- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Hyperemia
The content of the article:
- Forms of hyperemia
- Causes
- Signs
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
- Consequences and complications
Hyperemia is excessive filling of blood vessels with blood in any part of the peripheral circulatory system as a result of increased arterial blood flow or insufficient venous outflow.

Source: otvetprost.com
With the expansion of arterial vessels, resistance to blood flow decreases, blood pressure rises in small-caliber vessels, the number of functioning capillaries increases, the release of the liquid part of blood from venules and capillaries into tissue cracks and / or body cavities (extravasation) increases, while the volume of tissue or organ increases, and the local temperature rises.
With venous stasis, there is a slowdown in blood flow in microvessels, an increase in blood pressure in them, an increase in fluid extravasation, followed by the development of edema. Due to the weakening of blood flow, the local temperature decreases, and blood containing reduced hemoglobin gives the affected area a cyanotic hue.
Forms of hyperemia
Depending on the cause of the development of the pathological condition, the following forms of hyperemia are distinguished:
- arterial (active);
- venous (passive);
- mixed.
Arterial hyperemia can be physiological and pathological and is subdivided into neurotonic and neuroparalytic.
Depending on the localization of the pathological process, hyperemia of the skin, brain and meninges, internal organs, conjunctiva of the eye, etc.
Causes
Hyperemia refers to the clinical manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus, infectious diseases, pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, otorhinolaryngological diseases, diseases of the circulatory system. The pathological condition is accompanied by inflammatory processes, tissue damage, allergic reactions, etc.
The causes of hyperemia depend on its form.
The main reasons for the development of arterial hyperemia include:
- mechanical (friction, increased cardiac activity);
- physical (exposure to high temperatures, decrease in atmospheric pressure);
- chemical (exposure to alkalis, acids);
- biological (influence of toxins produced by microorganisms, foreign proteins);
- mental (a sharp change in emotional state).
Neurotonic arterial hyperemia occurs when the tone of the vasodilating nerves increases, which can be observed in the case of the development of neuroinfections of viral etiology. Neuroparalytic arterial hyperemia develops with a decrease in the tone of the vasoconstrictor nerves (the tone of the vasodilators becomes higher than the tone of the vasoconstrictors). This form of hyperemia is often preceded by ischemia.
Venous hyperemia can occur when the blood vessels are narrowed or squeezed in late pregnancy, when the hernial sac is infringed, renal pathology, scarring, and neoplasms. Also, this form of hyperemia develops with prolonged immobilization of the upper or lower extremities, abnormal (including vertical) position of the trunk, cardiovascular diseases, pulmonary emphysema.
Hyperemia of the brain and its membranes may appear due to physical stress (especially at elevated ambient temperatures), emotional stress, acute infectious diseases. Hyperemia of the conjunctiva and internal organs is usually associated with local inflammatory processes.
Signs
The main manifestations of arterial hyperemia include:
- redness of the skin area;
- an increase in volume and a local increase in the temperature of the hyperemic area;
- expansion of arterial blood vessels, as well as an increase in the number of active vessels in a certain area;
- increased pressure in the arterial vessels of the hyperemic area;
- reducing the difference between the oxygen content in arterial and venous blood vessels;
- acceleration of blood flow;
- increased lymph formation;
- pulsation in blood vessels, where there is usually no pulsation.
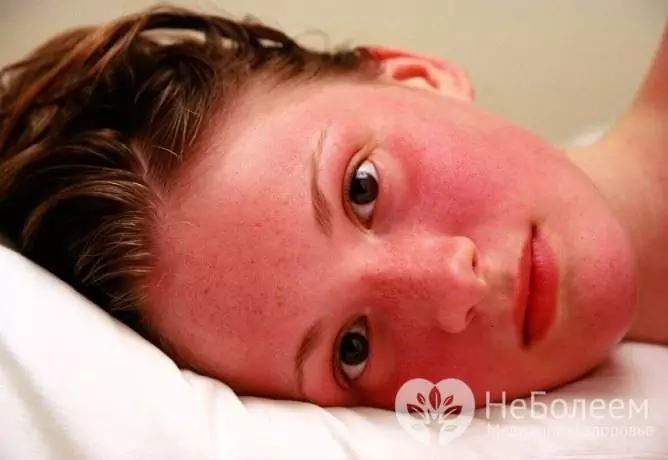
Neurotonic arterial hyperemia is manifested by reddening of the skin of the face in response to the influence of an emotional factor.
With neuroparalytic arterial hyperemia, there is a disruption in the supply of oxygen to the vessels and tissues due to paralysis of the neuromuscular apparatus, after which blood begins to flow to this area, which leads to a sharp expansion of the arterial vessels. In the case of the development of ischemia when the vessels are compressed by ascitic fluid during its rapid release, neuroparalytic arterial hyperemia occurs in the mesentery, which can cause the patient to faint.
With the development of venous hyperemia, there is a slowdown in blood circulation and stagnation of venous blood. The hyperemic area increases in volume and acquires a cyanotic color, while its temperature decreases.
With the development of cerebral hyperemia, pronounced redness of the mucous membranes, tachycardia, tachypnea are usually noted. Body temperature may rise or remain within normal limits, a local increase in temperature is detected by feeling the head. Patients complain of a feeling of pressure in the head, dizziness, lethargy, drowsiness, apathy, dullness of consciousness up to fainting, visual and hearing impairment, weakening of reflexes, and gait disturbance. The reaction to pain and sound stimuli decreases.
Source: morehealthy.ru
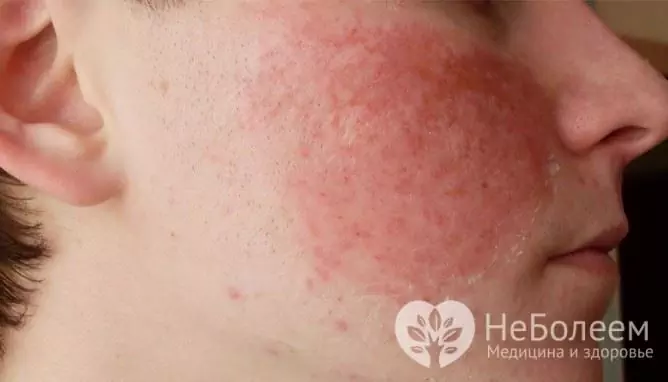
Flushing of the skin most often occurs in women over 40 years of age and usually manifests itself on the face. At the same time, spots of red or crimson appear on the skin, the temperature of the affected areas rises, and blood vessels expand at the place of redness.
During the examination of the oropharyngeal region, when the patient develops throat hyperemia, the reddening of the mucous membranes is accompanied by swelling of the tonsils, and an increase in regional lymph nodes is often observed. Patients complain of sore throat, difficulty swallowing, hoarseness.
With the development of hyperemia of internal organs, patients may experience swelling of the trunk, face, upper and lower extremities, a rapid increase in body weight, urination disorders, headaches, shortness of breath, palpitations, disorientation in space.
Conjunctival hyperemia - redness of the mucous membrane of the eye, especially pronounced near the transitional fold. The pathological process is accompanied by lacrimation, edema of the eyelids, sensation of a foreign body in the eye, photophobia.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of hyperemia consists in identifying the underlying disease, against which it arose.
Treatment
Therapy for hyperemia consists in treating the underlying disease that caused its appearance. In this case, first of all, it is necessary to eliminate the unfavorable factors that caused the development of hyperemia.
In case of facial hyperemia, it is recommended to use cleansers that do not dry the skin, and also to use protective ointments and creams. Hyperemic areas should be washed with warm water and wiped off with a soft towel with gentle dabbing movements. If necessary, medications are prescribed that normalize blood microcirculation. Avoid exposure to factors that can cause hyperemia and aggravate the pathological process (weathering, exposure to direct sunlight, overheating, hypothermia, the use of spicy foods, alcoholic beverages, caffeine-containing drugs, etc.).
In case of throat hyperemia, the main therapy can be supplemented by physiotherapy procedures, alkaline inhalations, gargling, irrigation or lubrication of the mucous membrane with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs, including of plant origin.
With hyperemia of the brain and its membranes, the patient is shown rest and bed rest, and the head should be in an elevated position in relation to the body. The patient is advised to adhere to a diet. The main treatment can be supplemented with steam baths, rubdowns, leg wraps, irritating compresses on the peripheral parts of the body, massage. The patient is also advised to walk barefoot on wet grass or asphalt.
Treatment of redness of the eyes can be supplemented by wearing a blindfold with biophotons, taking bee pollen (in the absence of contraindications), vitamin and mineral complexes (in particular, vitamin A and B vitamins).
The main treatment of venous hyperemia can be supplemented by physiotherapy exercises, diet, correction of excess body weight. Patients can be prescribed venotonics, anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, antioxidants and vitamin complexes. With the development of the inflammatory process and the presence of pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. In some cases, hirudotherapy (treatment with medicinal leeches) provides good results.
Arterial hyperemia is sometimes caused for medicinal purposes (including during physiotherapeutic procedures) when it is necessary to increase blood circulation in the affected area, which contributes to the early elimination of toxins, products of inflammation and the provision of oxygen to the affected area.
Prevention
Preventive measures aimed at preventing the development of hyperemia depend on the underlying disease that caused it.
Common measures to prevent hyperemia include:
- increased immunity;
- rejection of bad habits;
- balanced diet;
- normalization of body weight;
- moderate regular physical activity;
- avoidance of physical and mental stress.
Consequences and complications
Short-term hyperemia, as a rule, does not have pronounced negative consequences. With its prolonged course, the nutrition of the vascular wall, and then the surrounding tissues, may be disturbed, with the subsequent development of the inflammatory process.
Against the background of cerebral hyperemia, hydrocephalus can develop, there is a risk of death.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!