- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Adenoids: Surgery to remove adenoids in children
The content of the article:
- Preparation for adenotomy: examination
-
How is adenoid surgery in children
- Classical adenotomy
- Endoscopic adenotomy
- Minimally invasive methods for removing adenoids
- Postoperative period
- Possible complications
- When adenoid surgery is needed
- Contraindications to adenotomy
- Video
Operation on adenoids in a child (adenotomy) is performed only on strict indications, when the presence of adenoid vegetations is associated with a greater risk than their removal. This applies to situations when the adenoids create significant obstacles to nasal breathing, cause the child to lag behind in development, persistent hearing impairment, chronic otitis media, bronchial asthma, malocclusion and an adenoid type of face. In other cases, in the presence of pathology, conservative therapy is the method of choice.
Adenoids are pathological proliferation of the nasopharyngeal tonsil, which consists of lymphoid tissue and belongs to the organs of the immune system, whose task is to prevent the penetration of infection into the body through the upper respiratory tract. This disease occurs in childhood; children from 3 to 5 years old are most vulnerable to adenoids.
Frequent respiratory viral infections, childhood diseases, and allergies can contribute to adenoid growths, or vegetation.

Surgical removal of adenoids is resorted to when all other treatment options have been exhausted
The decision on the need for surgical treatment is made by the attending ENT doctor (otolaryngologist) together with the child's parents after a significant degree of adenoid proliferation has been established and the possibilities of conservative therapy have been exhausted. Parents should be informed about the possible consequences of canceling the operation, as well as the risks associated with it.
Preparation for adenotomy: examination
In preparation for the operation, a detailed medical examination of the child is carried out. Personal and family anamnesis is collected, as well as hardware and laboratory data.
Instrumental diagnostics is usually limited to radiography, however, in some cases, it may be necessary for computed tomography, as well as for additional diagnostics (for example, ECG for suspected heart disease, etc.).
Laboratory diagnostics includes a general and biochemical blood test, determination of blood group and Rh factor, coagulogram, tests for certain infections (HIV, viral hepatitis), general urine analysis.
How is adenoid surgery in children
Planned adenotomy is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia (it consists in applying anesthetic to the nasopharyngeal mucosa), less often under general anesthesia (inhalation and intravenous). In the case of concomitant diseases or complications, hospitalization for several days may be required. The operation to remove adenoids in children is not difficult, the whole procedure, together with anesthesia and antiseptic treatment, takes 10-15 minutes.
Classical adenotomy
Removal of the adenoids is carried out using a circular Beckman knife (adenotome). It is introduced into the oral cavity, placing it in such a way that the adenoid vegetation is completely covered by the ring, after which they are excised with a quick movement and removed through the mouth. The doctor then stops the bleeding, which is usually minor. If necessary, resort to vascular coagulation or treatment of the mucous membrane with a hemostatic.
The disadvantage of this method is the lack of visual control, which is why areas of lymphoid vegetation often remain, which subsequently grow again, providing a relapse of the disease. In addition, there is a risk of injury to the surrounding tissue, which can be quite serious.
Endoscopic adenotomy
The use of endoscopic technology, which provides complete visual control, significantly increases the efficiency and safety of the procedure. The endoscope displays a scaled image of the operating field on the monitor, the doctor fully controls the process of excision of the nasopharyngeal tonsil. The manipulator provides increased accuracy without leaving amygdala fragments. The excised adenoid tissue is removed through the oral cavity or through a nostril that is free from the endoscope.
The disadvantages of the technique include the fact that the procedure is somewhat longer and also requires special equipment and the skills of a surgeon.
Minimally invasive methods for removing adenoids
In addition to surgical excision, the removal of adenoids can be performed by electrocoagulation, radio wave surgery, coblation, and also using a laser. The latter method is one of the most popular, because, according to doctors, it provides a good result, no significant pain both during and after surgery, no bleeding and no risk of infection, and quick recovery.
Removal of adenoids with a laser is carried out in two versions: fast (one-time) and gradual (slow). The gradual treatment of adenoid vegetations with a laser is preferred by many pediatricians as the most gentle method. The method consists in laser action on the adenoid tissue, as a result of which it decreases from procedure to procedure (there can be up to 15 of them before complete removal of the adenoids).
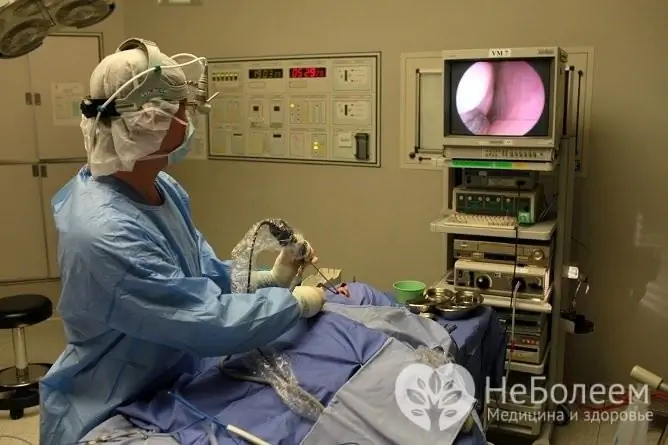
Endoscopic adenotomy allows you to see the surgical field in detail
Postoperative period
As a rule, after the operation on the adenoids, the child returns home the same day, after several hours of medical supervision. Due to postoperative edema, there is no immediate recovery of nasal breathing, it is restored within 7-10 days. In the postoperative period, the patient may be prescribed vasoconstrictor nasal drops, pain relievers. For one or two days, the body temperature may rise to subfebrile values (not higher than 38 ° C), in this case, you can give the child an antipyretic drug (Attention! Do not give acetylsalicylic acid, you can use paracetamol and ibuprofen).
Until the tissues are completely healed, it is necessary to provide the child with a gentle diet. Food is taken in a soft, grated form (mashed potatoes, mashed soups, viscous cereals, jelly), exclude solid and irritating to the mucous membrane products (sour, spicy, spicy, and carbonated drinks). Hot food is excluded (it can provoke bleeding), all meals are served warm or at room temperature. Food should be complete in composition and high in calories. It is better if you have 5-6 meals a day in small portions.
For the rehabilitation period, physical activity, bathing in hot water, and being in the heat are excluded. Since the child's body is weakened after the operation, it is necessary to avoid contact with patients with infectious diseases, as well as the child's stay in crowded places.
To shorten the recovery period, reduce edema, quickly restore the patency of the nasal passages, as well as form the child's nasal breathing habit, breathing exercises are recommended. Taking only a few minutes a day, it is devoid of side effects and at the same time is highly effective if performed regularly.
Uncomplicated breathing exercises help restore breathing through the nose
Possible complications
Complications after adenotomy are rare. These include infectious inflammation, ear disorders, trauma to the lower jaw or other tissues in the intervention area, neurosis in children with a labile psyche (such children are recommended adenotomy under general anesthesia).
Postoperative sore throat, difficulty in nasal breathing, one or two vomiting of blood clots are not complications.
When adenoid surgery is needed
In total, there are three degrees of proliferation of the adenoids. Initially, the nasal passages overlap by 1/3, at the second stage - from 1/3 to 2/3, at the third - more than 2/3.
At an early stage, adenoid growths are manifested in the child by periodic puffing and / or snoring during a night's sleep. As the growing seasons grow, snoring becomes constant, in a state of wakefulness, nasal breathing is disturbed, gradually the child increasingly begins to breathe through his mouth.
With adenoids of the third degree, there is constant nasal congestion, mucous or mucopurulent nasal discharge, dry cough, nasal voice, loss of appetite, weakness, and increased fatigue. Due to the lack of nasal breathing, chronic oxygen deficiency (hypoxia) develops, manifested by headache, impairment of memory and attention, and with prolonged hypoxia, the child begins to lag behind in development. Breathing through the mouth forces the child to keep it constantly open, which is why a specific adenoid type of face is gradually formed, and a pathological bite is formed.
The skin of patients becomes pallor, dark circles appear under the eyes. When the adenoids overlap the auditory (Eustachian) tube, hearing decreases, there is pain in the ears (usually in one ear), otitis media and eustachitis often occur. The adenoids themselves can also become inflamed, in which case adenoiditis develops. The palatine tonsils (tonsillitis) are often involved in the pathological process.
Children who are forced to breathe through the mouth inhale insufficiently heated and purified air, which leads to frequent respiratory infections, which, in turn, contribute to the further growth of the nasopharyngeal tonsil - a vicious circle is formed.
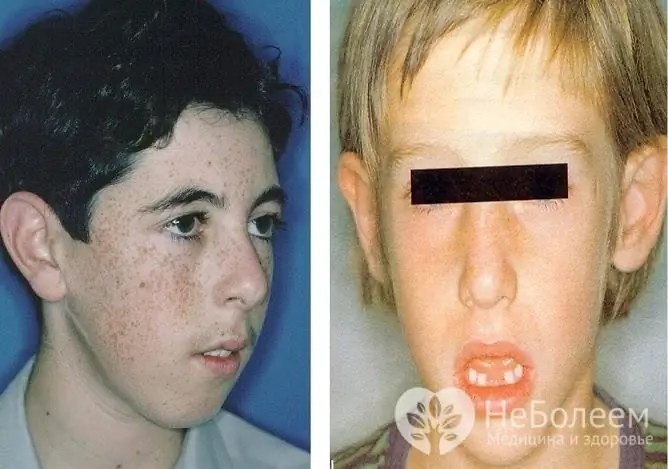
Adenoids gradually form a specific type of face in children
The listed symptoms associated with the third degree of adenoid vegetation are indications for surgical intervention. Adenotomy can be performed on a child of any age.
Contraindications to adenotomy
Contraindications to surgical treatment of adenoids can be:
- acute infectious disease (until complete recovery);
- recent vaccination (less than a month before the estimated date of surgery);
- bleeding disorders (require corrective therapy before surgery);
- severe concomitant diseases in the stage of decompensation.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.