- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
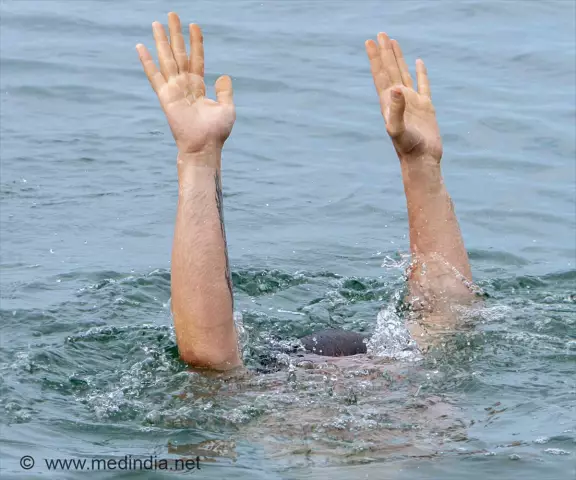
Drowning

Drowning is a type of mechanical suffocation that occurs when the lungs are filled with fluid. The time and nature of death in water depends on external factors and the state of the organism. About 70,000 people worldwide die from drowning every year. Mostly young men and children are targeted.
Reasons for drowning
Risk factors are alcohol intoxication, the presence of heart disease in a person, damage to the spine when diving upside down. Also, the reasons for drowning can be a sharp fluctuation in temperature, fatigue, and various injuries during diving.
The risk of drowning is increased in the case of a whirlpool, a high speed of water flow, and the presence of key sources. Being calm in an emergency and not panicking can significantly reduce the risk of drowning.
Types of drowning
There are three types of drowning.
The true form of drowning is characterized by the filling of the airways with liquid to the smallest branches - the alveoli. In the alveolar septa, capillaries burst under fluid pressure, and water or other fluid enters the bloodstream. As a result, there is a violation of the water and salt balance and the breakdown of erythrocytes.
Asphytic drowning is characterized by spasm of the airways, which ultimately leads to suffocation from lack of oxygen. When water or liquid enters the respiratory tract, laryngospasm occurs, which leads to hypoxia. In the last stages of drowning, the airways relax and fluid enters the lungs.
The syncope type of drowning is characterized by the onset of death from reflex cardiac arrest and respiration. This type of drowning occurs from hypothermia or severe emotional distress. It accounts for 10-14% of all drowning cases.
Signs of drowning
The main symptoms and signs of drowning depend on the type of drowning.
With true drowning, there is a sharp cyanosis of the skin and mucous membranes, pink foam is emitted from the respiratory tract, the veins on the neck and limbs are very swollen.
In asphytic drowning, the skin is not as blue as in true drowning. Pink fine bubble foam is released from the victim's lungs.
With syncope drowning, the skin is pale in color due to spasm of capillaries, such victims are also called "pale". This type of drowning has the most favorable prognosis. It is known that with syncope drowning, even after 10 or more minutes of being under water, revival is possible.
It should be noted that the prognosis for drowning in sea waters is more favorable than in fresh water.
Drowning aid
Drowning assistance consists of resuscitation. It must be remembered that the sooner the recovery measures are taken, the better the prognosis will be, and the higher the victim's chances of recovery.
The main care for drowning is artificial ventilation and chest compressions.

It is advisable to carry out artificial respiration as early as possible, even during transportation to the shore. First, it is necessary to free the oral cavity from foreign bodies. To do this, a finger, wrapped in a bandage (or any clean rag), is inserted into the mouth and all excess is removed. If there is a spasm of the masticatory muscles, due to which it is impossible to open the mouth, then it is necessary to insert a mouth dilator or any metal object.
Special suction units can be used to free the lungs from water and foam. If they are not there, then it is necessary to lay the victim with his stomach down on the knee of the rescuer and vigorously squeeze the chest. If within a few seconds the water does not leave, you need to start artificial ventilation. For this, the victim is put on the ground, his head is thrown back, the rescuer puts one hand under the neck, and the other on the patient's forehead. It is necessary to extend the lower jaw so that the lower teeth protrude forward. The rescuer then inhales deeply and, pressing his mouth over the victim's mouth or nose, exhales. When respiratory activity appears in the victim, artificial ventilation of the lungs cannot be stopped unless consciousness is restored and the breathing rhythm is disturbed.
If cardiac activity is absent, then simultaneously with artificial respiration, it is necessary to perform an indirect heart massage. The rescuer's arms should be placed perpendicular to the patient's sternum in its lower third. The massage is performed in the form of sharp jerks with relaxation intervals. The frequency of shocks is from 60 to 70 per minute. With the correct implementation of chest compressions, blood from the ventricles enters the circulatory system.
If the rescuer resuscitates alone, alternate cardiac muscle massage and artificial ventilation. For 4-5 pushes, one blow of air into the lungs should fall on the sternum.
The optimal time for resuscitation is 4-6 minutes after rescuing a person. When drowning in ice water, revival is possible even half an hour after being removed from the water.
In any case, at the first opportunity, even with the restoration of all vital functions, it is imperative to deliver the victim to the hospital.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!