- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Flat papillomas
The content of the article:
- Reasons for the appearance
- Forms of existence of papillomavirus
- Provoking factors
- Symptoms of flat papillomas
- Diagnosis of flat warts
- Flat papillomas treatment
- Traditional methods
- How to avoid relapses
- Video
Flat papillomas, also known as flat, juvenile, or juvenile warts, are benign skin growths. The cause of their occurrence is the human papillomavirus (HPV, papillomavirus), which becomes infected as a result of direct and indirect contact with a sick person. Formations are localized mainly on the dorsum of the hands, forearms, face in children, adolescents and young people. Treatment of flat papillomas includes various methods of their removal and systemic therapy with antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs.

Flat warts are called juvenile because they are more common in children and young adults.
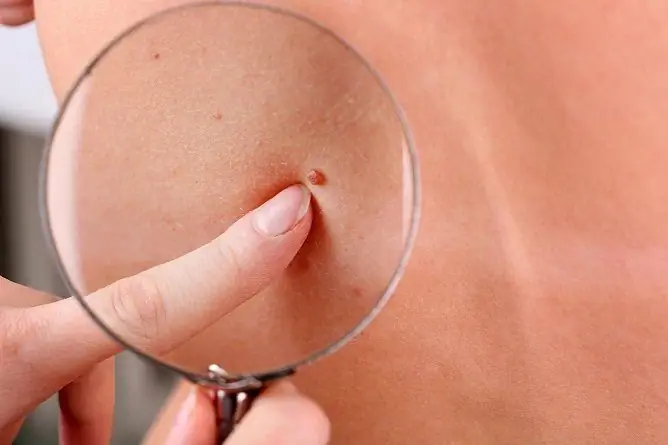
The photo gives an idea of the appearance of flat papillomas on the face and body.
Reasons for the appearance
The human papillomavirus causes juvenile warts. To date, more than a hundred species of the virus have been identified that can infect the skin and mucous membranes. Warts are one of the most common pathologies resulting from human papillomavirus infection. They are all divided into eight clinical varieties, each of which is associated with a specific type of HPV.
| Clinical type of wart | Papillomavirus genotype |
| Vulgar (common) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 27, 29, 57 |
| Palmar-plantar deep | 1, 3, 27, 29, 57 |
| Plantar mosaic | 2, 4 |
| Cystic | 60 |
| Flat | 3, 10, 28 |
| Butchers' wart | |
| Focal epithelial hyperplasia | 13, 32 |
| Epidermodysplasia verruciform | 5, 8, 9, 10, 12, 15, 19, 36 |
The penetration of the papillomavirus occurs through direct contact with the patient or through linen, towels, and care items. An indirect route of transmission of the virus is unlikely, but possible, since viral particles can remain viable for a short time in the peeling skin cells of the patient. For infection, the smallest damage to the surface of the skin and mucous membranes is sufficient.
Forms of existence of papillomavirus
In an infected cell, HPV can be in two different states.
| Intracellular form of papillomavirus | Characteristic |
| Episomal (benign) | The virus does not integrate into the chromosomal apparatus of the infected epithelial cell, being in an inactive or dormant state. There are no clinical manifestations of HPV infection. |
| Introsomal (malignant) | This form of parasitism of the virus is regarded as malignant not because it necessarily causes the growth of malignant neoplasms, but because of the aggressiveness of the viral particles. They wake up and enter the genome of the cell. This process provokes the reproduction of HPV-encoded proteins. In this case, the virus can have a productive or transforming effect on the epithelium. The first leads to the appearance of benign warts, the second - to the formation of dysplasias of varying degrees. In the absence of treatment, the progression of dysplasia leads to the development of cancerous tumors. |
Provoking factors
The form of existence of the virus in epithelial cells is largely determined by the state of the immune system. A decrease in the general resistance of the body occurs under a number of conditions, which include:
- prolonged hypothermia;
- traumatic injury;
- psycho-emotional overload;
- excessive physical labor;
- passion for strong alcoholic beverages;
- smoking;
- diseases of viral, bacterial, fungal origin;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- malignant neoplasms;
- endocrine system pathology;
- taking medications (antibiotics, cytostatics, hormones).
The action of provoking factors can be isolated and combined.
Symptoms of flat papillomas
Characteristics of warts, called flat, are presented in the table.
| Sign | Description |
| Localization | They occur most often on the hands (back of the hands, forearms), on the face (forehead, area around the mouth) and in areas where hair is regularly shaved: in men - the lower part of the face, in women - the legs. Linear placement of papillomas on the face and extremities is characteristic: they are localized along the course of scratching and habitual razor movements. The mechanism for the formation of such an arrangement is simply explained: a person himself carries viral particles to nearby areas of the skin when combing or removing hair while shaving. This route of infection is called autoinoculation, or self-infection. |
| Patient age |
They can be found in patients of different age groups, but most often in children and adolescence, for which they received one of their names - youthful warts. |
| Appearance | Usually represented by multiple small nodules, or growths, with a flat, slightly raised surface and clear outlines. The processes of keratinization of the skin in the area of papillomas do not occur, therefore they have a smooth and shiny surface without any outgrowths and skin pattern. The lesions often do not differ in color from normal skin, although color variations are possible: from pink to yellow-brown. The dimensions usually do not exceed a few millimeters (1-5 mm). |
| Symptoms | In most cases, the presence of papillomas is not accompanied by the appearance of complaints. Slight itching is possible. But flat papillomas, especially on the face, are a cosmetic defect and often cause psychological discomfort in the patient. |
Diagnosis of flat warts
When juvenile warts appear, patients usually see a dermatologist. To make a diagnosis, the doctor carries out:
- patient survey;
- visual inspection;
- dermatoscopy (study with an optical device - a dermatoscope);
- laboratory examination for the presence of HPV in the body and its typing (polymerase chain reaction method - PCR).
Differential diagnosis is carried out with other formations on the skin, the main differences of which are presented in the table.
| Type of skin formation | Distinctive features |
| Lichen planus | Flat knots of lilac, red-violet hue, arranged in groups in the form of garlands, lines, rings. Localization: on the flexion surfaces of the limbs, in the groin, axillary regions, trunk, oral mucosa. The nodules have a retracted center and a waxy surface. A characteristic feature is the presence of a net-like pattern on the surface of the largest formations. Severe itching is typical. |
| Seborrheic keratosis | Foci of seborrheic keratosis (thickening and keratinization of the skin) are characterized by darker pigmentation and look like "glued" skin formations with a flaky surface. A burning sensation is possible when localized on the face. |
| Common wart | Dry nodules with an uneven surface, covered with outgrowths of the keratinizing epithelium. They can sometimes merge to form plaques up to 1.5 cm in diameter. Typical localization is the hands, especially the fingers. |
Flat papillomas treatment
A spontaneous regression of formations is quite often observed, especially against the background of antiviral and immunostimulating treatment. Patients often insist on the primary destruction of flat warts, which are a cosmetic defect. The most effective therapeutic direction for skin neoplasms caused by the human papillomavirus is a combination of local destructive effects on warts and systemic use of drugs with immunomodulatory and antiviral effects. Treatment activities can be carried out simultaneously or in stages.

Flat warts can be removed with laser treatment
Removal of flat papillomas without systemic therapy leads to a high percentage of disease relapses within 6 months after destruction. In some cases, skin lesions form on the same areas of the skin as before. This is explained both by the stages of the papillomavirus life cycle and by a decrease in the general and local immune response.
The main therapeutic measures are presented in the table.
| Therapeutic direction | Characteristic |
| Removal of flat papillomas |
You can get rid of in several ways: the use of salicylic acid preparations, freezing with liquid nitrogen, laser therapy, radio wave removal. The treatment should not be traumatic and accompanied by the formation of scars. For this reason, surgical excision and electrocautery are usually not used, especially when localized papillomas on the face. The most widely used are salicylic acid preparations in the form of a liquid or a patch, as well as cryotherapy through applications of liquid nitrogen. The freezing procedure does not require anesthesia and therefore is well tolerated even by young patients. |
| Increased systemic and local immune response | To increase the body's resistance, immunomodulating and antiviral drugs are used: Interferon, Cycloferon, Allokin-alpha, Likopid, Immunomax, Aldara. The presence of drugs in various dosage forms (injection solution, ointment, cream) facilitates their combination in order to achieve an effective result. |
Traditional methods
There are folk recipes for getting rid of juvenile warts at home using celandine, garlic, lemon, acetic acid. However, only with their help it is difficult to effectively cope with the problem: even the successful destruction of the formations (which occurs infrequently with this method) does not lead to recovery. Antiviral drugs and correction of immunity are needed, otherwise a relapse of the disease is very likely. Do not self-medicate.
How to avoid relapses
For successful treatment, patients with flat warts need:
- follow the recommendations of a specialist;
- do not scratch the skin in the area of formations;
- do not use a razor used to remove hair in the area of lesions, on healthy areas of the skin;
- lead a healthy lifestyle.
A high level of immunity will avoid the reappearance of neoplasms.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.