- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Laser treatment of adenoids in children: reviews, benefits, indications and contraindications
The content of the article:
- Approach to the treatment of adenoids in children
- Types of laser treatment for adenoids in children
- Indications and contraindications for laser treatment of adenoids
- Preparation for laser therapy
- Overview of Adenoids
- Signs of adenoids in children
- Video
Laser treatment of adenoids in children is very popular, as it allows you to effectively fight adenoid growths even in cases where other methods do not bring results. In addition, laser therapy has a high safety profile.
Let's talk about what laser therapy is and why it is becoming more and more popular in ENT practice, especially when it comes to children.

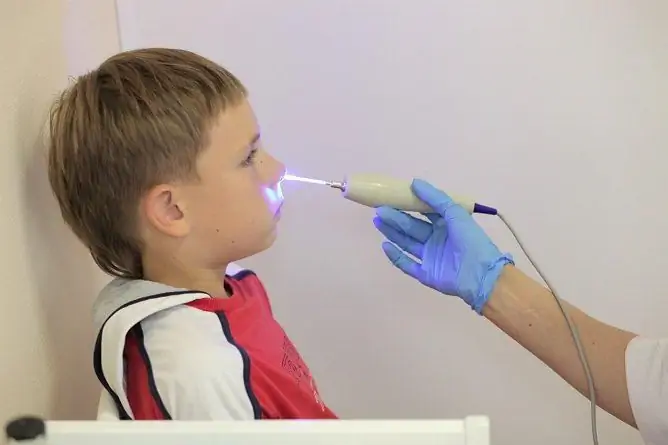
Laser therapy of adenoids is well tolerated by children, as it is practically painless
Approach to the treatment of adenoids in children
Treatment of adenoids in children can be conservative, surgical and combined. Most reputable experts, including Dr. Komarovsky, believe that conservative therapy should be given preference, resorting to the removal of adenoids only in cases where it cannot be done without it. There are several reasons for this - firstly, the removal of the adenoids does not guarantee complete recovery, since the risk of recurrence remains (the lymphoid tissue is almost impossible to remove completely), and secondly, the nasopharyngeal tonsil, which constitutes the adenoids, is an important part of the pharyngeal lymphoid ring, whose task serves to protect the body from infection entering the respiratory tract with the air. In addition, in classic adenotomy, there is a risk of serious complications associated with injury to the tissues of the nasopharynx.
An alternative to surgical excision of adenoids using an adenotome is minimally invasive methods, which are less likely to injure tissues. Such methods include laser removal of adenoids in children. In addition to being atraumatic, the advantages of laser treatment are the anti-infectious and anti-inflammatory effect, as well as the painlessness of the effect, which, according to doctors, ensures its high popularity.
Types of laser treatment for adenoids in children
Laser treatment of adenoids is of the following types:
- Removal of adenoids by laser coagulation (popular name - moxibustion). The method makes it possible to restore nasal breathing in about 98% of cases after the first exposure to the adenoid tissue. It can be used at any stage of the disease.
- Non-invasive laser therapy - implies the effect of laser radiation on adenoid vegetation, which helps to relieve edema, reduce inflammation, improve blood circulation and tissue regeneration. The method is most effective at stages 1-2 of the disease, but can also be used for grade 3 adenoids. The method allows you to significantly alleviate the patient's condition, reduce the hypertrophied tonsil and achieve its reduction.
- Intraoperative laser therapy (combined method) - is usually used in addition to surgical excision of the nasopharyngeal tonsil. After excision of the adenoids by the adenotome, the wound surface is treated with a laser in order to remove the remnants of the nasopharyngeal tonsil, reduce bleeding and improve tissue regeneration.
According to medical reviews, laser treatment of adenoids in children provides a lasting result and is well tolerated, complications are extremely rare. The only difficulty is keeping the young child still during the laser therapy session.
The number of therapy sessions and the duration of the procedure are determined by the attending physician, depending on the child's age and a number of additional factors. The standard course aimed at reducing the adenoids is 7-15 sessions.
Reviews of laser therapy for adenoids in children are the most positive. The procedure is practically painless.
After laser treatment, the child should limit physical activity for some time, avoid prolonged stay in stuffy and hot rooms (including refusing to visit a bath, sauna, pool), follow a sparing diet - it is not recommended to eat too hot and cold food, spicy, sweet and salty foods, hard biscuits, carbonated drinks.
Indications and contraindications for laser treatment of adenoids
Indications for the removal of adenoids by laser or other methods: long-term disturbance of nasal breathing, hearing impairment, impaired formation of the bones of the facial skeleton, child's developmental delay, ineffectiveness of long-term conservative therapy.
Indications for laser therapy are adenoid vegetation at any stage.
Contraindications to laser therapy are: increased body temperature, anemia, neoplasms in the area of intervention, hyper- or hypothyroidism, pathologies of the cardiovascular system, infectious diseases.
Preparation for laser therapy
Before the treatment of adenoids with a laser, the patient must be examined by an otorhinolaryngologist (ENT doctor). In preparation for the operation, a rhinoscopy, X-ray examination, computed tomography, laboratory tests (complete blood count, coagulogram) may be required.

Removal of adenoids is significantly less traumatic compared to classical adenotomy
Overview of Adenoids
Hypertrophy of the nasopharyngeal tonsil, called adenoid vegetations or adenoids, is the most common cause of impaired nasal breathing. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in children 3-7 years of age, but it also occurs in adults.
The nasopharyngeal tonsil consists of lymphoid tissue and takes part in the formation of immunity, being the first-line defense mechanism on the path of inhaled infectious agents.
During diseases of the upper respiratory tract, for example, ARVI, the nasopharyngeal tonsil enlarges, but subsequently returns to its original size. Sometimes there is no reduction, and the tissue of the amygdala grows pathologically, forming adenoids. Adenoid vegetation blocks the lumen of the nasal passages. According to this criterion, three stages (degrees) of adenoids are distinguished:
- 1 degree - a third of the height of the nasal passages is blocked;
- 2 degree - about half the height of the nasal passages is blocked;
- Grade 3 - the nasal passages are almost completely blocked.
Often, adenoids attract attention only at 2 or 3 stages, when a violation of nasal breathing becomes pronounced.
Signs of adenoids in children
The first signs of adenoids are subtle - children sleep with their mouths open, snort heavily in their sleep, snore periodically. With the progression of the disease, snoring during a night's sleep becomes regular, and breathing disturbance becomes noticeable in the waking state. In the third stage, the child is constantly forced to breathe through his mouth, which is why he is always open.
Adenoids can become inflamed - adenoiditis develops. This disease is manifested by a deterioration in the general condition, an increase in body temperature, the appearance of mucopurulent discharge from the nose, a reflex cough caused by the drainage of secretions along the back wall of the nasopharynx. Unlike the adenoids themselves, adenoiditis responds well to therapy, but its cure does not mean getting rid of adenoid growths.
Due to the prolonged lack of breathing through the nose, the child does not receive about 20% of oxygen, which leads to the development of weakness, fatigue, lethargy, headaches, impaired cognitive functions, and sleep disorders. Chronic hypoxia of the brain can lead to a delay in mental and physical development.
If the adenoids block the lumen of the auditory (Eustachian) tube, against the background of impaired ventilation of the middle ear, eustachitis, otitis media, and hearing impairment develop.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.