- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Diet for the liver

Treatment of diseases associated with impaired liver function (chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, cholecystitis, etc.) implies not only drug intervention. It is imperative to follow a diet for liver diseases.
What are the benefits of a diet for liver disease?
The main goal of the diet for the liver is to reduce the load on the diseased organ, to minimize the negative effects of harmful chemicals. At the same time, a full and balanced nutrition of the patient is preserved. Some restrictions that a diet requires for liver diseases contribute to the normalization of its work, as well as improve the functioning of the biliary tract and bile secretion, and normalize metabolic processes in the body.
Liver Diet Basics
People with liver disease are advised to enrich their diet with lipotropic components. This implies the inclusion in the diet of foods such as soy, cod, cottage cheese. For a long time, doctors have recommended liver fat diets for patients. On the one hand, this is quite logical, since after eating fatty foods, many patients complained of pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea and bitterness in the mouth. Recently, however, doctors have taken the opposite point of view, believing that the diet for liver disease should include fats. Only these should be fats that the body tolerates well. With the correct consumption of such fats, the patient's condition can improve significantly.
In a liver disease diet, the total amount of fat should be about 80-100 g. The optimal ratio is considered to be 30% vegetable and 70% animal fat. It is preferable to get fat from food rich in protein (fish, meat, cottage cheese). It has already been proven that a diet for liver disease that includes a mixture of vegetable and animal fats is much more effective than a diet containing exclusively animal or exclusively vegetable fats.
Vegetable oil is generally beneficial for liver diseases. It normalizes metabolism in the body and directly in the liver, and also has a good choleretic effect. If the patient has a delay in the outflow of bile, then it is recommended to increase the total amount of fat to 150 g, 50% of which should be vegetable fats. If the liver disease is complicated by jaundice, then the amount of fat consumed must, on the contrary, be reduced to 50-70 g.
The amount of carbohydrates in the diet for the liver should be 400-450 g per day. In this case, simple carbohydrates (baked goods, sugar, honey) should be 50-100 g. It is forbidden to consume excessive amounts of carbohydrates, as this promotes the deposition of fat in the liver cells.
Many chronic diseases of the biliary tract and liver develop under the influence of acute infections or as a result of prolonged abuse of alcoholic beverages, metabolic disorders. The most common forms of liver damage are cholecystitis and hepatitis. The diet for liver diseases is prescribed only by the attending physician and depends on the stage of the disease and the general condition of the patient. The main attention in the diet for liver disease is given to a sparing diet and a full ratio of carbohydrates, proteins, fats and vitamins.
Thus, with cholecystitis and hepatitis, the following rules should be followed:
- the amount of carbohydrates in the diet for liver disease should not be excessive, and for patients with heavy weight, it should generally be reduced;
- the diet should contain a sufficient amount of easily digestible, complete proteins;
- the amount of fat directly depends on the patient's condition: if there is a need to enhance the choleretic effect of the diet for the liver, the amount of proteins can be increased;
- all food must be thoroughly cooked;
- it is advisable to use only boiled dishes, as well as mashed or chopped food;
- fractional meals are recommended in small portions, as this improves intestinal motility, has a choleretic effect and maximally spares the diseased organ;
- it is necessary to include foods high in fiber in the diet for the liver, as this increases the choleretic effect and ensures maximum excretion of cholesterol from the body.
What foods are prohibited in the liver diet?
With liver diseases, you should not eat lamb, pork, duck, goose, any fried foods, canned food and smoked meats, refractory cheeses, sorrel, chocolate, cocoa, ice cream, cold drinks, mushrooms, spinach and any alcoholic beverages.
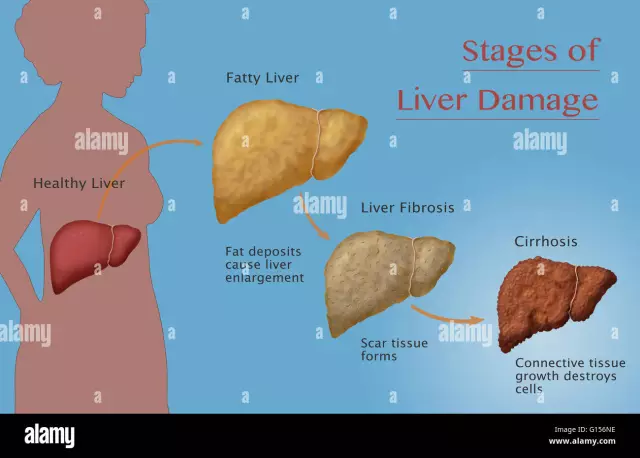
Diet for liver cirrhosis
Any liver disease requires a sparing diet, but the diet for cirrhosis of the liver contains very strict contraindications.

So, it is absolutely forbidden to eat any fatty meat, cooking fats, soups on strong broths, hard-boiled eggs, fatty fish, canned food, scrambled eggs, mushrooms, pickles, legumes, radishes, spinach, sorrel, green onions, radishes, ice cream, sour berries and fruits, black coffee, chocolate, mustard, pepper, cold drinks, horseradish. But the most important limitation in the diet for liver cirrhosis is the absolute contraindication to alcohol. Just a couple of glasses of strong alcohol can cause a severe relapse of the disease, even if it has not reminded of itself for a long time.
Unfortunately, liver cirrhosis is incurable. However, using an adequate method of treatment, in which diet therapy is mandatory, it is possible to stop the development of the disease.
Diets for the liver in modern medicine play a leading role in the treatment of liver diseases. To date, none of the existing medicinal techniques gives such an effective result as diet therapy.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.