- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Forms of the disease
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications and consequences
- Forecast
Dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi is a benign disease of a non-calculous (not associated with the presence of stones in the gallbladder and ducts) nature, manifested by a violation of the movement of bile along the biliary tract at the point of their confluence with the pancreatic duct.
Normally, the bile produced by the liver accumulates in the gallbladder and, mixing with the secretion of the pancreas, is dosed into the duodenal lumen through an anatomical formation called the large duodenal (or Vater) nipple. The frequency of secretion entering the duodenum, necessary for adequate digestion, is provided by a muscular organ located in the thickness of the Vater's nipple - the sphincter of Oddi.

Dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi leads to impaired movement of bile along the biliary tract
In the period between the phases of active digestion, the sphincter is in a state of increased tone, keeping bile and pancreatic juice outside the duodenum (constant discharge occurs normally even between meals, but in extremely small quantities - a few drops every minute). When partially processed food passes from the stomach into the small intestine, the sphincter begins to work on the principle of a pump, throwing the contents of the ducts into the lumen of the duodenum in small portions. The frequency of sphincter activity is from a few seconds to a minute, depending on the intensity of digestion.
In addition to regulating the discharge of digestive secretions into the intestine, the sphincter of Oddi prevents the return of small intestinal contents into the lumen of the common bile and pancreatic ducts.
Bile performs many functions necessary for optimal digestion of food: it neutralizes aggressive enzymes of gastric juice, creates a favorable environment for the activation of pancreatic enzymes, breaks down fats, stimulates the motor activity of the small intestine and the production of a number of biologically active substances, etc. Pancreatic juice contains lipase enzymes, protease, amylase, necessary for the breakdown of fats, proteins and carbohydrates.
With dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi, the flow of bile and pancreatic secretions is disturbed, their inclusion in the process of digesting food is incorrect, which leads to various disorders of the digestive mechanism.
Basically, the pathology affects women from 30 to 50 years old who have undergone cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder).
Causes and risk factors
Since dysfunction can be both organic and inorganic in nature, the causes that cause it vary.
Violation of the sphincter of Oddi of an organic nature (true stenosis) is a consequence of inflammation, hyperplasia or fibrosis of the duodenal mucosa.
The functional (inorganic) causes of a pathological condition include:
- diseases of the hepatobiliary zone;
- the consequences of surgery (resection, gastrectomy) for stomach diseases;
- conditions after bowel resection;
- endocrinopathies (hypo- and hyperfunction of the thyroid and parathyroid glands, diabetes mellitus, adrenal diseases);
- pregnancy;
- pharmacotherapy with hormonal drugs;
- metabolic diseases;
- systemic diseases (including autoimmune);
- conditions after cholecystectomy;
- taking drugs that affect the tone and motor activity of smooth muscles;
- diseases of the stomach and pancreas (gastritis, pancreatitis, gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer).

Pharmacotherapy with hormonal drugs can lead to dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi
Risk factors for dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi are:
- constant neuropsychic stress;
- excessive psycho-emotional stress;
- passion for unbalanced diets, including those based on severe restrictions on the amount of food intake.
Forms of the disease
According to the etiological factor, the following forms are distinguished:
- primary (developing without previous pathology);
- secondary (resulting from the underlying disease).
By functional state:
- dyskinesia with hyperfunction;
- dyskinesia with hypofunction.
In order to classify the type of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction in accordance with objective data, during the Rome Consensus (1999), diagnostic criteria were proposed:
- classic pain attack;
- at least a twofold increase in the level of liver enzymes (AST, alkaline phosphatase) in at least 2 consecutive studies;
- slowing down the evacuation of contrast agent over 45 minutes during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography;
- expansion of the common bile duct to 12 mm or more.
The types of dysfunction are defined according to the criteria:
- Biliary I - characterized by the presence of all of the above signs.
- Biliary II is a classic attack of biliary pain in combination with 1 or 2 diagnostic criteria.
- Biliary III - isolated pain syndrome without other signs.
- Pancreatic - pain syndrome characteristic of inflammatory processes in the pancreas (in combination with an increase in the level of pancreatic enzymes).
Symptoms
The clinical picture of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction is diverse:
- pain in the epigastric region, in the right hypochondrium of an expanding, dull nature, sometimes colicky, short-term, provoked by an error in the diet, psychoemotional overload, excessive physical exertion. The pains can radiate to the right scapula, shoulder, back, with a pancreatic type, they are shingles acute;
- a feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- nausea, vomiting of bile;
- bloating, pain in the umbilical region;
- a tendency to constipation;
- increased fatigue;
- irritability;
- sleep disorders.
The pain syndrome is paroxysmal; in most cases, there are no complaints in the interictal period.

The main symptom of dyskinesia of the sphincter of Oddi is paroxysmal pain in the epigastrium
Diagnostics
This pathology is characterized by the absence of clear, indicative data confirming the presence or absence of dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi during the period of well-being. The bulk of the research is informative, provided they are carried out during the attack:
- determination of the level of hepatic and pancreatic enzymes (characterized by the absence of changes in laboratory data in the interictal period);
- provocative tests (for example, morphine-prostigmine pain provocative test);
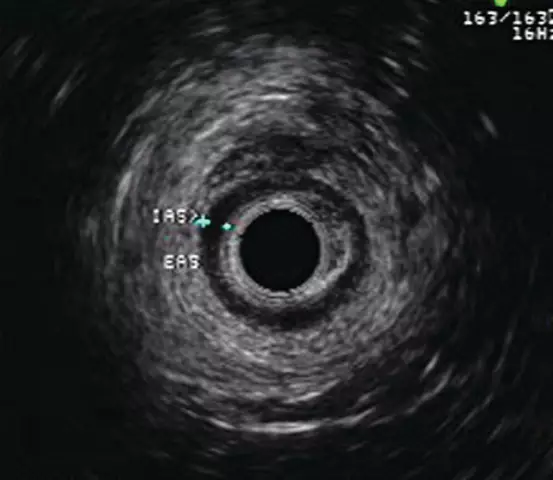
- endoscopic manometry of the biliary tract;
- Ultrasound examination;
- quantitative scintigraphy of the hepatobiliary zone;
- endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.

Endoscopic manometry to diagnose sphincter of Oddi dysfunction
Treatment
The treatment of the disease is carried out using invasive and non-invasive techniques.
Non-invasive (conservative) approaches to treatment:
- rational diet therapy (limiting salty foods, avoiding fried, fatty foods, introducing foods containing a large amount of dietary fiber into the diet);
- antispasmodic drugs [nitrates, anticholinergics, slow calcium channel blockers, myotropic antispasmodics, intestinal hormones (cholecystokinin, glucagon)];
- choleretics;
- cholekinetics.
With the ineffectiveness of the pharmacotherapeutic effect, invasive methods of dysfunction correction are used:
- endoscopic papillosphincterotomy;
- endoscopic balloon dilatation with temporary catheter-stents;
- injection of botulinum toxin into the vater papilla.

Endoscopic papillosphincterotomy - an invasive method for correcting sphincter of Oddi dysfunction
Possible complications and consequences
Complications of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction can be:
- cholangitis;
- cholelithiasis;
- pancreatitis;
- gastroduodenitis.
Forecast
The forecast is favorable. With timely initiated pharmacotherapy, the symptoms of the disease are leveled out in a short time. The effectiveness of invasive treatments is over 90%.

Olesya Smolnyakova Therapy, clinical pharmacology and pharmacotherapy About the author
Education: higher, 2004 (GOU VPO "Kursk State Medical University"), specialty "General Medicine", qualification "Doctor". 2008-2012 - Postgraduate student of the Department of Clinical Pharmacology, KSMU, Candidate of Medical Sciences (2013, specialty "Pharmacology, Clinical Pharmacology"). 2014-2015 - professional retraining, specialty "Management in education", FSBEI HPE "KSU".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!