- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Diverticulosis
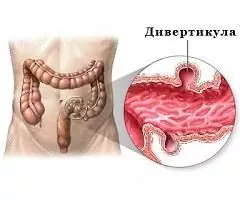
Diverticulosis is a morphological and functional pathological process characterized by the formation of saccular protrusions (diverticula) on the intestinal walls.
Intestinal diverticulosis is an acquired disease that most often occurs in older people living in developed Western countries with a high standard of living. In Africans and vegetarians, diverticular disease is observed much less often, which is associated with a decisive influence on the pathogenesis of diverticulosis of environmental factors.
Diverticula can form in different parts of the intestine. For example, diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon occurs in about 30% of cases, colon diverticulosis - in 15% of cases, total intestinal damage occurs much less often - in only 5% of cases.
Diverticulosis causes
Dystrophic changes in the muscle walls are of leading importance in the process of the appearance of diverticula: weakness of the connective tissue (congenital or acquired), discoordination of its motility, vascular pathologies. The etiopathogenesis of the disease is associated with changes in the lifestyle and diet of people in industrialized countries over the past 100 years. It is manifested by a decrease in the diet of people of vegetable origin, the predominance of meat and flour dishes, leading to constipation. The inhabitants of North America can become a model for the spread of diverticular disease, the proportion of vegetable fiber in the daily diet of which has decreased 10 times since the late 19th century.
In addition, abundant flatulence (flatulence), obesity, intestinal infections, and indiscriminate and prolonged use of laxatives contribute to the occurrence of intestinal diverticulosis.
There are also anatomical prerequisites for the appearance of diverticulosis, among which:
- Specific formation of the external muscle layer in the form of three stripes that weaken the intestine before external and internal influences;
- The nature of the location of the vessels, as a result of which places of least resistance are formed on the walls of the intestine;
- The presence of gaustres (folds in the colon), which create favorable conditions for increased intraintestinal pressure.
Diverticulosis symptoms
Most patients with intestinal diverticulosis report the absence of symptoms of the disease, however, in some cases, patients may complain of minor abdominal pain (most often in the left side of it), stool disturbances (constipation or diarrhea), rumbling, and bloating. With untimely treatment, the accumulation of feces in the diverticulum leads to an inflammatory process (diverticulitis), which is characterized by severe flatulence, severe abdominal pain, the presence of blood and mucus in the stool.
With diverticulosis of the colon, pain is localized mainly in the left ileal region - in the projection of the sigmoid colon - and is spastic in nature, increasing as the colon fills with feces. Often, when palpating the abdomen, it is impossible to determine the localization of the pathological process, which is associated with discoordination of intestinal motility.
Chills, fever, painful cramps in the lower abdomen indicate a complication of diverticular disease - diverticulitis.
Diagnosis and treatment of diverticulosis
The diagnosis of a disease such as colon diverticulosis is carried out by a gastroenterologist. In addition to a general examination, to identify the disease, the following studies must be prescribed:
- Analysis of blood and feces;
- CT scan;
- Ultrasound;
- Irrigoscopy (X-ray examination of the intestine after filling it with an enema with a contrast agent);
- Colonoscopy (examination of a section of the intestine with a flexible tube through the anus).
Both irrigoscopy and colonoscopy are unpleasant and painful procedures, but their implementation allows you to identify intestinal diverticulosis with sufficient reliability.
If there are no complications and symptoms of diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon, as well as the colon, then the treatment of this disease is carried out as follows:
- Diet;
- Reception of cerucal and festal;
- With diarrhea or flatulence, Intestopan, Biseptol, Sulgin are prescribed.
Diverticulosis in more complex cases is treated with:
- Gastric lavage;
- Unloading the intestines by enema;
- Infusion therapy with crystalloid solutions;
- Taking broad-spectrum antibiotics.
In severe forms of diverticulosis, complicated by recurrent bleeding, the disease is treated surgically. It is characterized by resection - removal of the affected areas of the intestine. In addition to resection, diverticulosis surgery involves intravenous antibiotics and abdominal drainage.
Nutrition for diverticulosis
In milder forms of the disease, diet can replace a full-fledged treatment of diverticulosis. Nutrition for diverticular disease should comply with the following principles:
- Eating foods rich in fiber: wholemeal bread, fruits, vegetables, whole grain cereals, bran;
- Restriction in refined food - white bread, cakes, pastries, semi-finished products;
- Consumption of enough water - at least 1.5 liters per day;
- Avoiding smoking and drinking alcohol;
- Restriction in products containing caffeine: chocolate, strong tea, coffee, Coca-Cola;
- Eating fermented milk products - kefir, yogurt, yogurt, with the exception of whole milk.
In addition to observing aspects of proper nutrition, patients with diverticulosis are advised to move more, do gymnastics, and in no case restrain the natural urge to defecate.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!






