- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Iron deficiency

Iron deficiency or anemia is a pathological condition of the body in which there is a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin in the blood and erythrocytes. Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells (erythrocytes) and is responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the organs and tissues of the body.
Iron deficiency in the body can occur at any age. It often becomes a companion of various diseases and some physiological conditions of the body (pregnancy, period of increased growth, lactation, etc.).
Causes of iron deficiency
The most common causes of iron deficiency in the body are:
- An inadequate diet that contains insufficient iron. This phenomenon is especially common among children and young women. Iron deficiency can often be seen in children who love milk but rarely eat iron-rich foods. Also, iron deficiency can often be found in young girls on strict diets.
- The period of increased growth of the body. Children under the age of three usually grow so quickly that their bodies simply do not have time to produce the required amount of iron.
- Pregnancy and lactation. Women at this time need double the amount of iron. That is why pregnant women should regularly be tested for anemia and supplement their diet with foods high in iron. It also doesn't hurt to take a daily iron supplement.
- Blood loss is one of the most common causes of iron deficiency in adults. In women, iron deficiency can be triggered by too heavy menstruation. Blood loss can be caused by internal bleeding, such as in the gastrointestinal tract. Many factors can trigger gastric bleeding: ulcerative colitis, stomach ulcers, prolonged use of aspirin, or cancer. Therefore, determining the cause of iron deficiency is an important consideration in patient care.
Most often, iron deficiency develops in women, which is associated with regular blood loss. Also, iron deficiency in the body develops when:
- endometriosis;
- surgical and gynecological operations;
- long and heavy menstruation;
- uterine myoma;
- dysfunctional uterine bleeding;
- the presence of intrauterine contraceptives;
- compliance with various diets, etc.
Iron deficiency symptoms
Conditionally, iron deficiency can be divided into two stages: latent iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia.
With latent iron deficiency, the following symptoms are observed:
- the level of hemoglobin in the blood is normal;
- tissue iron stores are reduced;
- there are no clinical symptoms of iron deficiency;
- the activity of iron-containing enzymes gradually decreases;
- for adults, a compensatory increase in iron absorption in the intestine is characteristic.
With iron deficiency anemia, the following symptoms are observed:
- iron stores in the body are depleted;
- saturation of erythrocytes with hemoglobin is significantly reduced, which leads to their hypochromia;
- dystrophic changes occur in organs and tissues;
- an increased amount of protoporphyrin is observed in erythrocytes;
- the level of hemoglobin in the blood and its production are reduced.
The characteristic symptoms of iron deficiency are headache, weakness, dizziness, heart palpitations and shortness of breath with little exercise, muscle weakness, impaired sense of smell and taste, decreased appetite, tinnitus, and flashing flies in front of the eyes.
Pallor of the skin is also a symptom of iron deficiency. There is dryness and flaking of the skin, brittle hair and loss of hair, brittle nails. In the corners of the mouth, seizures may appear, dyspeptic disorders occur. In many ways, all these signs depend on the severity of the disease and the duration of the existence of iron deficiency in the body.
Diagnosis of iron deficiency

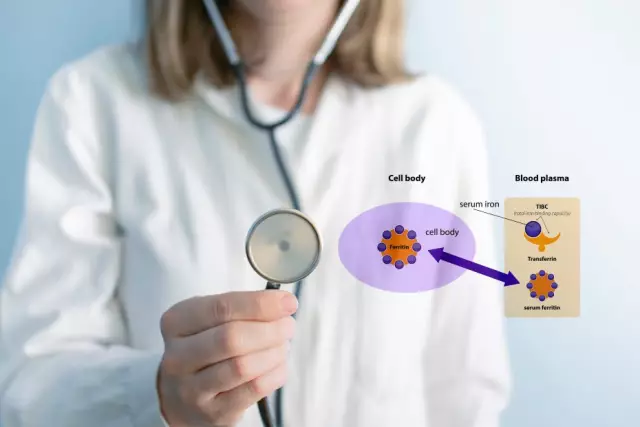
If anemia is suspected, the doctor advises the patient to have a complete blood count. The following signs can indicate the presence of iron deficiency in the body: a decrease in hemoglobin and erythrocytes in the blood, a decrease in serum iron and serum ferritin in the blood, an increase in the transferrin saturation coefficient.
Treatment principles for iron deficiency
It is impossible to fill the lack of iron only with iron-containing products. Without fail, doctors prescribe iron supplements. You should know that such drugs are prescribed for a long time, at least two months.
Diet also plays an important role. The menu must include ascorbic acid and protein, which contribute to the formation of complex iron compounds in the body and their better absorption in the intestine. Along with iron supplements, it is necessary to minimize or completely stop the use of dairy products and calcium, coffee, tea and other foods high in phosphates and oxalates.
Modern iron supplements are mostly free of side effects. In addition, they are covered with a special membrane that prevents the interaction of the digestive juice with iron, thus avoiding irritation of the gastric mucosa.
After the normal level of hemoglobin in the blood is restored, it is necessary to continue the treatment of iron deficiency for several months in order to replenish the reserves and avoid latent iron deficiency.
All iron deficiency states are reversible in nature. It is important to start treating iron deficiency as early as possible to restore the body's iron stores.
Prevention of iron deficiency
Certain types of anemia, especially those caused by poor diet, can be successfully prevented. To do this, you need to include iron-rich foods in your diet. These include seafood, nuts, whole grains, green leafy vegetables (spinach, broccoli), dried fruits (prunes, dried apricots, raisins), beans, iron-fortified cereals and bread.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!