- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Baby roseola
Brief description of the disease

Roseola infantile is an infection that usually affects young children, mainly up to two years of age.
The second common name for the disease is sudden exanthema. Roseola is also known as childhood fever, sixth disease, and pseudo-rubella.
The symptoms of baby roseola are often confused with signs of SARS, rubella, or allergies, so it can be difficult to make a diagnosis.
The causes of the disease
The cause of baby roseola is the causative agent of herpes types 6 and 7. In adults, these viruses cause chronic fatigue syndrome, and in children, roseola. The virus enters the skin and tissues, causes their damage, infects mononuclear cells, reacts with immune cellular factors and provokes the appearance of exanthema (skin rash).
The disease is widespread among children, but the mechanism of infection is still not understood. It is assumed and most likely that the virus that causes roseola is transmitted by airborne droplets. The incubation period is 5-15 days, on average 3-7 days.
Most often, roseola develops in children in spring and autumn.
Baby roseola symptoms
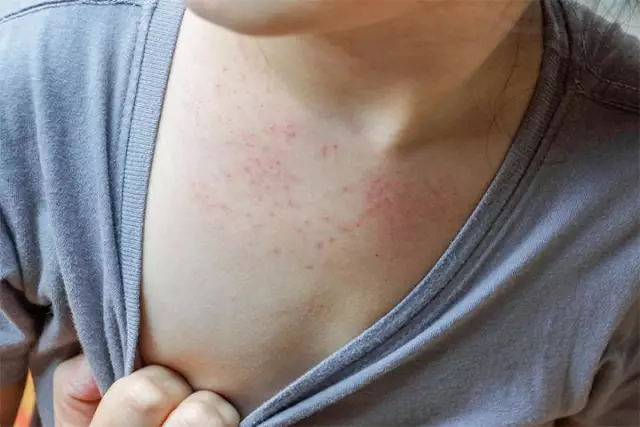
Roseola for children begins with a sharp rise in the child's body temperature to 39-40.5 degrees. Vomiting, runny nose, cough, catarrhal phenomena, stool changes are not observed. The temperature is kept at a high level of 3-5 days, while the effectiveness of antipyretic drugs is minimal. A critical drop in temperature occurs on the 4th day, and 10-20 hours after the condition has stabilized, pink papular spotty rashes appear on the whole body, slightly raised above the skin. The rash persists for several hours or days.
After the rash appears, the rise in temperature is no longer recorded. Exanthema passes without spots and peeling after 4-7 days.
A characteristic symptom is that the rash begins to spread from the body, then spreads to the face, neck, arms, legs. The most profuse rashes are observed on the child's body.
Additional symptoms of roseola: enlargement of the cervical, ear (posterior) lymph nodes, the child is lethargic, eating poorly, irritable. Sometimes there is an increase in the liver, spleen.
In the blood, there is an increase in lymphocytes, a decrease in the number of leukocytes.
Diagnosis of the disease
In addition to external examination and assessment of the symptoms of baby roseola, a blood test is done, sometimes serological diagnostics are used (there is a fourfold increase in the titer of immunoglobulin G).
When making a diagnosis, it is important to distinguish roseola from a drug rash, enterovirus non-polio infections, infectious erythema, sepsis, otitis media, bacterial pneumonia, meningitis, rubella, measles.
Treatment of baby roseola

There is no specific treatment for baby roseola. To alleviate the condition of the child during the rise in temperature, he is given antipyretic drugs - paracetamol or nurofen, make sure that dehydration does not occur. The room where the sick child is located should be constantly ventilated.
Symptomatic treatment of baby roseola for children with immunosuppression (suppression of immunity due to recent diseases, stress) is complemented by the appointment of acyclovir and foscarnet.
If the effectiveness of the means for relieving fever is minimal and the child begins to have seizures, you should seek medical help.
Prevention of the disease
Due to the fact that the cause of baby roseola is infection with a virus, prevention is only to limit the child's contact with children who are supposedly infected with it.
Therefore, children who have this disease, as with other contact infection, should be isolated until they are completely recovered.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!