- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Cirrhosis of the liver
Cirrhosis is a consequence of chronic liver disease and results in loss of organ function. The liver affected by the disease is dense, reduced or enlarged, rough and bumpy.

Ascites (fluid retention in the abdomen) is the most common complication of liver cirrhosis and is associated with a poor quality of life and an increased risk of infection. Other potentially life-threatening complications include confusion, hepatic coma, and bleeding caused by esophageal varices.
Liver cirrhosis is an irreversible process; its treatment is usually aimed at preventing the complications it causes. Later stages of cirrhosis require a liver transplant.
Cirrhosis of the liver is one of the six diseases in the world due to which patients die at the age of 35-60 years.
Symptoms of liver cirrhosis
The initial stages of the disease (class A) are not accompanied by symptoms, since complications do not yet arise. This time is ideal for eliminating the cause of the onset of the disease, since the liver is an organ capable of regenerating its cells - this allows you to maintain healthy liver tissue and lead a normal and healthy lifestyle.
The main signs and symptoms of liver cirrhosis are:
- An enlarged abdomen;
- Changes in consciousness and behavior;
- Bleeding gums;
- Nosebleeds.
Also, the symptoms of liver cirrhosis are:
- Increased fatigue;
- Slimming;
- Decreased appetite;
- Jaundice;
- Light-colored or discolored feces;
- Darkening of the urine;
- The tongue is crimson;
- Dyspepsia;
- Stomach ache;
- Swelling of the legs;
- Vascular telangiectasias;
- Itchy skin;
- Bleeding;
- Frequent bacterial infections
- Erythema of the palms;
- Decreased libido;
- Dull or aching pain in the liver area;
- Gynecomastia in men.
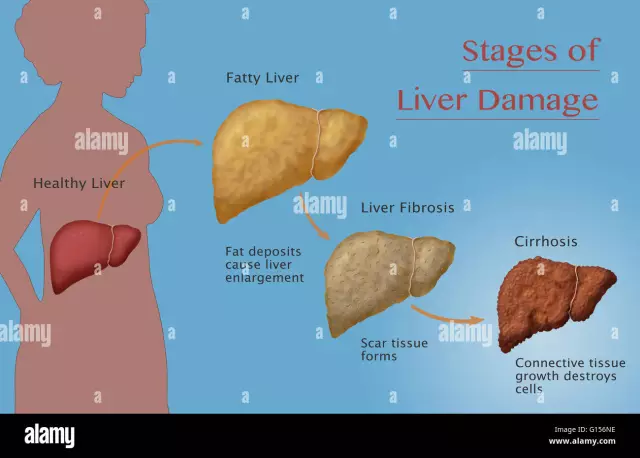
Stages of liver cirrhosis
The development of the disease occurs very slowly, therefore, during its course, the following stages of liver cirrhosis can be distinguished:
- The stage of compensation is the absence of symptoms, due to the increased functioning of the liver;
- The stage of subcompensation - the first signs of the disease appear, which are expressed in weight loss, decreased appetite, weakness and a feeling of discomfort in the right hypochondrium, since the liver is no longer able to function at full capacity;
- Decompensation stage - jaundice, portal hypertension syndrome and hepatic coma appear, which pose a threat to human life.
Diagnostics and treatment of liver cirrhosis

Diagnosis of liver cirrhosis is carried out by a hepatologist or gastroenterologist, who, after a thorough examination of the patient, conduct a biochemical blood test, ultrasound examination of the liver and abdominal organs, a blood test for markers of viral hepatitis, gastroscopy, computed tomography, radioisotope study, and, if necessary, liver biopsy.
After the diagnosis and confirmation of the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis, the stage of treatment begins. This disease cannot be completely cured; it can only be slowed down and the development of complications slowed down. Treatment of liver cirrhosis consists in carrying out such therapeutic measures as:
- Taking diuretics;
- Appointment of a diet (no intake of fried and fatty foods, salt and alcoholic beverages);
- Taking glucocorticoid hormones (for autoimmune disorders);
- Antiviral therapy (for viral hepatitis);
- Reception of hepatoprotectors.
If, during the treatment of cirrhosis of the liver, the process of the course of the disease becomes aggravated, and complications appear, urgent hospitalization is necessary. Also, when treating cirrhosis of the liver, you may need such surgical treatment as:
- Bypass surgery to create new blood pathways;
- Paracentesis - a puncture of the abdominal wall;
- Liver transplant.
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!