- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
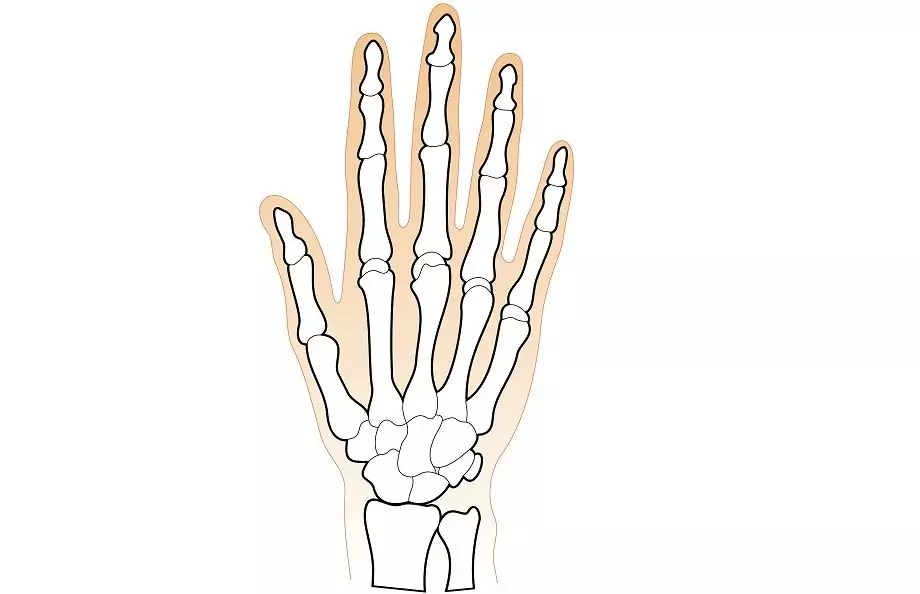
Wrist bones
Bones of the wrist. general information
The wrist bones form a collection of 8 small cancellous bones, which are arranged in two rows, each of which contains 4 bones.

The first or proximal row, closer to the forearm, consists of the following bones, presented in order, starting with the thumb:
- scaphoid or os scaphoideum;
- lunar or os lunatum;
- triangular or os triquetrum;
- pea or os pisiforme.
The connection of the first three bones forms an elliptical articular surface that articulates the wrist and the distal end of the radius. The pisiform bone of the wrist, which is usually referred to as the sesamoid bone, is in turn attached to the triangular bone.
The second row of wrist bones - distal - is formed by the following bones:
- trapezium or os trapezium;
- trapezoidal or os trapezoideum;
- capitate or os capitation;
- hook-shaped or os hamatum.
The surface of each bone is equipped with special articular facets that help the bones to connect with the nearest bones. Also on the palmar surfaces of a number of wrist bones are tubercles, to which ligaments and muscles are attached. These bones include: scaphoid, trapezium, hook-shaped.
The general view of the bones of the wrist is in the form of a vault, the convex part of which is located on the back of the hand, the concave part on the palmar.
Almost all 8 bones of the wrist have six surfaces (except for the pisiform). In this case, all bones, without exception, belong to the articular: their lower surface forms the articular fossa, and the upper one forms the articular heads. There are also joints between the lateral surfaces of the bones that connect the wrist bones to each other.
Damage to the bones of the wrist
The most common wrist injuries are sprains and fractures:
- Dislocation of the bones of the wrist. Dislocations come in a variety of ways, depending on the bones involved in the injury. Most often there are dislocations of the lunate bone, a little less often - scaphoid, rarely - pea. Dislocation of the lunate bone is quite difficult to recognize even with the help of an X-ray examination. However, the main symptoms are the following: the presence of a protrusion in the center of the palmar side of the wrist and a depression on the back, a feeling of pain when straightening the fingers, which are often immobile or bent. In addition, the wrist joint is swollen from the side of the palm, the movements are painful. Dislocation is repaired by counter-pull, traction or pushing according to the Beler method. Dislocation of the scaphoid is often accompanied by a fracture. It is possible to diagnose it only with the help of an X-ray examination. Such a dislocation is repaired under anesthesia or local anesthesia by traction, after which a bandage is applied, special gymnastics and physiotherapy are prescribed. Dislocation of the wrist pisiformis usually does not adversely affect the functioning of the hand and wrist. Surgical treatment is prescribed, in which the bone is sutured into place, and sutures are applied to the ligamentous apparatus;
- Fractures of the wrist bones are rare, but the scaphoid is most susceptible to fractures. In more rare cases (as in dislocations), fractures of the lunate and pisiform bones are possible. Fractures of other wrist bones are exceptional cases. A fracture of the scaphoid is possible in situations involving a fall on a bent arm, a blow with a fist on a hard surface, or a direct blow to the palm. In most cases, a fracture breaks the scaphoid in two. Symptoms of a fracture are as follows: soreness of the wrist joint, aggravated by stress on fingers I or II, inability to compress the hand into a fist due to pain. Diagnosis is carried out using X-ray examination, treatment includes immobilization for a period of 1 to 6 months. If the fracture of the wrist bone is not accompanied by displacement,It is recommended to apply a plaster cast for about 3 months. In the presence of displacement, osteosynthesis of bone fragments is performed with screws. In this case, the immobilization period is increased to 2 months. A fracture of the lunate bone occurs when a fall on the hand or as a result of a direct blow. After injury, there is swelling of the joint, pain, aggravated by extension of the hand to the back. Treatment involves the imposition of a plaster cast, which is worn for 1.5 to 2 months. As a rule, complications during bone fusion are not observed. The rarest type of wrist fracture is a pisiform fracture, which is caused by blows to the damaged area or a blow with the edge of the hand on a hard surface. Symptoms are pain in the wrist joint from the little finger,which is aggravated by clenching the hand into a fist or trying to bend the little finger. Treatment involves immobilization lasting at least 1 month.

Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.