- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Keratoconjunctivitis
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Forms of the disease
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications and consequences
- Forecast
- Prevention
Keratoconjunctivitis is an inflammatory disease of the conjunctiva with involvement of the cornea in the pathological process. Keratoconjunctivitis is one of the most common ophthalmic pathologies due to the quick response of the conjunctiva to endogenous and exogenous stimuli. Women and men are equally susceptible to the disease.

Lachrymation and redness of the conjunctiva are the main symptoms of keratoconjunctivitis
Causes and risk factors
The reasons for the development of keratoconjunctivitis can be:
- blinking disorder;
- infection (bacteria, viruses, microscopic fungi, helminths can act as agents) during ophthalmic procedures, with non-compliance with personal hygiene, etc.;
- violation of the tear film;
- systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and other systemic diseases;
- a foreign body in the cornea or conjunctiva;
- constant wearing of contact lenses;
- allergic processes;
- infectious diseases.
Forms of the disease
Depending on the etiology, keratoconjunctivitis is distinguished:
- herpetic;
- hydrogen sulfide;
- epidemic;
- dry;
- chlamydial;
- tuberculous-allergic;
- adenoviral;
- spring;
- atopic, etc.
Depending on the nature of the course:
- acute;
- chronic.
Symptoms
Acute keratoconjunctivitis is characterized by a lesion at the beginning of one eye, then the second eye is also involved in the pathological process. The inflammation can be asymmetrical - one eye can be involved in the process more, the other less. Symptoms of the disease vary depending on the form. Signs common to all forms:
- itching and / or burning of the eye;
- lacrimation;
- redness of the conjunctiva and cornea of the eye;
- mucopurulent discharge from the eye;
- swelling of the conjunctiva;
- photophobia;
- sensation of a foreign body in the eye;
- sharp pain in the eye.

Itchy and burning eyes are the main symptoms of keratoconjunctivitis
With chlamydial keratoconjunctivitis, general symptoms are complemented by the formation of peripheral subepithelial infiltrates. Keratoconjunctivitis against the background of an allergic reaction is accompanied by lacrimation, itching and severe burning sensation. The dry form of the disease is manifested by dry eye syndrome. Viral keratoconjunctivitis is often accompanied by hemorrhage under the conjunctiva. In the case of epidemic keratoconjunctivitis, a coin-shaped cornea becomes opaque.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, an ophthalmological examination and instrumental and laboratory research are required, including:
- collection of complaints and anamnesis;
- objective examination;
- biomicroscopy, visometry, perimetry, etc.;
- bacteriological and histochemical examination of the lacrimal fluid;
- general analysis of blood and urine;
- Wasserman reaction (or express diagnostics of syphilis); and etc.
Treatment
The tactics of treating keratoconjunctivitis depends on the form of the disease, as well as on the depth and prevalence of the inflammatory process. An anti-infective drug is selected depending on the type of infectious agent that caused the pathological process.
With dry keratoconjunctivitis, in addition to anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs that moisturize the surface of the eyes are used.
When treating an allergic form of keratoconjunctivitis, first of all, the allergen is eliminated, then antihistamines are prescribed.
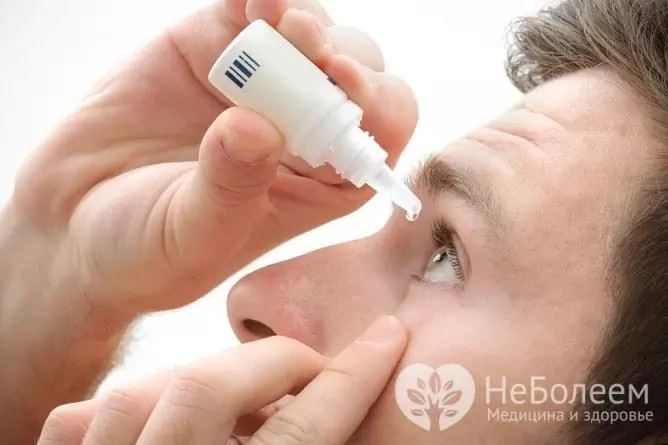
For the treatment of keratoconjunctivitis, anti-infectious, anti-inflammatory drugs and drops that moisturize the conjunctiva are used
In some cases, with keratoconjunctivitis, patients are shown surgical intervention. Surgical treatment is carried out mainly for keratoconjunctivitis caused by a foreign body entering the eye or other trauma.
If the therapy fails and the symptoms worsen, corneal transplantation may be performed.
Possible complications and consequences
Against the background of keratoconjunctivitis, corneal opacity may develop with a concomitant decrease in visual acuity, filamentous keratitis, leucorrhoea, etc. The most severe complication is complete loss of vision.
Forecast
With early diagnosis of keratoconjunctivitis and timely adequate treatment, the prognosis is favorable; in the absence of treatment, the prognosis for visual function worsens.
Prevention
There is no specific prophylaxis for keratoconjunctivitis. Non-specific preventive measures:
- observance of the rules of personal hygiene, washing only with clean water;
- compliance with the rules for wearing contact lenses;
- wearing swimming goggles when visiting the pool;
- strengthening immunity.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!






