- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Papillomas in the vagina
The content of the article:
- Reasons for the appearance of vaginal papillomas
- How pathology manifests itself
- Diagnostic methods
-
How to treat
- General therapy
- Destructive treatments
- Are vaginal papillomas dangerous?
- Is it possible to prevent the disease
- Video
Papillomas are benign growths that can appear anywhere on the skin and mucous membranes, from the head to the genitals. The cause of their appearance is human papillomavirus infection (human papillomavirus, HPV). Papillomas in the vagina not only bring discomfort to a woman, but are also associated with a high oncogenic risk. There is no specific drug treatment for papillomatosis, surgical removal of formations is used - cryodestruction, laser therapy, electrocoagulation.

Papillomas in the vagina are found during a pelvic exam
Reasons for the appearance of vaginal papillomas
The main reason for the appearance of genital warts and warts is papillomavirus infection. Today, about 100 species and more than 600 strains of papillomaviruses are known. Some of them have oncogenic properties, that is, they can cause malignant degeneration of tissues - cancer of the cervix, external genital organs.
The disease develops in people with weakened immunity. The following conditions may contribute to a decrease in the function of the immune system:
- taking glucocorticoids and cytostatics;
- oncological diseases of any localization;
- chronic intoxication;
- irradiation;
- chronic infectious diseases (viral hepatitis, helminthiasis);
- deficiencies of vitamins and proteins in the diet;
- kidney disease (chronic glomerulonephritis, chronic renal failure);
- consequences of injuries and massive operations.
In most cases, infection occurs through sexual contact. But papillomas at the entrance to the vagina can appear even without sexual contact, for example, with household infection - visiting public places (swimming pool, bathhouse, toilet). Infection is facilitated by a violation of the integrity of the skin and mucous membrane - scratches, minor injuries, abrasions. Self-infection is also possible during epilation and shaving. The incubation period is 1-2 months, that is, the growth does not appear immediately after infection.
How pathology manifests itself
Papillomas are small formations in the form of nodules that rise above the skin. What do vaginal papillomas look like (seen in the photo):
- Outwardly, they look like a papilla, they can grow, taking the form of a cock's comb.
- In most cases, they are flesh-colored, the color can vary from white to brown.
- They can be single or multiple (in this case, the disease is called papillomatosis).
- The size is from 0.2 to 2 mm, much less often the formation grows to 1-2 cm.
- Localization can be different: the walls of the vagina, the area of the labia majora and labia majora, the perineum, near the anus.
- In most cases, additional symptoms are absent, the disease has asymptomatic treatment. Formations are detected only on examination.
Diagnostic methods
If papillomas are found in the vagina, it is better to consult a doctor. Diagnosis of pathology is not difficult - papilloma can be detected during a routine examination.
What studies can be assigned additionally:
- Colposcopy is a method of visual assessment of the vaginal mucosa under 10x magnification.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of vaginal scrapings. With the help of PCR, you can determine the pathogen and its type, the degree of oncogenicity.
After examination and research, a decision is made on the need to remove neoplasms.
How to treat
There are no specific medications that would allow getting rid of human papillomavirus infection. Therapy consists in the removal of neoplasms, that is, in the fight against the effects of viruses. For this purpose, surgical methods are used, folk remedies are ineffective and can damage the mucous membrane.
General therapy
Drug treatment is prescribed in severe cases when there is a high risk of carcinogenicity. In this case, systemic and local antiviral drugs (Acyclovir) and immunomodulators are used.
Destructive treatments
Treatment consists of surgical removal of the growths. For this purpose, methods such as cryodestruction, laser therapy, electrocoagulation, and surgical excision can be used. Less commonly used chemical moxibustion.
| Treatment method | How is | Advantages and disadvantages |
| Cryodestruction |
Cryodestruction is based on the action of liquid nitrogen. The procedure is performed without anesthesia and lasts 5-30 seconds. Under the influence of liquid nitrogen, the tissues freeze, a bubble forms at this place, which disappears in 2 weeks. Cryodestruction is suitable for removing small lesions. |
The advantages include the minimally invasiveness and painlessness of the method. The disadvantage is that it is impossible to remove large formations, sometimes several sessions are required. |
| Laser therapy | With the help of a laser, it is possible to remove formations, regardless of their location. Due to the high precision of laser action, no traces remain on the skin and mucous membranes. | The main advantage of the operation is minimally invasiveness and lack of consequences. The disadvantages include high cost. |
| Electrocoagulation | Electrocoagulation is a method of treatment based on exposure to electric current. The skin at the site of exposure is burned with an electric current. | The advantages include the availability of the method and the low risk of postoperative complications. |
| Surgical excision | Surgical excision consists of removing the papilloma with a scalpel and suturing the wound. The operation is performed under general or local anesthesia. | The disadvantages include the radical nature of the operation, as well as the fact that after removal, a scar remains on the skin. |
| Chemical moxibustion | To remove papillomas, chemicals can be used - nitric and trichloroacetic acid, Solkoderm. | The disadvantages include the less effective treatment, the likelihood of getting a burn of the vaginal mucosa. The advantages are affordability and minimally invasiveness. |
Are vaginal papillomas dangerous?
Not in all cases, neoplasms on the vagina pose a danger to the human body. It all depends on the type of papillomavirus - whether it has oncogenic properties or not.
Papillomas on the genitals are much more often caused by oncogenic viruses, which is why their appearance alarms doctors.
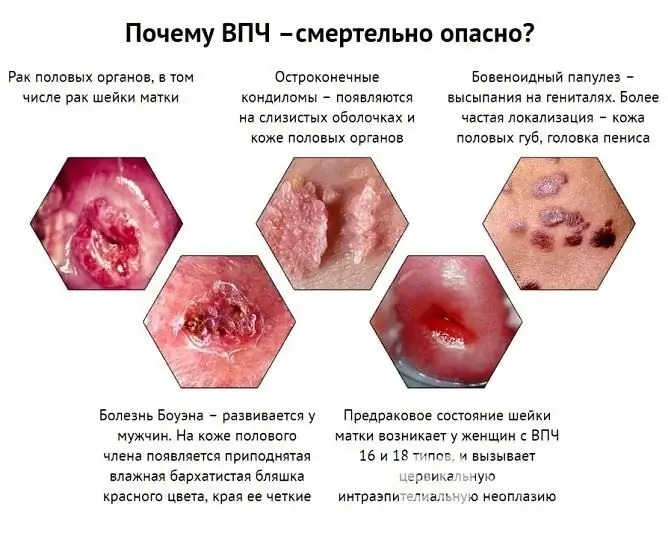
Vaginal papillomas pose a danger in relation to possible degeneration into cancer
Is it possible to prevent the disease
The appearance of neoplasms on the vagina can be prevented. There are methods of specific and non-specific prevention. Specific prevention of the papilloma virus in the vagina is vaccination. There are two vaccines that help avoid the development of human papillomavirus infection (infection with oncogenic strains):
- Gardasil;
- Cervarix.
Girls are vaccinated three times, starting from 10-11 years old. Vaccination protects against oncogenic HPV strains and thus against the development of some malignant tumors, including cervical cancer.
The methods of non-specific prevention include barrier contraception, adherence to the rules of personal hygiene. Barrier contraception does not allow you to avoid all cases of infection, since even when using condoms, damaged skin areas can come into contact with viruses. Reduces the risk of infection by observing the rules of personal hygiene, as well as strengthening immunity - nutrition with a sufficient intake of vitamins and proteins, an active lifestyle, hardening.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.






