- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Vibration sickness
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Forms of the disease
- Disease stages
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications and consequences
- Forecast
- Prevention
Vibration disease is a complex of pathological changes that develop in the body as a result of prolonged exposure to vibration.
Vibration disease arises from the action of vibration (from the Latin vibratio - "trembling, vibration") or frequently repeated mechanical influences. Usually occurs as an occupational disease.
For the first time the pathology was described in 1911 by the Italian physician J. Loriga.
Synonyms: vibration syndrome, vibrational angioneurosis, pseudo-Raynaud's disease, white finger syndrome.

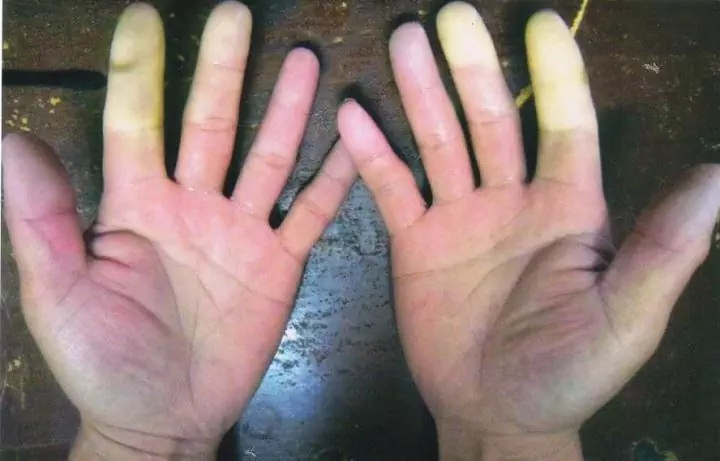
External manifestations of vibration disease
Causes and risk factors
The causes of vibration can be:
- local - the traumatic effect is on a certain part of the body, for example, on the hands when working with pneumatic tools, hand rammers;
- general - the effect is on the entire surface of the body (in transport, etc.);
- combined - combining local and general exposure to vibration.
The mechanism of development of the disease is based on the reflex-humoral reaction of the body in response to vibration. This reaction involves receptors in the skin, cardiovascular, muscular and skeletal systems. Vibration causes microtrauma to the peripheral nervous and circulatory systems and is manifested by impaired blood circulation and trophism (nutrition) of the tissue.

Vibration sickness is caused by vibration
The effect of vibration on the body depends on the strength, frequency and duration of exposure. One of the important parameters is the oscillation frequency, which is measured in hertz (Hz). There is evidence of the following reactions of the body to a certain frequency of oscillations:
- vibrations up to 15 Hz cause a reaction of the vestibular apparatus, displacement of organs;
- fluctuations of 15-25 Hz lead to changes in the tissues of bones and joints, can manifest themselves as sensations of separate shocks (palleesthesia);
- fluctuations of 50-250 Hz cause reactions from the cardiovascular and nervous systems.
Higher frequencies are related to ultrasound, which entails a transformation of mechanical energy into heat.
The most dangerous range for humans is from 15 to 250 Hz.
In addition, risk factors include:
- individual sensitivity of the body;
- incorrect posture during work, tense or forced body position;
- overwork, constant background noise, hypothermia and other factors that reduce the body's resistance to stress.
Forms of the disease
It takes time for the development of vibration disease: as a rule, we are talking about years and even decades spent in conditions of regularly exposed vibration, therefore, the pathology is characterized by a chronic course. The acute form is extremely rare - in cases of intense vibration or explosion; this form of the disease is called vibration trauma and is considered a separate pathology.
Disease stages
The staging of vibration disease is considered taking into account the degree, area and time of vibration exposure. In total, there are 4 stages of vibration disease:
- Initial.
- Moderately pronounced.
- Expressed.
- Generalized.

Stages of vibration disease
Symptoms
The disease in the initial (I) stage has the following manifestations:
- malaise;
- low body temperature;
- decreased sensitivity (slight numbness) and slight pain in the fingers, muscles of the shoulder girdle;
- rare spasms of the fingers.
At this stage, all changes are reversible.
At stage II, the body's compensatory mechanisms are depleted. Her symptoms:
- persistent decrease in body temperature;
- decreased sensitivity of the fingers;
- cramps in the fingers of the upper and lower extremities;
- weakness and pain in the limbs - aching, breaking, pulling, which are sometimes accompanied by "goose bumps" and disturb at night or during rest;
- increased fatigue;
- anxiety, nervousness.
Stage III disease is rare, the changes are persistent and difficult to treat. Her symptoms:
- paroxysmal cramps of the hand and foot (one or both), calf muscles;
- stiff fingers;
- with cooling (and sometimes spontaneously), a sharp whitening, and then an equally sharp blue in one or both hands;
- thinning and deformation of the nail plates of the fingers;
- a decrease in the sensitivity of certain muscle groups of the shoulder girdle, indicating the defeat of individual centers in the spinal cord;
- disorders of the endocrine system.

Persistent circulatory disorders are characteristic of the later stages
At stage IV, violations take on a general, generalized nature:
- persistent circulatory disorders that cause tissue trophic disorders up to the formation of foci of necrosis (usually localized on the extremities);
- violation of cerebral circulation (manifested by a decrease in memory and concentration of attention, a disorder of coordination of movements, etc.);
- pathological changes in the spine (osteochondrosis and other pathologies).
In addition, at stages III and IV of vibration disease, the following are noted:
- general poor physical and psycho-emotional well-being;
- persistent headaches;
- sleep disorders;
- nausea and motion sickness when traveling in transport;
- constricting pain in the heart and stomach;
- gastrointestinal disorders;
- endocrine disorders.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is assumed on the basis of a characteristic clinical picture and anamnesis data, the connection between complaints of well-being and working conditions is revealed.
They also resort to a number of laboratory and instrumental methods. It is mandatory to conduct:
- general and biochemical blood test, general urine test;
- electrocardiography;
- X-ray of the chest cavity organs, hands, feet, spine.
In order to confirm the diagnosis, special methods are used:
- cold test - the state of the sympathetic nervous system is assessed;
- Paul's test - the blood filling of the vessels of the same name on different limbs is determined;
- white spot test - the time of the onset of vasospasm of the hands is estimated;
- test for reactive hyperemia - to restore vascular tone after compression;
- algesimetry - pain sensitivity of the forearm, lower leg, fingers and toes is established;
- pallesiometry - the threshold of vibration sensitivity is determined;
- skin thermometry - the severity of vascular changes in the hands is established;
- capillaroscopy - changes in the capillaries of the nail bed on the fourth finger of the right hand and the first finger are detected;
- hand dynamometry - the strength of flexion of the fingers is determined;
- thermoesthesiometry - the ability to distinguish temperature differences up to 5 ° C is established;
- hemodynamic test (Bogolepov's test) - for blood filling of the hands when the position of body parts in space changes;
- Doppler ultrasound (USDG) - examines the arterial and venous blood flow of the extremities;
- rheovasography - the pulse filling of the vessels of the hands and forearm with blood is determined.

Doppler ultrasound examines the arterial and venous blood flow of the extremities
There are other ways to study the effects of vibration sickness.
Treatment
The main condition for effective treatment is the elimination of vibration loading. Therapeutic measures for vibration disease are aimed at restoring blood circulation and metabolic processes in the muscular and nervous system. For this purpose, the following are used:
- drug therapy (vitamins, vasodilators, drugs that improve tissue trophism and microcirculation);
- physiotherapy (electrophoresis, galvanic and mineral baths, UHF and UV irradiation, massage, acupuncture, mud applications);
- physiotherapy;
- spa treatment.

Physiotherapy is indicated as part of the complex treatment of vibration disease
Possible complications and consequences
The prolonged course of vibration disease causes deep and varied disturbances in the nervous, cardiovascular, digestive and endocrine systems. The extreme degree of manifestation of the disease is profound disability.
Forecast
With timely diagnosis, treatment and adherence to medical recommendations, the prognosis is favorable.
Prevention
To prevent vibration disease, people whose work activity is associated with constant exposure to vibration must:
- comply with labor protection measures;
- in the process of work, use tools, equipment, special work clothes with devices that damp vibration;
- timely undergo preventive medical examinations;
- after each shift, self-massage the limbs;
- eat well, make sure that the diet contains sufficient amounts of foods containing vitamins B1 (bran, meat, liver, brewer's yeast, eggs, seeds) and C (rose hips, black currants, citrus fruits, bell peppers, tomatoes, onions, leafy greens).
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!