- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Diverticulitis

Diverticulitis is an inflammatory process of one or more hernial protrusions of the walls of the large or small intestine, the so-called diverticulum, which occurs against the background of infection.
Diverticula are formed during the development of a child in utero or are formed for various reasons throughout life, more often in the elderly. With a delay in the diverticula of food debris, fecal stones are produced, provoking bacterial infections and, against their background, diverticulitis. The inflammation is limited to one diverticulum or can spread to nearby tissues and organs, resulting in an interintestinal abscess, peritonitis, or retroperitoneal phlegmon.
Diverticulitis: symptoms
Typically, the symptoms of diverticulitis are as follows:
- Increased body temperature, fever;
- Chronic dull pain in the left lower abdomen or in the suprapubic region;
- Bloating, constipation, or difficulty defecating;
- Constant feeling of nausea, vomiting.
An experienced surgeon can suspect the presence of diverticulitis in a patient during the initial examination by listening to the patient's complaints and palpating the abdomen. In some cases, the symptoms of diverticulitis can be mistaken for a clinical picture of appendicitis, so a plain x-ray, abdominal ultrasound, or computed tomogram is necessary. After the removal of the acute inflammatory process, it is necessary to conduct an irrigoscopy or colonoscopy.
Intestinal diverticulitis
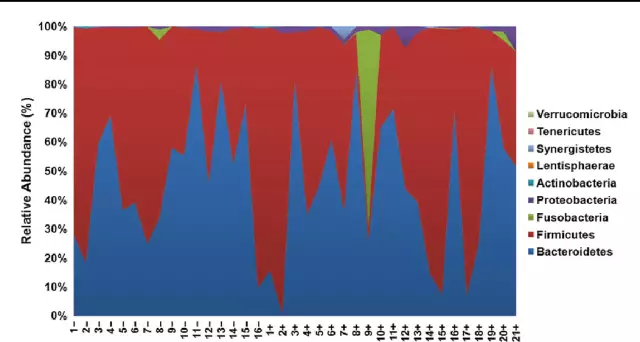
The large intestine is most often the site of localization of diverticula, which provokes the appearance of intestinal diverticulitis. This disease develops mainly in old and senile age. In advanced economies, life expectancy has increased significantly, as a result, the group at risk of intestinal diverticulitis has increased to 30% of the total population. A significant depletion of the daily diet in plant fibers and coarse fiber plays a significant role in the massive spread of the disease. The lack of these nutritional components leads to the formation of constipation, the accumulation of feces in the large intestine, which, in turn, increases the risk of intestinal diverticulitis.
Diverticulitis: Treatment
Depending on the complexity of the disease, diverticulitis can be treated with the following methods:
- Drug therapy;
- Surgical intervention.
Mild diverticulitis is treated at home, antibiotics are prescribed, rest and a special diet consisting mainly of liquid meals is recommended. Symptoms usually disappear after a few days of this treatment. In the future, you should strictly follow the prescriptions and recommendations of the attending physician, in order to avoid relapses.
In case of complications with clear signs of an infectious process, hospitalization is necessary. Patients are prescribed the introduction of antibiotics and intravenous fluids, strict bed rest and are prohibited from drinking and eating until the condition improves and the pain symptoms are relieved.

If abdominal pain and fever increase, the doctor may decide whether surgery is necessary. The operation is required for about 20% of patients with diverticulitis, since other methods of treatment do not give tangible results. In some cases, if there is a high risk of developing severe complications, the operation is recommended for preventive purposes.
Emergency surgery is required for patients with peritonitis, bowel perforation, massive bleeding. The purpose of such an operation is to remove the affected part of the small or large intestine as a source of diverticulitis.
Diverticulitis: diet
With uncomplicated diverticulitis, the diet should contain foods high in plant fiber, which will shorten the time that food is in the intestines, speed up the process of its excretion and help cleanse the body. The diet must include:
- Whole grain bread and bran;
- Cabbage, carrots, broccoli, cauliflower;
- Apples, grapefruit.
Should be excluded from the diet:
- Bloating foods: grapes, watermelon, all types of legumes;
- Products with very coarse fiber content: radishes, pineapples, persimmons;
- Foods that can linger in diverticula: seeds, grains, nuts.
For recurrent or acute diverticulitis, the diet consists solely of liquid foods:
- Mashed soups;
- Dried fruits compote;
- Decoctions of medicinal herbs;
- Various jelly;
- Tea.
In any case, if you have symptoms of diverticulitis, you should immediately see a doctor.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!