- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Forms of the disease
- Symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis
- Potential consequences and complications
- Forecast
- Prevention
Adenoviral conjunctivitis (pharyngo-conjunctival fever) is an infectious and inflammatory disease caused by adenoviruses and occurs with signs of conjunctival lesions (swelling of the eyelids, discharge from the eyes, burning, pain), symptoms of nasopharyngitis and fever. Outbreaks of the disease are most often recorded during the cold season among children attending organized groups.

Symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis
Causes and risk factors
Sporadic cases of adenoviral conjunctivitis are most commonly caused by type IV, VI, VII and X adenoviruses. Epidemic cases are usually caused by type III, VIIa and XI adenoviruses.
The infection is transmitted by household contact or by airborne droplets. When sneezing, coughing, or through dirty hands, adenovirus enters the mucous membrane of the eyeball.
Risk factors that increase the risk of developing adenoviral conjunctivitis are:
- stress;
- hypothermia;
- trauma to the organ of vision (including operating ones);
- non-compliance with the rules of wearing and caring for contact lenses;
- swimming in public pools and open water.
From the moment of infection to the moment the first symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis appear, it takes from 2 to 10 days (in most cases, the duration of the incubation period is 5-7 days). In the process of vital activity, adenoviruses lead to the destruction of epithelial cells, which is characterized by hypertrophy of the nucleoli, breakdown of chromatin, and vacuolization.
Forms of the disease
Depending on the characteristics of the clinical course, three forms of adenoviral conjunctivitis are distinguished:
- catarrhal;
- follicular;
- filmy.
The first two forms of the disease can be observed in patients of any age, and the latter occurs mainly in children.
Symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis
The first symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis are:
- headache;
- increased body temperature;
- dyspeptic disorders;
- submandibular lymphadenitis;
- nasal congestion;
- runny nose;
- sore throat;
- dry cough.

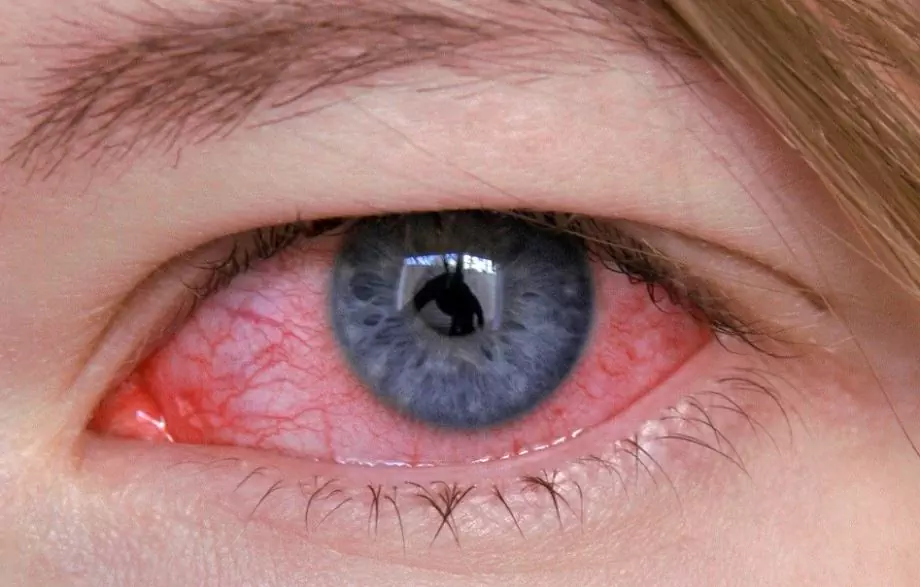
Headache, lacrimation, fever are the main symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis
After a few days, the body temperature decreases, and then it rises again. At this moment, the patients show signs of conjunctival damage, first of one, and then of the other eye:
- redness and swelling of the eyelids;
- itching;
- burning;
- foreign body sensation;
- unsharp blepharospasm;
- photophobia;
- lacrimation;
- abundant discharge of mucous or mucopurulent character.
Hyperemia (redness) of the conjunctiva covers all its parts, and also extends to the lower and lunate fold, the lacrimal meatus.
For the catarrhal form of adenoviral conjunctivitis, mild symptoms of local inflammation are characteristic. The amount of discharge is insignificant, the redness of the mucous membrane of the eyes is moderate. The duration of the disease does not exceed a week. Corneal complications do not develop.
With follicular adenoviral conjunctivitis, follicles (small bubbles) 1-2 mm in size, filled with translucent gelatinous contents, appear on the mucous membrane of the eyes. They can cover the entire surface of the mucous membrane or concentrate in the corners of the eyelids.
Attention! Photo of shocking content.
Click on the link to view. Adenoviral conjunctivitis in children in 25% of cases is represented by a membranous form. The disease is characterized by the appearance on the conjunctiva of thin delicate films of grayish-white color. In most cases, they can be easily removed with a cotton swab, but sometimes they take the form of dense fibrous deposits adhered to the mucous membrane. In this case, they are removed with difficulty; after removal, the conjunctival areas under them bleed. Some patients develop infiltrates and hemorrhages in the subconjunctival space. After recovery, they are completely absorbed. With membranous adenoviral conjunctivitis in children and most adults, the general condition suffers: the body temperature rises to 38.5-39.5 ° C, general malaise, weakness, and headache appear. The duration of the febrile period is 3 to 10 days.
Diagnostics
It is possible to assume pharyngo-conjunctival fever in a patient if a history of contact with a patient suffering from this disease is identified. During the examination, attention is paid to the combination of signs of conjunctivitis with regional lymphadenopathy and inflammation of the upper respiratory tract.
Confirmation of the diagnosis is carried out by virological, cytological and serological research methods. For early diagnosis of the disease, an immunofluorescence method is used, which allows the detection of specific viral antigens in the detachable mucous membrane of the eye.
It is possible to detect DNA of adenovirus in scraping from the conjunctiva by staging a polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which is highly informative. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), the compliment binding reaction (CSC) allow to determine the content of antibodies to adenoviruses in the blood serum. In adenoviral conjunctivitis, the diagnostic criterion is an increase in antibody concentration by at least 4 times.

ELISA for adenoviral conjunctivitis detects an increase in antibodies to adenoviruses by more than 4 times
For the isolation and identification of adenoviruses on cell culture, a virological study of the discharge from the conjunctiva is performed.
With the follicular form of adenoviral conjunctivitis, differential diagnosis with trachoma is performed. In trachoma, the follicles are localized in the upper eyelid, and in addition, the disease is not accompanied by fever and nasopharyngitis. The membranous form of adenoviral conjunctivitis in some cases is mistaken for eye diphtheria.
Treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis
Therapy for adenoviral conjunctivitis is performed on an outpatient basis. In the first week of the disease, antiviral drugs are instilled into the conjunctival sac 6-8 times a day. In the second week, the frequency of their use is reduced to 2-3 times a day. Antiviral ointments can also be used, which are placed behind the eyelids 3-4 times a day.
In order to prevent the addition of a secondary bacterial infection, the use of eye drops and ointments with antibiotics or sulfa drugs is indicated.

Antiviral eye drops are prescribed to treat adenoviral conjunctivitis
During the course of treatment for adenoviral conjunctivitis, patients are prescribed antihistamines.
To prevent the development of xerophthalmia (dry eye syndrome), patients are recommended to instill moisturizing eye drops of the "artificial tear" type several times a day.
Potential consequences and complications
Untimely initiated or inadequate treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis can cause complications:
- toxic-allergic conjunctivitis;
- bacterial conjunctivitis;
- keratitis;
- dry eye syndrome;
- otitis;
- tonsillitis;
- adenoiditis;
- scarring of the conjunctiva.
Forecast
In most cases, the prognosis is favorable, after 15-30 days it ends with a full recovery. If a patient develops dry eye syndrome, it becomes necessary to use moisturizing eye drops for a long time.
Prevention
Prevention of infection with adenoviral conjunctivitis includes the timely isolation of sick children from an organized team, regular wet cleaning, airing the premises, and careful adherence to personal hygiene rules.
Swimming pools require careful monitoring of chlorination and compliance with current sanitary standards.
To prevent iatrogenic infection of patients with adenovirus infection, careful sterilization and disinfection of medical instruments (eye sticks, pipettes) should be performed, routine and general cleaning should be carried out in the ophthalmological office using disinfectants and subsequent quartzing.
YouTube video related to the article:

Elena Minkina Doctor anesthesiologist-resuscitator About the author
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute, specializing in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly passed refresher courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the city maternity complex, resuscitator of the hemodialysis department.
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!