- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Skin candidiasis
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Forms of the disease
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of skin candidiasis
- Potential consequences and complications
- Forecast
- Prevention
Skin candidiasis is an opportunistic mycosis that affects the upper layers of the skin. In patients with severe immunodeficiency conditions, the spread of infection is possible, which leads to the development of disseminated forms of the disease, in which internal organs are also affected (visceral candidiasis).
The incidence of fungal infections, including candidiasis of the skin, is increasing every year. This is largely due to the widespread irrational use of antibacterial drugs.
Causes and risk factors
The causative agent of candidiasis of the skin are yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. They belong to conditionally pathogenic microflora and normally live on the mucous membrane of the vagina, mouth, intestines, as well as on the skin. The activation of fungal infection and the development of the disease occurs in the event of a decrease in the general defenses of the body and a violation of the normal microbiocenosis.

Risk factors for the development of cutaneous candidiasis are:
- metabolic diseases (diabetes mellitus, obesity, dysproteinemia);
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- chronic somatic diseases;
- hypovitaminosis conditions;
- hyperhidrosis;
- therapy with antibiotics, corticosteroids, or cytostatics;
- vaginitis;
- taking oral contraceptives.
There are also a number of environmental factors, the influence of which increases the risk of developing skin candidiasis. These include, first of all, high humidity and elevated ambient temperatures, which create optimal conditions for the life of Candida fungi, help to move the infection into an active state. That is why candidiasis of the skin is often diagnosed in dishwashers, housewives, bath and pool workers. Similar conditions conducive to the development of fungus on the skin are created when wearing clothes made of artificial fabrics that do not allow air to pass through.
Candidiasis of the skin is often detected in workers of confectionery shops. In the raw materials used in the confectionery industry, fungi are present in considerable quantities. In conditions of high ambient temperatures, skin sweating increases, which creates favorable conditions for the development of mycotic lesions. A prerequisite for their occurrence is the systematic maceration of the skin of the workers' hands with organic acids (apple citric, lactic) and sugary substances.
Forms of the disease
Depending on the location of the lesion, candidiasis of the skin is divided into the following forms:
- candidiasis of the genital skin (as a rule, it occurs in combination with damage to the mucous membranes of the genital organs);
- candidiasis of large (inguinal, axillary) folds of the skin (candidal intertrigo);
- candidiasis of the skin of the feet, hands and interdigital spaces;
- candidal folliculitis - mycotic lesion of the hair follicles of the scalp, armpit, mustache and beard (candidiasis of the facial skin);
- diaper dermatitis - affects the skin of the perineum in infants and bedridden patients when using diapers (the most common form of skin candidiasis in children);
- bandage cutaneous candidiasis - occurs on the back in bedridden patients, as well as under plaster casts under conditions of increased skin moisture (especially in patients with diabetes mellitus).
Symptoms
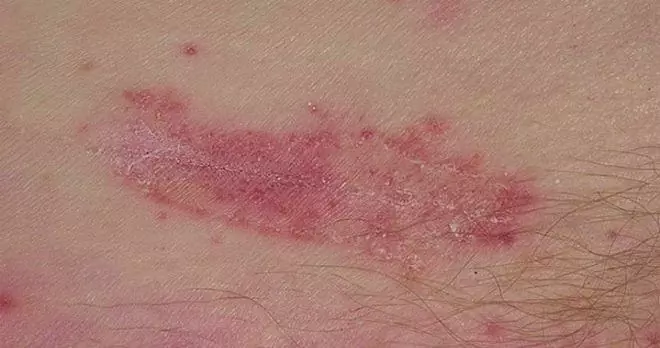
Lesions in candidiasis of the skin are usually initially located in large natural folds (in the groin, armpits, between the buttocks and under the mammary glands). In the future, they can spread to other parts of the body, leading to the development of candidiasis of the skin of the face, genitals.
In the affected area, hyperemic edematous areas appear on the skin, the surface of which is covered with papules, pustules and vesicles. After the opening of the bubbles, erosion forms in their place, having clearly defined scalloped edges. The erosive surface is smooth and shiny, covered with a characteristic whitish bloom. On the periphery of the lesion there are separately located pustules, vesicles, edematous-erythematous spots, papules.
With candidiasis of the skin of the face, small bubbly rashes are mostly localized around the perioral region. In addition, patients complain of seizure and cracks in the corners of the mouth, increased dryness of the skin.
Diaper dermatitis is the most commonly observed form of skin candidiasis in children. The cause of its occurrence is usually a violation of the rules of hygienic care for the child. The main symptom of diaper dermatitis is the appearance on the inflamed skin of the perineum of vesicular-pustular rashes or a scaly rash, which are accompanied by severe itching.
Candidiasis of the skin of the interdigital spaces is usually observed in people who are often in contact with the ground (rural residents, workers in greenhouses and greenhouses, owners of summer cottages) and preschool children. It is characterized by reddening of the skin between the fingers and the appearance of small bubbles on it.
Candidiasis of the genital skin in most cases is combined with fungal balanitis, balanoposthitis in men or colpitis, vulvovaginitis in women.
In rare cases, candidiasis of the skin takes on a chronic course. Most often, this is facilitated by defects in T-lymphocytes, i.e., insufficient immune system. Exacerbations of the disease occur several times a year, with each exacerbation, the affected area slightly increases. In the most severe cases, infiltrates appear on the skin, which have indistinctly outlined contours, the surface of which, at the time of exacerbation, is covered with serous-bloody crusts pierced with mycelium filaments.
Diagnostics
To confirm the diagnosis, a scraping is taken from the lesion for subsequent direct microscopy (the detection of oval-shaped cells with fungal pseudomycelium is a diagnostic sign of candidiasis).

Source: likar.info
Also, in order to determine the pathogen, methods of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), immunofluorescence (RIF) reactions and PCR diagnostics can be used.
The quantitative determination of Candida fungi is of greater diagnostic value, since they are present on the skin and mucous membranes of a person and in normal conditions. For this purpose, a bacteriological examination of the scraping material is carried out (inoculation on Sabouraud's medium). In addition, this analysis allows you to accurately identify the pathogen, and most importantly, to determine its sensitivity to antifungal agents.
To identify concomitant diseases that could provoke the development of skin candidiasis, the following laboratory tests are additionally prescribed:
- determination of antibodies to HIV;
- immunogram;
- determination of glucose concentration in blood serum;
- clinical blood test.
Skin candidiasis requires differential diagnosis with the following diseases:
- erythematous lupus;
- recurrent genital herpes;
- favus (wolf lichen, scab);
- psoriasis of skin folds;
- seborrheic dermatitis;
- eczema.
Treatment of skin candidiasis
Therapy for skin candidiasis consists in taking antifungal agents:
- preparations of the azole group (Fluconazole, Econazole, Miconazole, Clotrimazole, Isoconazole, Ketoconazole);
- antifungal antibiotics (Levorin, Natamycin, Amphotericin B, Nystatin);
- other antimycotic drugs (undecylenic acid preparations, Naftifine, Terbinafine, Cyclopirox, Dequalinium chloride, Flucytosine).
In the case of single lesions, antifungal agents are used topically, in the form of ointments.

Source: napalce.ru
With a widespread process, local treatment is combined with systemic, that is, the use of antifungal ointments is accompanied by the intake of drugs of the same action inside. The duration of the course, the frequency of taking medications and their dosage is determined in each case by a dermatologist.
Self-medication is unacceptable! An excess of the required dosage can lead to the development of a toxic effect, which is significantly pronounced in antifungal antibiotics, and an insufficient dosage will contribute to the transition of the disease into a chronic form and the development of resistance of the pathogen to traditional therapy.
Treatment of intestinal candidiasis, in addition to eliminating the pathogen, is aimed at restoring its functions, strengthening the defenses of the patient's body, and treating concomitant diseases.
The complex therapy of skin candidiasis includes a diet low in carbohydrates, especially easily digestible ones (sugar, confectionery, honey).
During treatment, the skin in the lesions should be kept clean and dry.
Potential consequences and complications
Without the necessary treatment, candidiasis of the skin can become chronic, resistant to standard therapy. With each relapse, the pathological process expands, affecting new areas of the skin.
With a significant weakening of the immune system, candidiasis of the skin can turn into a common severe form with the development of damage to the kidneys, brain, heart, eyes and liver, anemia, osteoporosis, fungal pneumonia. Life-threatening complications are candidal meningitis and endocarditis.
The entry of Candida fungi into the systemic circulation in combination with an immunodeficiency state threatens the development of mycotic sepsis, which in most cases ends in death.
The erosion formed on the skin is the entrance gate for a secondary bacterial infection, due to which candidiasis of the skin can be complicated by the development of purulent diseases (furuncle, phlegmon).
Forecast
The prognosis, subject to accurate diagnosis, timely and complete treatment, is favorable. The prognosis is slightly worse in patients with reduced immunity and the presence of concomitant diseases. In this case, candidiasis of the skin can become chronic, leading to the development of complications.
Prevention
Prevention of cutaneous candidiasis includes:
- the use of antibiotics only in the presence of strict indications in the dosage prescribed by the doctor;
- normalization of body weight;
- correction of serum glucose levels;
- refusal to wear tight clothing made of fabrics with poor hygroscopic properties;
- timely detection and treatment of other forms of fungal infection (candidiasis of the oral cavity, mucous membranes, nail plates).
YouTube video related to the article:

Elena Minkina Doctor anesthesiologist-resuscitator About the author
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute, specializing in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly passed refresher courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the city maternity complex, resuscitator of the hemodialysis department.
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!