process is localized in the synovial bursa of the elbow joint
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Knee bursitis is an inflammation of the periarticular sac. The causes of the disease can be different; for proper treatment, their exact establishment is necessary
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Shoulder bursitis is an inflammation of the bursae of the shoulder joint. It can be aseptic or infectious, acute or chronic
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Infection with household syphilis occurs through contact and household contact. The transmission channel does not affect the severity of the disease
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Dacryocystitis is a blockage of the nasolacrimal canal due to inflammation of the lacrimal sac. The standard of treatment for dacryocystitis is the systemic application of massage. The purpose of the massage is to break the gelatinous film
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
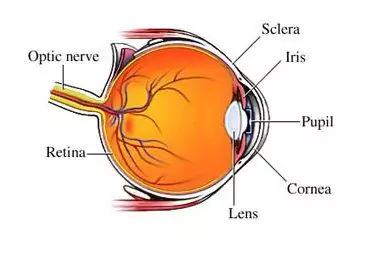
Farsightedness or hyperopia is an ophthalmic disease with impaired visual acuity when looking at nearby objects. The main sign of hyperopia is poor vision at close range
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Color blindness is called a violation of the color perception of the eye, the inability to distinguish mainly between green and red. There are currently no effective treatments for color blindness
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Dementia or dementia is one of the types of cognitive mental disorders associated with the cognitive sphere of a person. There is currently no effective treatment for dementia