- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Dermatofibroma

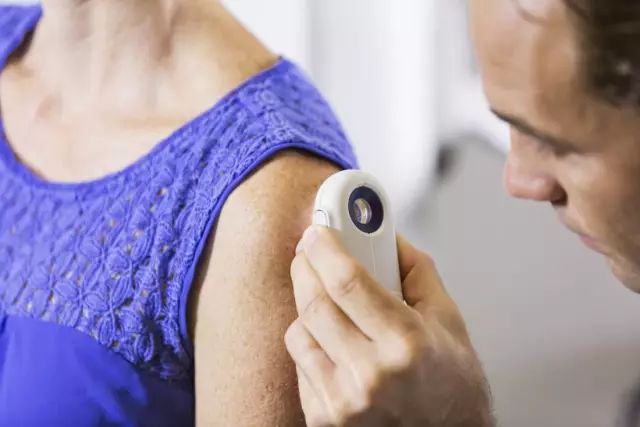
Dermatofibroma is a small, benign skin mass. Dermatofibroma can appear anywhere on the body, but the most common are the shoulders, upper back, feet, and ankles. More often you can find education in adults, in children - much less often. The formation can be gray, pink, brown or red, sometimes it changes color over time. To the touch, dermatofibroma is hard and resembles a lump hardened under the skin. The cutaneous growth is predominantly formed by fibrous fibrous tissue and contains histiocytes and fibroblasts. If the dermatofibroma is squeezed on the sides, then a small fossa will appear on its surface. Dermatofibroma is also called sclerosing hemangioma or fibrous histiocytoma.
As a rule, dermatofibromas do not cause significant inconvenience. They are virtually painless, but may cause itching and mild pain in some people. Most often, you can see single dermatofibromas, but in some patients you can also find multiple. Formations are rarely more than one centimeter in diameter.
Dermatofibroma causes
It used to be thought that dermatofibroma is a reaction to the bites of various insects or trauma, but this version has not spread. The exact cause of dermatofibroma is unknown. This can partly be explained by the persistent nature of the disease. At first, the formation resembles a dense nodule, the size of a small pea. Over time, the size of the dermatofibroma, its color and density change slightly.
Doctors identify the following likely causes of dermatofibroma:
- Sexual predisposition. Women are more susceptible to the disease than men.
- Damage to the skin. Dermatofibroma can occur as a result of an insect bite, thorn prick, etc.
- Hereditary factor. The cause of the disease is often a hereditary family factor.
- Age. Most often, dermatofibroma is formed in middle-aged people. In children, the disease is rare.
Dermatofibroma symptoms
The most common symptoms of dermatofibroma are:
- a lump that occurs above the surface of the skin, which, if damaged, can bleed;
- neoplasms most often form on the legs in the area below the knee, but can appear on the arms and trunk;
- when pressed, the dermatofibroma bends inward;
- the color of the dermatofibroma differs significantly from the normal skin tone;
- in people with dark skin, the formation, as a rule, has a darker shade;
- sometimes, when touching a tumor, soreness and itching may occur.
You should know that very often dermatofibrosarcoma (a type of skin cancer) in the first stage has similar symptoms to dermatofibroma. Therefore, it is important not to waste time, but see a doctor when the first symptoms appear. It is especially worth paying attention when the formation rapidly increases in size, changes color or shape, causes severe pain or bleeds.
Diagnostics of the dermatofibroma
A doctor, as a rule, can diagnose dermatofibroma after a visual examination of the patient. If the growth on the skin does not bleed and does not visually look like a dermatofibroma, the doctor may do a biopsy. To do this, the doctor will remove a small piece of the formation and carefully examine it under a microscope. A biopsy can diagnose various diseases, including tumors. Before the biopsy, the patient undergoes local anesthesia.
Dermatofibroma treatment

The disease itself does not go away, and without appropriate treatment, dermatofibroma remains with the patient throughout his life. If the formations are in too noticeable places or the patient constantly touches them (in the process of dressing or when performing other actions), then dermatofibroma removal is preferable. It is also better to choose the removal of dermatofibroma if it causes discomfort, soreness and itching in the patient.
Since dermatofibromas are located deep under the skin, incisions are made in the deep layers of the skin to remove them. After removal of dermatofibromas, quite noticeable scars often remain. If the procedure goes well, the patient is allowed to go home on the same day. Complications develop extremely rarely and they are associated, as a rule, not with the disease itself, but with a poorly performed procedure.
An alternative treatment for dermatofibroma is to cut the top off. But most often, after such treatment, it increases in size again after several years.
After removal of the dermatofibroma, the scar remains very noticeable for some time, often causing itching. Over time, it smoothes out and becomes paler. Today, there are many cosmetic procedures that make the scar practically invisible. However, you should know that these procedures can only be performed some time after the treatment of dermatofibroma. For scar treatment, you can choose one of the following methods:
- laser treatment, with which you can effectively eliminate redness;
- injections of steroids into the rumen;
- special silicone gel to help smooth the edges of the scar;
- with very large scars, you can resort to surgery.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!