- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
How to determine sinusitis at home without a doctor
The content of the article:
- How to find out if you have sinusitis without a doctor
- How to identify sinusitis in a child
- How to identify sinusitis in an adult
- Treatment and prevention measures
- Video
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the maxillary sinus. The disease is more common than other sinusitis. It occurs primarily when an infection enters the upper respiratory tract against the background of acute respiratory viral infections or acute respiratory infections (acute respiratory viral infection or acute respiratory disease), or secondarily with concomitant chronic inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, the presence of carious upper molars, osteomyelitis, after surgical interventions in the upper jaw or in the result of injury.

To independently determine the disease at home, you need to know its main symptoms.
Risk factors are:
- curvature of the nasal septum;
- congenital narrowness of the nasal passages;
- allergic rhinitis;
- the presence of polyps or cysts in the nose;
- a general decrease in immunity.
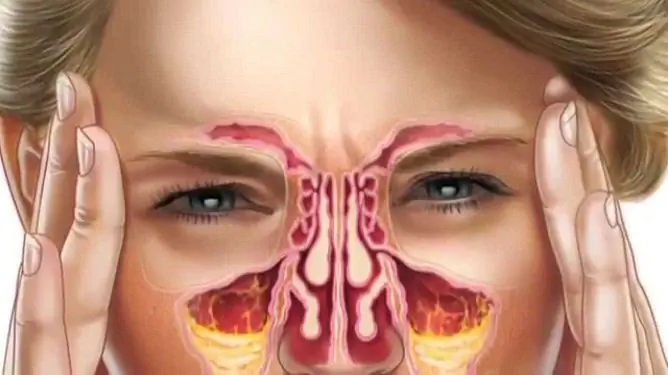
In this disease, the cavity of the maxillary cavity is filled with mucus and pus.
For diagnosis, an X-ray examination of the paranasal sinuses is prescribed. To exclude the generalization of the process, the X-ray must be done in several projections:
- naso-chin: the maxillary sinuses are determined;
- chin: visualizes the maxillary sinuses without layering the shadow of the temporal bone pyramids;
- nasolabial: visualizes the frontal sinuses and ethmoid labyrinth.
According to X-ray examination, diffuse clouding or darkening with an upper horizontal level in the lower and middle third of the maxillary sinus, thickening of the mucous membrane of the paranasal cavities is determined. To recognize inflammation of the maxillary sinuses on an X-ray image, as a rule, does not cause difficulties for the doctor. In more complex clinical cases, computed tomography is prescribed.
How to find out if you have sinusitis without a doctor
The following symptoms can help determine sinusitis at home:
- pressing pain in the area of the nose, eye sockets and cheeks, aggravated by pressure on the bridge of the nose and tilting the head down; with a unilateral process, painful sensations are localized mainly on the side of the sinus lesion;
- sore throat or sore throat in the morning;
- pain in the upper jaw and swelling of the gums (with odontogenic sinusitis);
- nasal congestion and profuse purulent discharge;
- headaches and throbbing in the temporal region;
- increased body temperature;
- redness of the skin of the nose, cheeks;
- changing the timbre of the voice;
- inability to recognize smells and tastes;
- ear congestion.
How to identify sinusitis in a child
Due to insufficient development of the sinuses, sinusitis is rare in children under five years of age. In older children, inflammation of the maxillary sinus is diagnosed more often than in adults. The presence of polyps, adenoid vegetations, anatomical defects of the nasal wall can provoke frequent relapses.

Sinusitis in children may occur with high fever
In the occurrence of sinusitis in children, hereditary diseases play an important role, in particular cystic fibrosis. Sinusitis can begin against the background of ARVI. Its symptoms are similar to those of allergic rhinitis.
The mucous discharge from the nose may be green or yellow, the voice becomes nasal. Possibly bad breath and nose odor (with bacterial infection), body temperature rise to 38 ° C and above. The child continues to actively move, play even with high fever (from 38 ° C). Therefore, it is very important to monitor body temperature and, if necessary, give antipyretic drugs to avoid complications. It is important to remember that a child's external condition does not always reflect the severity of his condition.
With bilateral sinusitis, the child begins to breathe through the mouth, snore and cough during sleep. By pressing on the central region of the cheeks and the bridge of the nose, he notes pain. With severe intoxication of the body, weakness, refusal to eat, and severe apathy are possible.
Lack of oxygen supply to the child's body due to prolonged disturbance of nasal breathing can lead to a delay in general development, the occurrence of otitis media and hearing loss. If symptoms of sinusitis are detected, it is necessary to consult an otolaryngologist as soon as possible.
How to identify sinusitis in an adult
Signs of inflammation of the maxillary sinus in an adult appear more clearly and much faster than in a child, which is associated with anatomical differences in the structure of the paranasal sinuses. The most common cause of inflammation of the maxillary cavity in adults are viruses, Haemophilus influenzae and streptococci.

Sinusitis is characterized by pressing pain in the nose
The risk group includes workers with industrial hazards: when working in workshops with dry air of high temperature, in conditions of the risk of chemical fumes, industrial dust entering the respiratory tract. Also, regular use of drops to treat rhinitis can thin the nasal mucosa, leading to its atrophy and, as a result, to the development of sinusitis.
Unlike a child, an adult immediately notes an increase in body temperature for signs of body intoxication:
- general weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- sweating;
- pain and aches in muscles and joints;
- nausea and vomiting (in rare cases).
Pain in the nasal region often radiates to the eyebrows, zygomatic bones and temporal region, aggravated by tilting or turning the head. In the evening, the intensity of the pain increases, the head begins to ache. Variable congestion of the right and left halves of the nose is possible, while abundant, thick, mucous discharge becomes green and yellow within a few days. In the morning, there are attacks of coughing due to mucus and pus, which flow down the throat. Deterioration of the general condition leads to disruption of performance.
Treatment and prevention measures
In order for the acute process not to become chronic, it is necessary to consult a doctor to select an adequate treatment regimen. Therapy includes:
- antibiotics: to eliminate the infectious agent;
- antihistamines and vasoconstrictor drops: to relieve swelling of the nasal mucosa.
Physiotherapy is also prescribed, including laser therapy, which enhances the effect of drugs. At the second stage, to consolidate the achieved effect, electrophoresis, UHF (ultra-high-frequency therapy), UFO (ultraviolet irradiation) are performed. Speleotherapy is useful for patients with sinusitis - this is a therapeutic stay in a salt mine or karst cave, where the body is favorably affected by clean, cool, ionized air of low humidity.
With timely treatment, the complications of sinusitis can be avoided: otitis media, phlegmon of the orbit, meningitis, encephalitis, osteomyelitis, bacterial damage to the myocardium and kidneys.

Hardening is one of the effective measures for the prevention of sinusitis
Methods for preventing sinusitis include:
- hardening;
- strengthening immunity;
- proper nasal hygiene;
- sufficient daily fluid intake;
- proper nutrition;
- timely detection and treatment of viral and bacterial diseases;
- sanitation of chronic foci of infections.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Alina Ervasova Obstetrician-gynecologist, consultant About the author
Education: First Moscow State Medical University. THEM. Sechenov.
Work experience: 4 years of work in private practice.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.