- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Hemorrhoids: treatment, reduction, stages
The content of the article:
- Causes of knot formation
- Clinical forms of hemorrhoids
- Symptoms
- Stages of hemorrhoids
- Treatment of hemorrhoids
- How to correct fallen out hemorrhoids
- Video
Hemorrhoids (hemorrhoids) are an important indicator that internal hemorrhoids are progressing and progressing to advanced stages. With external hemorrhoids, external nodes are formed immediately. What is it, why are they formed and how to treat such formations?

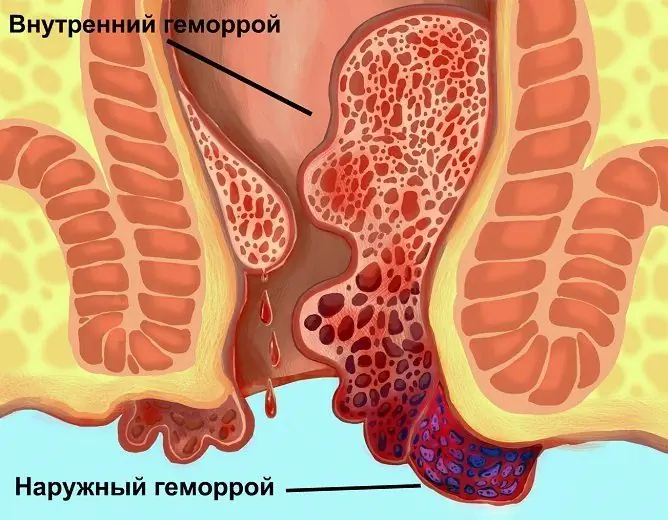
External hemorrhoids are found in the early stages of hemorrhoids, and internal ones can only be visible when they fall out
Hemorrhoids are an extremely common disease that can develop in a person of any age, gender and occupation. One of the problems contributing to the development and progression of hemorrhoids is delayed diagnosis. As a rule, patients do not attach much importance to the symptoms of early stages of hemorrhoids, until nothing hurts, and many do not find the time or hesitate to see a doctor even at later stages of the disease. Meanwhile, it depends on how early hemorrhoids were diagnosed by what methods and how long the treatment will take, and whether it will be possible to get rid of hemorrhoids at home, or home methods will only be able to temporarily reduce the symptoms.
Causes of knot formation
Connecting with each other, the veins of the rectum form plexuses in different layers of the intestinal walls. In the lower part of the rectum, there are two types of veins: ordinary and cavernous (in the walls of which there are direct blood vessels connecting arteries with veins - arteriovenous anastomoses). Clusters of cavernous veins are localized in the submucosal layer of the anal canal and resemble a bunch of grapes. When filled with blood, these structures thicken and seal the anal canal. With the urge to empty the intestines, the circular muscle of the sphincter relaxes, blood flows from the corpora cavernosa and defecation becomes possible.
If blood stagnation occurs in the pelvic region and its outflow is disturbed, the cavernous vascular tissue undergoes hyperplasia. The discrepancy between the inflow of arterial blood to the cavernous bodies and the outflow of venous blood from them leads to an increase in vascular plexuses and a weakening of the walls of blood vessels, an increase in the number of arteriovenous anastomoses, and the formation of nodes from hemorrhoidal veins.
Adverse factors contributing to the development of the disease include:
- chronic constipation;
- diseases of the pelvic organs (gynecological diseases, prostate adenoma, etc.);
- bowel diseases (inflammatory processes, tumor formations, intestinal infections);
- lifting weights, excessive physical activity;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- obesity;
- sedentary or standing work;
- alcohol abuse;
- violation of the diet (overeating or irregular eating, unbalanced diet);
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- hereditary predisposition.
Clinical forms of hemorrhoids
The disease can be acute and chronic.
Primary chronic hemorrhoids develop gradually, it is characterized by a long latency period. It may take several years from the onset of the disease to the appearance of its pronounced symptoms. Erased symptoms complicate early diagnosis of the disease. In the later stages, frequent prolapse of hemorrhoidal veins and exacerbation of the disease are possible.
Acute hemorrhoids may appear initially, but exacerbation of the chronic form is more common. It is characterized by severe pain, itching and burning in the anal region, bleeding during bowel movements, when walking, coughing or sneezing. It should be noted that the acute form of hemorrhoids cannot be identified with the prolapse of nodes.
Each of the clinical forms of the disease is subdivided into external, internal and combined (mixed) hemorrhoids, depending on the localization of pathological changes in the cavernous vessels.
With external (external) hemorrhoids, hemorrhoidal cones are found in the outer region of the rectum, around the anus. A characteristic feature of external hemorrhoids is the insignificance of hemorrhoidal bleeding. With an exacerbation of the disease, the nodes swell and become inflamed, the skin in the anus acquires a purple hue, severe pain, itching and burning in the anal region appear, and spotting may occur.

Signs of hemorrhoids are itching, burning in the anus, pain during bowel movements
With internal hemorrhoids, the nodes are located inside the anus, under the intestinal mucosa.
The combined (mixed) form of the disease is characterized by inflammation of both internal and external hemorrhoids.
Symptoms
The following clinical signs indicate inflammation of hemorrhoids:
- burning and itching in the anus;
- perianal edema;
- pain that gets worse during exercise and bowel movements;
- the appearance of discharge;
- heaviness in the anal area;
- bleeding during bowel movements;
- prolapse of hemorrhoidal cones from the anus;
- depletion and necrosis of rectal tissue.
External nodes are often found by the patient during hygiene procedures. Internal nodes in the early stages of the disease can be seen only with the help of special equipment (anoscope, sigmoidoscope), in the later stages - after their loss.
Stages of hemorrhoids
At the initial stage of the disease, the nodes are small, they stick out only into the lumen of the rectum, without leaving the anus, the skin around the anus has a natural color. With external hemorrhoids, collapsed nodes may not pay attention to themselves, too, for a long time.
As the disease progresses, the cavernous bodies increase, their wall becomes thinner and loses its elastic properties. It is more and more difficult for the atrophic mucous membrane to keep them inside the anal canal; with the next exacerbation, the nodes fall out. In advanced cases, the mucous membrane falls out with them.
The appearance of prolapsed nodes indicates the progression of the disease and the onset of the second stage of hemorrhoids. At the same time, the painful sensations intensify, the nodes fall out from time to time, usually with significant physical exertion. The nodes are independently retracted into the rectum when changing the position of the body.
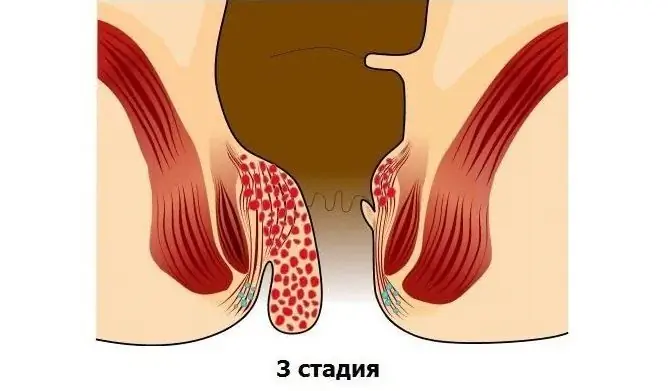
The third stage is characterized by the loss of nodes with minimal physical exertion. Lumps hanging from the anus can no longer be adjusted into the rectum on their own, but they can be carefully adjusted with your hands. There is pain during bowel movements, itching and burning in the anal region, swelling of the anus.
The fourth stage of hemorrhoids is characterized by constant prolapse of nodes, frequent bleeding, painful defecation. Due to constant inflammation and trauma of the mucous membrane, erosion is formed. This condition requires surgical intervention, as it is fraught with the development of complications, including rupture of hemorrhoids.
How different stages of hemorrhoids look can be seen in the photo of hemorrhoids.
Treatment of hemorrhoids
In the early stages, the disease can be effectively treated with conservative methods. First of all, they are prescribed topical preparations that quickly provide a therapeutic effect - ointments, creams (for external hemorrhoids), rectal suppositories (for internal hemorrhoids).
To normalize venous outflow and increase vascular tone, general action vascular venotonic drugs (Detralex, Phlebodia, Venarus) are used, anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Nise, Nurofen) are prescribed to eliminate focal inflammation, thrombolytics (Aktilize), which prevent the formation of blood clots, pain stop with analgesics (Analgin, Baralgin). If necessary, hemostatic drugs, antiseptics, wound healing and regenerative agents are prescribed.

It is possible to eliminate hemorrhoids using minimally invasive methods, such as photocoagulation or latex ligation.
For the treatment of stage 2-3 hemorrhoids, the latex ligation method is used. Its essence lies in putting special latex rings on the knot with the help of a ligator, as a result of which the knot is ligated, due to which the blood flow to it stops.
In the later stages of hemorrhoids, they resort to surgical removal or excision of the nodes. Both radical and gentle, minimally invasive techniques can be used. The latter include thromboectomy, photocoagulation (laser, infrared coagulation) of nodes.
Is it possible to treat hemorrhoids at home? Yes, but only on condition that the treatment is prescribed and monitored by a doctor. The therapeutic complex for hemorrhoids also includes adherence to dietary rules, giving up bad habits, and performing special exercises.
How to correct fallen out hemorrhoids
How to remove a dropped knot? If there is no inflammation and bleeding, reduction of the node can be done at home, however, it should be understood that this is a temporary measure and is not a cure. However, it is important to do this in a timely and correct manner in order to prevent the development of thrombosis of hemorrhoidal cones, inflammation and tissue necrosis.
How to correct a dropped knot:
- Perform a thorough toilet of the anogenital area.
- Anesthetize the tissues of the anal area. You can use anesthetic sprays or ointments (Lidocaine, Proctosan, Relief). The easiest way is to place a bag of ice cubes on your anus for a few minutes.
- Put on a medical glove or disposable rubber fingertip on the hand that will be reduced.
- Squat down, get on all fours or bend over with your legs apart.
- Spread the buttock with one hand on the side opposite to the inflamed lump, dip the middle finger of the other hand in baby cream or petroleum jelly, gently and slowly push the knot inward, inserting the finger behind it into the anus.
- Gently pull out your finger, squeeze the sphincter muscles with force, press the buttocks tightly against each other.
- Lie quietly for 30 minutes, in the near future try not to strain, not cough, not understand heavy objects.
The fallen out nodes can be infringed by the spasmodic sphincter, blood circulation in them is disturbed, the nodes swell and become inflamed. The patient develops excruciating bursting pains and a foreign body sensation in the anus. In case of acute infringement of hemorrhoids, inflamed nodes should not be attempted to be adjusted manually, you should immediately seek medical help.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.