- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Silicosis
General characteristics of the disease
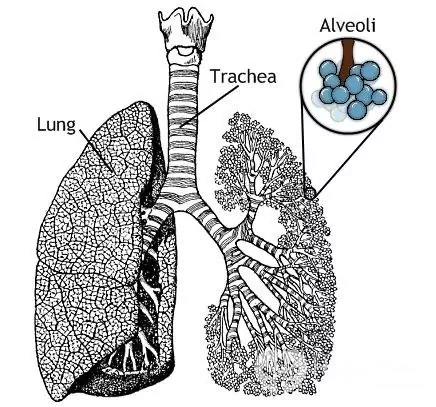
Silicosis is one of the occupational diseases. It occurs after prolonged inhalation of dust containing free silicon dioxide. Most often, lung silicosis occurs in people associated with the mining, metallurgical, porcelain and pottery and engineering industries.
The greatest danger to humans is represented by fine dust, the particle diameter of which is 2-3 nm. They easily penetrate the bronchioles and alveoli, contribute to the development of fibrosis and other pathologies. Note that the severity of symptoms and the number of complications depend on the amount and duration of exposure to silicon compounds. If the concentration of harmful substances in the air significantly exceeds the norm, and at the same time the workers do not use personal protective equipment, then within 1-3 years they develop an acute form of silicosis.
Unlike pneumoconiosis, the disease has a favorable course, however, the treatment of silicosis is often complicated by the addition of the tuberculous process and other disorders of the normal functioning of the respiratory system. In addition, in the acute form, pulmonary fibrosis and other complications continue to progress after the termination of contact with silicon dioxide, which also affects the success of treatment.
Symptoms and clinical picture of the disease
For a long period of time, silicosis disease does not bother the patient in any way, which is explained by its chronic course. The initial symptoms are scanty:
- shortness of breath, especially with physical exertion;
- chest pain;
- rare, dry cough;
- sputum production.
As the pathological process progresses, the symptoms begin to manifest themselves more clearly. Shortness of breath increases, often occurs even at rest. Associated diseases such as bronchial asthma and chronic bronchitis are added to the underlying disease. The intensity of pain also increases. The cough continues to remain dry, occasionally sputum production is observed in patients. A large number of it indicates the occurrence of complications (bronchiectasis, chronic bronchitis).
The appearance of patients practically does not change, but with an X-ray examination and a careful examination of the patient, early symptoms of emphysema, a decrease in the mobility of the pulmonary edges and a weakening of breathing can be detected. In some cases, lung silicosis can be identified by hard breathing and dry wheezing.
In severe forms of the disease, the cough becomes constant, profuse sputum is released, chest pain increases, a feeling of squeezing in the chest, cyanosis appears. Some patients experience hemoptysis and impaired cardiovascular function. Further contact with dust containing quartz leads to the development of a hypertrophic process and causes changes in the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract.
Silicosis treatment
First of all, it is necessary to exclude any contact with silicon dust. Further, patients are prescribed oxygen inhalation and breathing exercises. It is not recommended to take sedatives and antihypertensive drugs during this period. Acute pulmonary silicosis involves bronchoalveolar lavage. With obstructive syndrome, bronchodilators are prescribed.
If tuberculin skin tests are positive, then patients should take anti-tuberculosis drugs, such as Isoniazid. In silicotuberculosis, when the disease silicosis and tuberculosis are combined, patients are prescribed at least 3 anti-tuberculosis drugs, including rifampicin.
With a severe course of the disease with the development of massive fibrosis, doctors are inclined to the need for surgical intervention, which consists in lung transplantation.
Treatment of silicosis is necessary, because otherwise the disease causes many complications and provokes the appearance of concomitant respiratory diseases, in particular: pneumothorax, pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary emphysema, tuberculosis, fungal pulmonary infection.
Treatment projections for silicosis depend on the nature of the disease and its stage. Chronic silicosis is almost asymptomatic and in the initial stages the prognosis is almost always favorable. Acute or chronic progressive pulmonary silicosis, on the contrary, forms numerous complications, leading to the appearance of pulmonary fibrosis and secondary pulmonary hypertension. I would also like to note that with these forms of the disease, adverse changes continue to manifest themselves even after the complete cessation of contact with silicon oxide.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!






