- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Stones in the kidneys
Urolithiasis is the official medical name for a disease in which stones are formed in the kidneys and in other organs of the urinary system.
Age groups at risk of disease
Almost all groups of the population are susceptible to the development of urolithiasis. The disease can even occur in newborn babies. But the older the person, the greater the risk of kidney stones.
Types of kidney stones

The type of calculi (stones) depends mainly on the age of the person. The elderly usually suffer from uric acid stones. Other types of calculi are less common. They can form not only directly in the kidneys, but also in the bladder and ureter. Their size can be different: from a few millimeters (small ones are called "sand") to several centimeters.
Kidney stones: causes of formation
One of the main reasons for the development of urolithiasis is a violation of metabolic processes in the body. Kidney stones appear when the water-salt and chemical composition of the blood changes. Also, a number of additional reasons affect their education:
- Heredity;
- Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system: gastritis, colitis, pyelonephritis, prostatitis, cystitis, etc.;
- The presence of injuries and various bone diseases;
- Infectious diseases leading to a violation of the water-salt balance;
- Disruption of the parathyroid glands;
- Vitamin D hypervitaminosis;
- The use in the diet of too salty, acidic and spicy foods that increase the acidity of urine, as well as hard water containing high levels of salts;
- Excess ultraviolet rays.
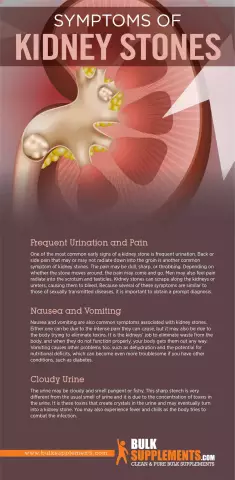
Kidney stones: symptoms
Very rarely, urolithiasis is completely asymptomatic and kidney stones are discovered quite by accident, when a patient is examined for any other disease.
The most common symptom of kidney stones is pain in the lumbar region on one or both sides. It can worsen during exercise or when body position changes. A stone trapped in the ureter causes severe pain in the lower abdomen and groin - renal colic. Other symptoms of kidney stones include:
- Changes in urine color;
- Renal colic, recurring and subsiding. Stop after the stone comes out;
- High blood pressure;
- Swelling.
Kidney stones: treatment
Therapy of urolithiasis today includes surgical and conservative methods of treatment. The main goals of treating kidney stones are:
- Removal of stones;
- Prevention of recurrent calculus formation;
- Elimination of infection.
With the conservative treatment of kidney stones, medications are used to dissolve calculi, normalize metabolism, and stop inflammatory processes in the urinary system. Diet therapy is also recommended for patients. If the size of the stones is small, then this method is quite effective. Treatment of urolithiasis is carried out under the direct supervision of a urologist.
Surgical treatment of kidney stones is resorted to in the presence of large stones or having a complex coral shape. Currently, there is an excellent alternative to open surgery - crushing kidney stones using extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. This method of treating urolithiasis is based on the use of focused electrohydraulic acoustic shock waves. Under their influence, the stones in the kidneys, ureter and bladder are crushed. In fact, urinary stones turn into fine sand, which is naturally discharged outside without any difficulty.
Kidney stones: folk remedies for solving the problem

There are many unconventional methods of treating urolithiasis, including the intake of various decoctions of plants that help crush kidney stones and remove them painlessly. But before resorting to the treatment of kidney stones with folk remedies, you should definitely consult with your doctor. This is due to the fact that urinary stones can have a different chemical nature (oxalates, urates, protein, etc.), and therefore different means are needed to dissolve them. Incorrectly selected herbal medicine will not only not lead to crushing of the kidney stone, but, on the contrary, can provoke its further growth or the development of an attack of renal colic.
Diet for the prevention and treatment of urolithiasis
The diet for urolithiasis should be made taking into account the acid-base reaction of urine, the chemical composition of calculi and the characteristics of metabolic disorders. Its main principles are:
- Abundant fluid intake, which allows you to remove salt sediments and small stones, the so-called sand, from the urinary tract;
- Eating food products that maintain the necessary pH of urine for better dissolution of existing stones and prevention of the formation of new ones;
- Limiting the diet of foods that contribute to the formation of kidney stones.
Diet therapy for urolithiasis must necessarily be based on concomitant diseases. So, for example, if the patient has circulatory failure, the use of a large amount of fluid recommended for the treatment of urolithiasis is excluded. With a combination of kidney stones and obesity, the diet should be low in calories.
With urate stones, foods rich in purine bases (legumes, mushrooms, peanuts, cauliflower, radishes, figs, sorrel, spinach, chocolate, meat by-products) should be excluded from the diet.
With oxalate stones, you should limit the use of foods rich in oxalic acid (beets, potatoes, onions, carrots, black currants, citrus fruits, blueberries). At the same time, it is necessary to consume as many products as possible that bind and remove oxalic acid from the body. These include: plums, pears, apples, light grapes, dogwood.
With phosphate kidney stones, a diet with a sharp restriction of almost all fruits, vegetables and dairy products is recommended. The menu includes eggs, meat, fish, beans, grains and some types of fruits, berries and vegetables (lingonberries, sour apples, cranberries, green peas, pumpkin). This diet is not physiological. Therefore, it should be adhered to only for a short time, for example, during an exacerbation of the disease.
Additional recommendations
Don't forget about physical activity. During exercise, calcium is transferred from the blood to the bones. This reduces the risk of kidney stones forming.
It is necessary to monitor not only the quality of the water used, but also to consume it in sufficient quantities: at least 1.5-2 liters per day. Due to drinking plenty of water, urine becomes less concentrated, which prevents the precipitation of salts.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!