- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
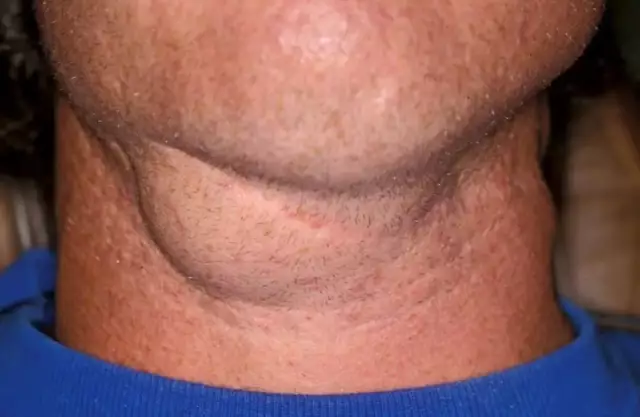
Submandibular lymphadenitis

Submandibular lymphadenitis is a common inflammatory pathology of the lymph nodes. Such nodes are peripheral accumulations of lymphoid tissue. They perform a protective function in the body, becoming a kind of barrier against infection. By localization, lymphadenitis of the cervical, axillary, inguinal, submandibular and other lymph nodes is isolated. Submandibular lymphadenitis, like any lymphadenitis in general, can be purulent and non-purulent, acute and chronic. Most often, inflammation is caused by streptococci, staphylococci and their toxins, which enter the lymph nodes with the flow of blood or lymph from the focus of inflammation. Sometimes lymphadenitis can be caused by specific microorganisms - Koch's bacillus (the causative agent of tuberculosis), pale treponema (the causative agent of syphilis). Lymphadenitis is simple (edema develops),hyperplastic (the tissues of the node increase in volume) and destructive (the node itself and the surrounding tissues are destroyed).
Causes of submandibular lymphadenitis
The cause of submandibular lymphadenitis is most often an infectious process in the oral cavity. It can be tonsillitis, paratonsillar abscess, periodontal disease, gingivitis, periostitis, osteomyelitis of the upper or lower jaw, multiple caries. In rare cases, if the infection has entered the lymph nodes during their injury, submandibular lymphadenitis may be the primary disease.
Symptoms of submandibular lymphadenitis
The first manifestation of the acute form of the disease is pain in the area of the affected lymph nodes. At first, the pain can be only with pressure, and then it becomes constant, pulsating, shooting, intense, intensifying with movement. The pain makes the patient take a forced position, interferes with sleeping on the affected side, talking, swallowing food. Sometimes the pain prevents you from opening your mouth. At the site of inflammation, hyperemia (redness) of the skin develops, edema appears. After a while, the skin becomes bluish. By touch, you can identify a dense, enlarged, painful lymph node. The temperature of the skin over the affected lymph nodes is higher than over the neighboring areas. In addition to local symptoms, the general one also develops. The body temperature rises (sometimes above 40 degrees). Chills, sweating, weakness appear,headache, insomnia. In the chronic form of the disease, the pain syndrome is not so intense, enlarged lymph nodes are determined for a long time, the general condition suffers little. Diagnosis of the disease in typical cases is not difficult for specialists. Only with severe submandibular lymphadenitis may need differential diagnosis with osteomyelitis, phlegmon. In chronic submandibular lymphadenitis, a puncture biopsy of the node is sometimes needed to establish the diagnosis. Only with severe submandibular lymphadenitis may need differential diagnosis with osteomyelitis, phlegmon. In chronic submandibular lymphadenitis, a puncture biopsy of the node is sometimes needed to establish the diagnosis. Only with severe submandibular lymphadenitis may need differential diagnosis with osteomyelitis, phlegmon. In chronic submandibular lymphadenitis, a puncture biopsy of the node is sometimes needed to establish the diagnosis.
Submandibular lymphadenitis treatment

Submandibular lymphadenitis is treated by a surgeon or general practitioner. First of all, the rehabilitation of the focus of infection is carried out. Sometimes urgent dental intervention is required (tooth extraction, opening of the jaw abscess). Submandibular lymphadenitis itself is often treated conservatively. The patient is prescribed rinsing with Burov's liquid, lotions, antibiotics, vitamins, physiotherapy (UHF). If there is a purulent fusion of the lymph node, surgical intervention is necessary. If a single lymph node is involved in the process, the surgeon makes an incision in the skin over it, inserts drainage under the capsule, and washes the surgical wound. If several nodes are affected at once, the skin is opened in the submandibular region, drainage is established in the fatty tissue to ensure the outflow of pus. Antibiotics are prescribed. Preference is given to drugs in the form of injections (injections). Usually, the doctor chooses a modern broad-spectrum antibiotic, taking into account the sensitivity of microorganisms to it. If a specific nature is established (syphilis, tuberculosis), the treatment of submandibular lymphadenitis is carried out with drugs according to the developed schemes.
Prevention of the disease
The main prevention for submandibular lymphadenitis is the timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!