- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Hemangioma

We have all met in life people on whose face there were large "birthmarks", although hemangioma is not a birthmark. Hemangioma is a benign vascular tumor that looks like red, purple or blue spots, flat or raised above the skin, which can occupy a significant area - from 0.5 cm to 10-15 cm in diameter.
Hemangioma in children is the most common type of tumor. Its favorite localization is on the face or neck, although hemangiomas are also found in other parts of the body, and even hemangiomas of internal organs. Hemangioma only in rare cases is capable of causing harm to health, as a rule, these are hemangiomas of internal organs - the rarest type of hemangiomas. But being located in open areas of the body, having a large size and striking the eyes of others, hemangioma can significantly affect the psycho-emotional state of a person, worsening it, especially when it comes to girls. By the way, girls have hemangioma more often than boys.
Causes of hemangioma
Researchers have not yet learned the causes of hemangioma, but long-term observations and statistics have made it possible to make several assumptions.
Since hemangioma occurs in children, and young children, there is a violation during the prenatal period of the child's development. This is the intake of certain medications by a pregnant woman, the poor environmental situation in the area of residence, possibly a viral disease suffered during pregnancy. Also, endocrine disorders are suspected in the appearance of hemangiomas in children, since gender dependence is traced - in girls it occurs more often.
Hemangioma manifestations
It was previously believed that hemangioma in newborns does not appear, and the first signs of hemangioma appear between the ages of several weeks and three months. However, in recent years, cases of hemangioma in newborns have been increasingly recorded. Pediatricians find it difficult to name the reason, and assume that the deterioration of the environment is to blame.

Hemangioma in newborns, as a rule, looks like a small speck. The color of the speck can vary from light pink to purple-cyanotic. As a rule, hemangiomas in newborns are dark pink or light red.
As already mentioned, such a speck may not appear immediately, but when the baby is several weeks old. Hemangioma in children is usually not immediately recognized as a vascular tumor. The speck is small and dim, and the parents simply treat it with anti-inflammatory ointments. However, the speck begins to grow, and sometimes this growth is quite rapid. As a rule, as the hemangioma grows in children, it darkens. Hemangioma grows in children under one year old, then growth stops.
As a rule, superficial hemangioma does not cause any special manifestations, except for external ones. Hemangiomas located inside can have different symptoms, depending on the location and the degree of impact on the surrounding tissues.
The appearance of the hemangioma, as well as its effect on health, largely depend on the location and type of tumor.
Hemangioma in children has the following localization (descending list):
- the scalp, especially the back of the head;
- on the face: eyelids (including the inside of the eyelid), nose, cheeks;
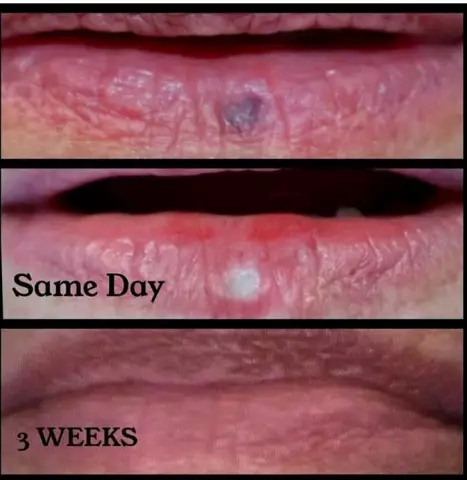
- oral cavity;
- genitals;
- upper body;
- arms;
- legs;
- internal organs, bones, etc.
There are the following types of hemangiomas:
- simple (capillary) hemangioma. It can be flat, lumpy-nodular, lumpy-flattened. Has a red, purple or cyanotic color, clear boundaries, is located on the surface of the skin. When pressed, the stain turns pale;
- cavernous (cavernous) hemangioma. It is located under the skin, looks like a knot, usually bumpy, covered with either unchanged skin or skin of a bluish tint. When pressed, the knot collapses;
- combined hemangioma. Combines the signs of a simple and cavernous vascular tumor;
- mixed hemangioma. Hemangioma, in which not only blood vessels are involved in the tumor process, but also other tissues. The type of such hemangiomas differs depending on their composition.
Hemangioma treatment
There is no consensus on how and at what age it is better to treat hemangioma, and whether to carry it out at all. The reason for the disagreement is that sometimes hemangiomas disappear by the age of seven without any intervention. Therefore, some pediatricians believe that until this age, only observation of the tumor is enough.
Another part of doctors is inclined to believe that the removal of the hemangioma is necessary, and this should be done as early as possible, without allowing the tumor to grow. A child who has been operated on for up to six months practically does not have scars; at a later age, the cosmetic effect is worse. Another reason for removing hemangiomas: only one fifth of hemangiomas disappear on their own, and even then, in most cases, these are hemangiomas located on areas of the body covered by clothing.
The need to remove a hemangioma is beyond doubt only when it is located near vital organs, and poses a threat to them: on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, on the inside of the eyelid or nose, on internal organs or bones, on the genitals, where it will be permanent get injured.
Hemangioma treatment can be conservative. Usually conservative treatment of hemangioma is prescribed for large tumors. For this purpose, hormonal drugs are prescribed. Self-treatment with hormonal drugs is unacceptable, due to the possibility of serious side effects.

Surgical treatment of superficial hemangiomas is carried out mainly by modern means of gentle surgery: cryodestruction, laser exposure, the introduction of sclerosing substances (drugs that force the walls of the vessels that make up the tumor to grow together) or a combination of these methods. The previously accepted method of removing hemangioma using electrocoagulation is currently almost not used, as it is very painful. The classical surgical removal of hemangioma is used when the tumor is located internally.
Treatment of hemangioma with folk remedies
Treatment of hemangioma with folk remedies is quite common. For example, for this purpose it is recommended to use celandine juice. However, pediatricians strongly do not recommend treating hemangioma with folk remedies.
Soft agents, such as decoctions and herbal infusions, are not able to affect the vascular tumor, and powerful agents, like the same celandine juice and other cauterizing substances, can cause ulceration of the tumor, and the subsequent attachment of a secondary infection.
In addition, although it is very rare and only some types, nevertheless, hemangiomas can become malignant, that is, from a benign tumor they can turn into a malignant one. Therefore, the treatment of hemangioma with folk remedies is permissible only in the form of a decoction of medicinal herbs that have a disinfecting and hemostatic effect, in the case when the hemangioma was slightly injured.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!