- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Cerebral atherosclerosis
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Forms of the disease
- Disease stages
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Cerebral atherosclerosis treatment
- Possible complications and consequences
- Forecast
- Prevention
Cerebral atherosclerosis is one of the types of atherosclerosis, in which atherosclerotic plaques form in the vessels of the brain, which leads to disturbances in cerebral blood supply.

The main cause of cerebral atherosclerosis is a violation of cerebral circulation due to atherosclerotic plaques in the vessels
Cerebral atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels accounts for about 20% in the structure of general neurological pathology, as well as about 50% of all cases of cardiovascular diseases. Atherosclerotic lesions of cerebral vessels can be noted as early as 20-30 years old, however, pronounced clinical manifestations of the disease usually occur in patients over 50 years old. The disease is more susceptible to males, however, with age, cerebral atherosclerosis is recorded in men and women with approximately the same frequency. This is due to the fact that after the onset of menopause, the level of estrogens in a woman's body decreases, which inhibits the development of atherosclerotic vascular lesions.
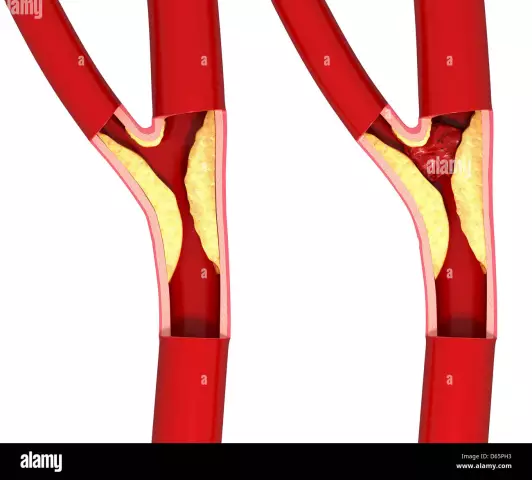
The main clinical manifestations of the disease are due to cerebral circulatory insufficiency gradually developing against the background of damage to cerebral vessels, leading to tissue ischemia. The formation of an atherosclerotic plaque occurs in several stages (from a lipid spot to atherocalcinosis, or calcification). The formed plaque increases in size and gradually blocks the lumen of the affected blood vessel, contributing to its clogging with blood clots. A decrease in the lumen of a blood vessel and, accordingly, a deterioration in the blood supply to the area of the brain leads to the development of hypoxia and a deficiency of nutrients. The progression of the pathological process causes degenerative changes and death of individual neurons. Part of the atherosclerotic plaque can be torn off and transported with the blood flow to the vessels of a smaller caliber,which leads to a sudden occlusion of the blood vessel. Violation of the elasticity of the vascular wall at the site of atherosclerotic plaque formation, especially against the background of concomitant arterial hypertension, can lead to rupture of the vascular wall and the development of hemorrhagic complications.
Of all cerebral vessels, the arteries of the pons varoli, thalamus and subcortical nodes are more susceptible to atherosclerotic lesions.
Causes and risk factors
Cerebral atherosclerosis is referred to as polyetiological diseases. First of all, the risk of developing cerebral atherosclerosis of the cerebral vessels increases with age. Its onset at an earlier age usually occurs against the background of poor nutrition, metabolic disorders, overweight, insufficient physical activity, tobacco smoking, and alcohol abuse. In addition, arterial hypertension contributes to the development of pathology. Often, patients have a combination of cerebral atherosclerosis and high blood pressure, with both conditions aggravating each other's course.

The risk of developing cerebral atherosclerosis increases with the wrong lifestyle
Also, risk factors include chronic infectious processes and intoxication of the body, which have an adverse effect on the vascular wall. A certain role is played by an unfavorable psychoemotional state, mental stress, as well as frequent stressful situations. Genetic predisposition also matters. In clinical practice, family cases of the development of such a complication of cerebral atherosclerosis as stroke are often recorded.
Forms of the disease
Cerebral atherosclerosis is classified by localization and clinical course.
Depending on the location of the lesion, the posterior cerebral artery, the anterior cerebral artery, the internal or common carotid artery, the brachiocephalic trunk, and smaller blood vessels may be involved in the pathological process.
According to the clinical course, cerebral atherosclerosis is divided into intermittent, slowly progressive, acute and malignant.
Disease stages
In the clinical picture of cerebral atherosclerosis, three stages are distinguished:
- Development of functional vasomotor disorders, symptoms appear only occasionally, unstable.
- The development of functional and morphological disorders, the symptoms become more stable.
- Organic damage to blood vessels, symptoms are constantly present, complications often develop.

Development of cerebral atherosclerosis
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations of cerebral atherosclerosis occur against the background of tissue ischemia, which develops when the cerebral blood flow is blocked by an atherosclerotic plaque.
At the initial stage of the disease, the manifestations of cerebral atherosclerosis are transient, usually they occur during physical and / or mental overstrain and disappear at rest. Patients complain of weakness, lethargy, fatigue, increased irritability, impaired concentration, memory impairment. Periodic disturbances of night sleep, insomnia, daytime sleepiness, dizziness are noted (especially when changing the position of the body from horizontal to vertical). The predominant symptom at this stage of the disease may be headache, which is combined with noise in the head, in the ears or in one ear. In addition, patients may complain of numbness of the lower extremities, tingling in the face, a feeling of heat in the occipital region, blurred speech, decreased visual acuity,hearing loss (up to its complete loss), taste disturbances.

With cerebral atherosclerosis, patients complain of dizziness when changing body position
With the further development of the pathology, intellectual-mnestic disorders are aggravated, depression may develop. The patient develops anxiety, suspiciousness, rapid mood swings. The noise in the head can be disturbing all the time. Also, at this stage, gait and coordination of movements may be disturbed, tremor of the head and / or fingers may be noted. Working capacity is gradually lost.
With further progression of the disease in patients with cerebral atherosclerosis, memory lapses, apathy, loss of the ability to navigate in time and in the environment are noted, and self-service skills are lost.
An important sign that you should pay attention to in the presence of cerebral atherosclerosis is the development of a cerebral or hypertensive crisis. This condition is accompanied by intense headaches, weakness in one of the upper and / or lower extremities, speech disorders and visual impairments. Usually the crisis lasts no more than two days, after which the patient's condition stabilizes. The persistence of symptoms for more than two days may indicate a complication of cerebral atherosclerosis by stroke.
Diagnostics
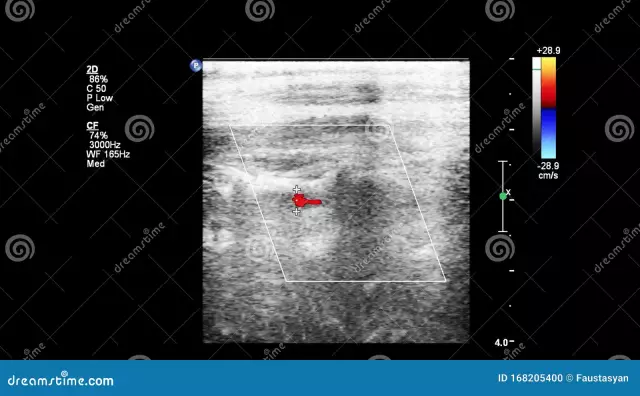
For the diagnosis of cerebral atherosclerosis, the patient must be examined by a neurologist. Diagnosis of the disease is based on history data, clinical manifestations, as well as data from a number of additional examinations. Duplex scanning makes it possible to assess the condition of the extracranial arteries that feed the brain. This diagnostic method, in combination with ultrasound examination of the cranial arteries, provides information on the localization of atherosclerotic lesions, the degree of vasoconstriction, and the nature of the atherosclerotic plaque. The state of the blood vessels in the brain can be assessed by performing an angiographic examination. Computed tomography is usually used in patients with cerebral atherosclerosis who have had a stroke,to clarify the localization of the lesion and the choice of tactics for further treatment. Magnetic resonance imaging is also used to assess the state of cerebral vessels. The functional state of the brain can be assessed using electroencephalography. Pathological changes in retinal vessels can be detected during ophthalmoscopy. In case of hearing impairment, the patient must be examined by an otorhinolaryngologist with audiometry. An immunological study may be required, as well as a biochemical blood test to determine the level of cholesterol and lipoproteins (lipid profile). Pathological changes in retinal vessels can be detected during ophthalmoscopy. In case of hearing impairment, the patient must be examined by an otorhinolaryngologist with audiometry. An immunological study may be required, as well as a biochemical blood test to determine the level of cholesterol and lipoproteins (lipid profile). Pathological changes in retinal vessels can be detected during ophthalmoscopy. In case of hearing impairment, the patient must be examined by an otorhinolaryngologist with audiometry. An immunological study may be required, as well as a biochemical blood test to determine the level of cholesterol and lipoproteins (lipid profile).

Confirmation of the diagnosis of cerebral atherosclerosis allows MRI of the vessels of the brain
Cerebral atherosclerosis treatment
Cerebral atherosclerosis is incurable, but with timely adequate therapy, it is possible to slow down its progression. When treating cerebral atherosclerosis, first of all, it is necessary to eliminate the unfavorable factors that caused the development of the pathological process.
Conservative treatment of cerebral atherosclerosis is primarily aimed at improving cerebral circulation, as well as preventing thrombus formation.
If a patient with cerebral atherosclerosis has arterial hypertension, antihypertensive therapy is carefully selected. In order to correct the content of cholesterol and / or lipoproteins in the blood, lipid-lowering drugs are used. Taking nootropic drugs helps to improve cognitive abilities. If necessary, patients with cerebral atherosclerosis are prescribed antiplatelet drugs, vasodilators, drugs that reduce the inflammatory process in the blood vessels. In order to prevent the development of circulatory disorders, coronary artery drugs are prescribed. In addition, in some cases, they resort to cascade filtration of blood plasma and cryoapheresis.
Patients are shown a diet that excludes foods with a high cholesterol content (margarine, fatty meats, eggs, sausages, canned fish, etc.), with increased body weight, the daily caloric intake of the diet is reduced.

With cerebral atherosclerosis, an anti-cholesterol diet is indicated
Repeated transient ischemic attacks, occlusion of the carotid artery with a decrease in its lumen by more than 70%, a history of minor stroke become indications for surgical treatment of cerebral atherosclerosis. The main surgical methods for this disease are the removal of an atherosclerotic plaque with a portion of the intima of a blood vessel (endarterectomy), as well as the creation of a vascular shunt that goes around the affected area of the artery.
Endarterectomy in the case of cerebral atherosclerosis is performed in a closed, i.e., endoscopic way using balloons and stents. For this purpose, an endoscope with a stent is inserted into a wide blood vessel, then, under X-ray control, it moves to the site of clogging of the artery by an atherosclerotic plaque, where the stent is installed, which increases the lumen of the blood vessel and, accordingly, restores blood flow. According to indications, prosthetics of the brachiocephalic trunk, the formation of an extra-intracranial anastomosis can be performed.
Bypass grafting of cerebral vessels is an operation that consists in creating another pathway for blood flow, bypassing a vessel affected by atherosclerosis. A shunt is created from the patient's vein or an artificial one is taken. It is sewn into the affected artery in front of and after the blockage, without removing the damaged area.
Possible complications and consequences
In the absence of timely diagnosis and correctly selected treatment against the background of cerebral atherosclerosis, dementia, chronic cerebral ischemia, stroke, myocardial infarction, paralysis, etc. develop.
Forecast
The prognosis for cerebral atherosclerosis largely depends on the age of the patient, the timeliness of the initiation of treatment, as well as the ability to eliminate the risk factors that caused the disease.
The development of severe complications of cerebral atherosclerosis can lead to the patient's disability, as well as death.
Prevention
In order to prevent cerebral atherosclerosis, it is recommended:
- timely treatment of diseases that can cause the appearance of cerebral atherosclerosis;
- correction of excess weight;
- avoidance of stress and mental strain;
- full sleep;
- sufficient physical activity;
- balanced diet;
- rejection of bad habits.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!