- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Inexpensive and effective cough syrups for adults
The content of the article:
- The main groups of drugs for cough syrup
- How to make a cough syrup at home
- Cough and its types
- Video
Cough syrup for adults can be purchased at a pharmacy or made independently according to folk recipes, it can be effective in both cases. The pharmaceutical market offers a large number of inexpensive and effective cough syrups for adults and children. They differ in composition, indications for use (the type of cough against which it is directed), the age group of patients, and also in the mechanism of action.
The mechanism of action of the agent depends on the substances that make up its composition. For example, a syrup can have anti-inflammatory, antitussive, antispasmodic effects, help thin sputum, and increase its amount. It should also be borne in mind that pharmaceutical preparations with the same active ingredients may have different commercial names and differ significantly in price.
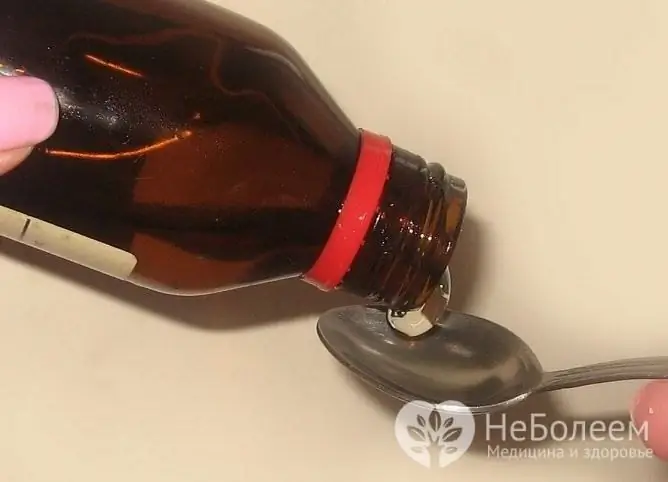

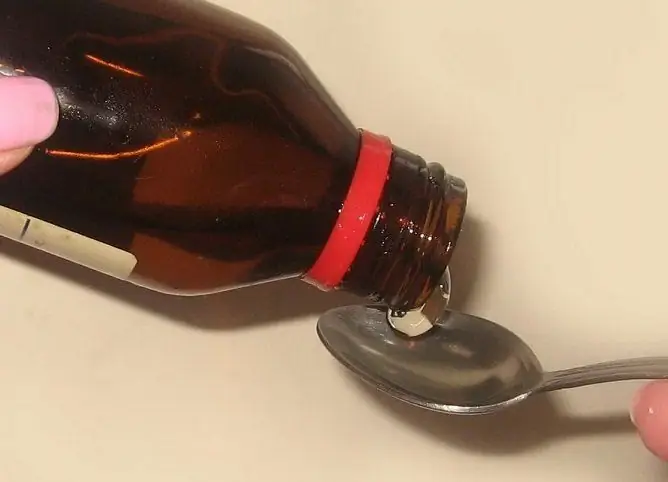
Cough syrups can be bought at the pharmacy, or you can prepare yourself at home
The composition of the drug often includes herbal ingredients - licorice root, ginger, aloe, fine basil, etc., they can be alcohol-free or contain ethyl alcohol.
The drug is selected depending on the cause and nature of the cough itself. For uncomplicated coughs, herbal cough syrups are generally preferred.
Cough medicines, regardless of the form of release, are not recommended for use without consulting your doctor. If, after using the drug, the patient's condition worsens, you should stop using it and report the problem to the doctor.
The main groups of drugs for cough syrup
Expectorant cough syrups for adults are used to increase the amount of phlegm and make it thinner. They are usually prescribed for mucociliary transport disorders. The list is extensive. According to the mechanism of action, there are two main groups of drugs: secretomotor and mucolytic.
Secretomotor - drugs that stimulate expectoration, which, in turn, are divided into two subgroups - reflex and resorptive. The former have the ability to reflexively stimulate expectoration by acting on the gastric mucosa, which leads to irritation of the cough center in the medulla oblongata. This stimulates the production of liquid bronchial mucus, and also enhances the cough reflex. These include syrups with thermopsis, licorice root.
Preparations of resorptive action contribute to the enhanced production of the liquid part of the secretion in the bronchi, which also contributes to the dilution of sputum and improves its excretion. These include agents based on sodium or potassium iodide, etc. Expectorant drugs are prescribed for coughing up sputum in patients with laryngitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, bronchiectasis and other pathologies of the respiratory tract, which are accompanied by the release of viscous sputum. This group includes Gerbion, Pertussin.
Mucolytic - they have the ability to thin thick mucus and reduce its ability to adhere to the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, accelerate the transition of an unproductive cough to a productive one. The action of mucolytics is aimed at breaking the bond of mucopolysaccharides and activating the glands that produce secretions, as a result of which sputum liquefies, which facilitates its excretion. A feature of the action of mucolytics is that they dilute sputum without increasing its amount. In addition, mucolytic drugs provide some anti-inflammatory effect. Mucolytics can be prescribed together with bronchodilators, expectorants, antibacterial agents. They are used for pneumonia, bronchial asthma, cystic fibrosis. This group includes Abrol, Ambrobene, Ambroxol.
Expectorant and mucolytic syrups are prescribed for a wet cough in the event that sputum is difficult to separate. During treatment with such drugs, it is recommended to consume more fluids.

Drink more than usual while taking expectorant medications
The action of antitussive drugs is aimed at suppressing coughing. They are used if the cough is not physiologically justified. There are antitussives of central action that act on the cough center (non-narcotic and narcotic), local anesthetics and mixed-action drugs. With prolonged use of narcotic antitussives, addiction develops, so they are used in a short course. These drugs are prescribed for pathologies accompanied by obsessive attacks of dry cough: at the initial stage of colds, with laryngitis, whooping cough, bronchial asthma. Drugs that suppress cough should not be taken with mucolytics, as this can only worsen the patient's condition. This group includes Butamirate, Oxeladin.
From dry cough syrups, adults are often prescribed Gederin, Abrol, Sinekod. During pregnancy, syrups are used by Doctor Mom, Herbion, Bronchicum.
How to make a cough syrup at home
A cough medicine can be prepared at home. So, a good folk remedy is onion syrup, which is effective against infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract. To prepare the syrup, you need to peel 1 large onion, remove the core from it, fill the onion with honey or granulated sugar, place in a glass or porcelain container and leave overnight. The onion syrup is ready for use the very next day. The product should be taken 1 tablespoon every 2 hours throughout the day.
According to another recipe, 1 onion needs to be peeled, chopped and added to it 3 tablespoons of honey, pour 100 ml of water and cook over low heat for about 5 minutes, then leave for 2 hours. The syrup is taken 1 teaspoon 4 times a day.
The third recipe: peel and chop 0.5 kg of onion, add 3 cups of sugar and 50 g of honey to it. The mixture is placed in an enamel saucepan, pour 1 liter of water and cook over low heat for 3 hours, stirring occasionally. After that, the syrup is allowed to cool, filtered, poured into glass containers and stored in the refrigerator. Take 2 tablespoons about 5 times a day.
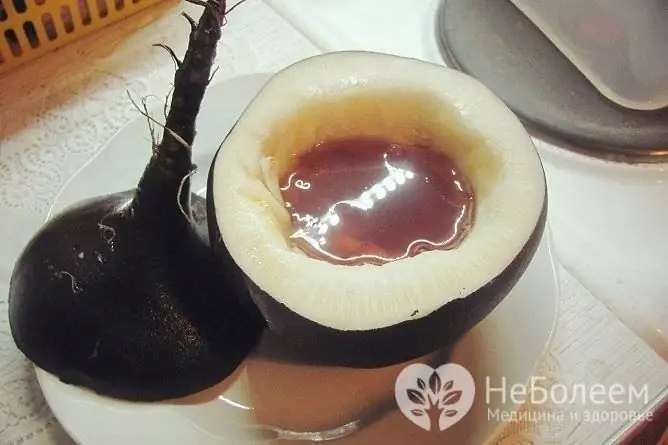

Black radish and honey syrup is one of the most effective and popular antitussives
Excellent patient reviews about the antitussive black radish syrup, for the preparation of which you need to wash 1 radish, cut off the top from it and cut out part of the pulp. Honey should be placed in the resulting depression so that there is room for the juice to be secreted. The top is set in place, the radish is left for several hours. Ready syrup is taken for cough 1 tablespoon 3 times a day before meals. Honey can be added to the radish for another 2 days, after which it must be replaced (if necessary, continue treatment).
Radish and honey syrup can also be prepared in a different way. To do this, 1 large black radish must be thoroughly washed, peeled and cut into small cubes. The pieces are placed in a glass container, 2 tablespoons of honey are poured on top. The container is covered with gauze and left in a dark place for 2 days. Ready syrup is consumed 1 teaspoon before each meal.
If you need to quickly prepare a cough radish syrup at home, rub 1 washed and peeled radish on a fine grater, squeeze the juice through cheesecloth and mix with 2 teaspoons of honey. Syrup is drunk 1 tablespoon 3 times a day before meals.
Cough and its types
Coughing is the body's defensive response to irritation of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract. In this case, the irritating effect can be caused by chemical, physical, and organic factors. Cough accompanies many illnesses - from colds to malignant tumors.
The most common causes of cough are allergies and airway inflammation. It can also occur against the background of smoking, mental stress, disorders of the thyroid gland, gastrointestinal system, etc.
Respiratory tract diseases are extremely widespread, especially during the off-season and winter. The cough can be dry (no expectoration, nonproductive cough) or moist (expectorate, productive cough). In the patient's sputum, impurities of pus, blood can be found, depending on this, it can be transparent, yellowish, greenish, with a brown tint.
Self-medication of cough should not be dealt with, so there is a high risk of erroneous diagnosis and aggravation of the patient's condition. If a persistent cough appears, you need to consult a doctor who will select the best medicines for each specific case.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.