- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Stage 4 hemorrhoids: treatment, symptoms, causes
The content of the article:
- The reasons
- Symptoms of stage 4 hemorrhoids
- Hemorrhoid treatment stage 4
-
Methods of surgical treatment of hemorrhoids
- Classic hemorrhoidectomy
- Operation Longo
- Preoperative preparation
- Postoperative prophylaxis
- Contraindications to hemorrhoidectomy
- Video
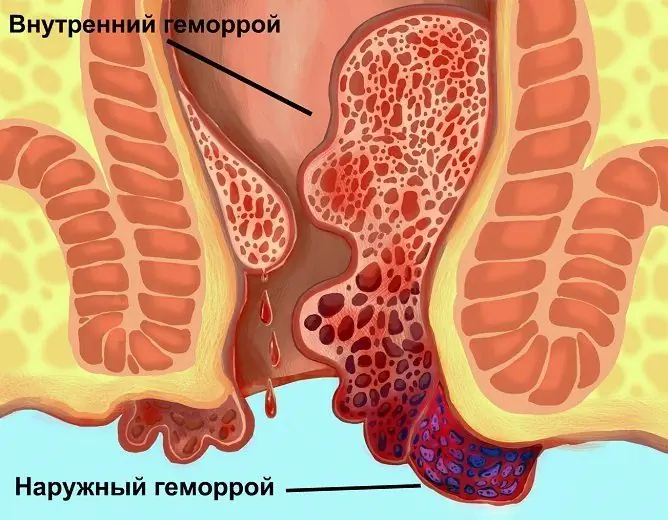
Stage 4 hemorrhoids are the most severe. With its development, the patient experiences constant and significant discomfort, the risk of complications is high - anemia, infringement of the hemorrhoid, anal fissures, etc.
Conservative therapy in such cases does not bring tangible results, the only effective method is surgical removal of hemorrhoids.
The reasons
Hemorrhoids are called "sedentary disease" because the main cause of hemorrhoids is a sedentary lifestyle. Modern people are characterized by a long stay in a sitting position due to the specifics of their profession (mainly of an administrative, office nature or driving a car). With insufficient physical activity, venous blood stagnates in the pelvic region, overflows the vessels, the elasticity of their walls decreases, they stretch to form knots - the so-called hemorrhoidal cones.

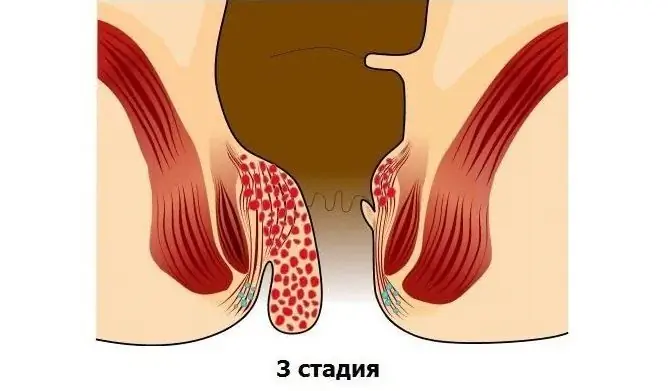
The fourth stage of hemorrhoids cannot be cured by conservative methods, surgical intervention is required
In women, the cause of the disease is often pregnancy and childbirth. Stagnation in the hemorrhoidal veins occurs as a result of their squeezing by the growing fetus. The cavernous veins fill with blood. The condition of the already dilated rectal nodes is further aggravated by straining in childbirth.
Other reasons include constant heavy lifting and chronic constipation, as well as hereditary weakness of the vascular wall.
Hemorrhoids respond well to therapy in the early stages, but the reason that patients seek help only at an advanced stage is the specific location of hemorrhoids. Many patients have been trying to cope with the disease on their own for a long time, making attempts at home treatment using photos and videos from the Internet, advice from friends, and are embarrassed to consult a doctor. In such conditions, the disease is steadily progressing, and sooner or later patients experience such a significant decrease in the quality of life that they are forced to seek medical help. As a rule, in such cases we are talking about the last stage.
Symptoms of stage 4 hemorrhoids
The last stage of hemorrhoids is characterized by the following symptoms:
- hemorrhoids fall out of the anus, they can not be adjusted either independently or manually;
- pain in the anus becomes almost constant, aggravated by defecation, walking, sitting on a hard surface, coughing and sneezing;
- bleeding from the anus becomes regular or constant;
- stool disorders, which can be caused, among other things, by psychological reasons (defecation is painful, so the patient tries to avoid it, postpone it).
Often, patients go to the doctor when there are complications. Constant bleeding causes the development of anemia, which is manifested by weakness, shortness of breath, pallor of the skin and other disorders. Thrombosis of hemorrhoidal veins or entrapment of the node with subsequent tissue necrosis may develop.
Stage 4 hemorrhoids, and even more the appearance of the consequences, are the reason for an immediate visit to the doctor.
Hemorrhoid treatment stage 4
Effective treatment of stage 4 hemorrhoids is impossible without surgery. All drugs that can be prescribed during this period can bring only temporary relief, and usually, if they are used, it is only in preparation for surgery.
Modern methods of surgical treatment of hemorrhoids, including advanced ones, are highly effective, and subject to medical recommendations in the postoperative period, the risk of recurrence of the disease is minimal.
Methods of surgical treatment of hemorrhoids
Surgery to remove hemorrhoids is called hemorrhoidectomy. Its essence lies in the excision of varicose hemorrhoidal veins protruding into the lumen of the rectum. This can be done with a scalpel, electric or laser coagulator. General or spinal anesthesia is used.
There are two main methods of hemorrhoidectomy, the question of how to treat hemorrhoids in the last stage, that is, by what method, is decided by the surgeon, taking into account individual indications.
Classic hemorrhoidectomy
After stretching the sphincter, the hemorrhoid is captured using a fenestrated clamp. The mucous membrane on both sides of the node is dissected, the leg of the node is captured, a hemostatic clamp is applied to it. After that, the hemorrhoid is cut off, the leg is stitched and tied up. The wound is stitched along the edges. External nodes are excised separately.

Hemorrhoidectomy consists of removing hemorrhoids with a scalpel, electrocoagulator, or laser
After using this method, relapses occur in no more than 1-3% of cases.
Operation Longo
During surgery, hemorrhoids are not removed with this method, but are pulled up by excision of the mucous membrane. The operating wound is sutured along the edges with titanium staples using a circulating device, the principle of which is similar to the functions of a stapler. After tightening the hemorrhoids, blood flow is disturbed in them, and after a certain period of time they decrease and are gradually replaced by connective tissue.
Preoperative preparation
As before any planned surgical intervention, the patient undergoes a medical examination, including fluography, electrocardiogram, clinical blood and urine analysis, etc. A few days before the operation, it is necessary to stop taking anticoagulants (discussed with the attending physician).
A slag-free diet is prescribed 1-2 days before the intervention. An enema is given the night before and in the morning of the operation, or the intestines are cleansed with Fortrans. The drug is dissolved in 3-4 liters of boiled water and drunk in a glass every 15 minutes, which causes multiple bowel movements.
Postoperative prophylaxis
Since stool is undesirable in the first few days, the patient is advised to fast for 24 hours, and in the future - a slag-free diet. Postoperative pain is relieved by intramuscular administration of analgesics. Drains and tampons can cause significant discomfort. After 5-6 days, the patient is able to defecate on his own. With the first stool, slight bleeding from the anus is possible. Because of the pain, the patient may have a psychological fear of defecation. In order to facilitate the process of bowel movement, oil enemas and rectal suppositories with anesthetic effect can be prescribed. The latter also accelerate the process of tissue regeneration, contributing to a speedy recovery.
Contraindications to hemorrhoidectomy
Hemorrhoidectomy is contraindicated in the following cases:
- pregnancy;
- severe arterial hypertension;
- decompensated cardiovascular diseases;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- Crohn's disease;
- oncological diseases;
- severe immunodeficiency.
In the presence of these pathologies, the patient is prescribed a course of therapy, after which the question of the possibility of prompt removal of hemorrhoids is again considered.
Video
We offer you to watch a video on the topic of the article.

Nikita Gaidukov About the author
Education: 4th year student of the Faculty of Medicine No. 1, specializing in General Medicine, Vinnitsa National Medical University. N. I. Pirogov.
Work experience: Nurse of the cardiology department of the Tyachiv Regional Hospital No. 1, geneticist / molecular biologist in the Polymerase Chain Reaction Laboratory at VNMU named after N. I. Pirogov.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.