- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Signs of a stroke in men: symptoms, how to recognize it in time, an algorithm of actions
The content of the article:
-
Signs of stroke and microstroke in men
- Ischemic stroke
- Hemorrhagic stroke
- Erased form
- Microstroke
- How to recognize a stroke
- First aid for stroke
- What is a stroke
- Forms of the disease
- What are the causes and risk factors for stroke
- Treatment
- Rehabilitation
- Forecast
- Prevention
- Video
Stroke symptoms in men are usually more pronounced than in women, and less often atypical. This is a favorable factor that allows you to recognize the pathology in time and prescribe adequate treatment.

The main symptom of a stroke is an acute intense headache.
Signs of stroke and microstroke in men
Harbingers of a stroke in a man may be unmotivated weakness, increased fatigue, frequent and persistent headaches that are difficult to relieve with analgesics, dizziness, sudden mood swings, changes in behavior, nausea not associated with food intake. An impending attack may be indicated by sudden and unreasonable increased sweating, numbness of the upper and lower extremities (usually on one side of the body), and slowing of the pulse. The harbingers of stroke are most often short-lived, they can appear several times and pass on their own after a while, which is why the patient does not pay enough attention to them.
The first sign of a stroke in men is usually an intense headache. Patients often describe this pain as unbearable, the most intense pain they have ever experienced. The headache may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting that does not bring relief.
Ischemic stroke
With ischemic stroke, the headache usually increases gradually, getting worse for no apparent reason. In addition to her, usually there is numbness of the face, dilated pupil on the side of the lesion, paresis or paralysis of the limbs, impaired coordination of movements, speech disorders (misuse of words, incomprehensible speech), disturbances on the part of the visual analyzer (usually on one side), difficulty swallowing, increased body temperature, agitation, disorientation. On the side opposite to the lesion, muscle atony is observed (manifested in the drooping of the corner of the mouth, drooping of the upper eyelid, weakness of the limbs).
So, in the case of thromboembolism of large-caliber cerebral arteries, respiratory failure, sudden loss of consciousness, generalized convulsions, epileptic seizures are possible. Such symptoms are an unfavorable prognostic sign.

One of the signs of a stroke is a drooping corner of the mouth.
Hemorrhagic stroke
In a hemorrhagic stroke, an intense headache usually occurs abruptly (called dagger pain). Headache is accompanied by painful sensations in the eyes, a feeling of pulsation in the head, nausea, vomiting, respiratory distress, palpitations, hemiparesis and hemiplegia, impairment of consciousness, including stupor and coma, is possible. Pendulum eye movements, a blank gaze, and urinary and fecal incontinence may occur.
Erased form
Stroke symptoms in men are rarely atypical, but patients with diabetes can have an erased form of the disease. In this case, the headache is absent or moderate, there is a general deterioration in well-being. Despite the weak severity of the signs, the disease in this case is no less dangerous than the usual form.
Microstroke
The symptomatology of a microstroke is generally similar to that of a stroke, but its symptoms are less pronounced. Often there is only severe headache that cannot be relieved by conventional pain relievers and / or muscle atony on one side of the body.
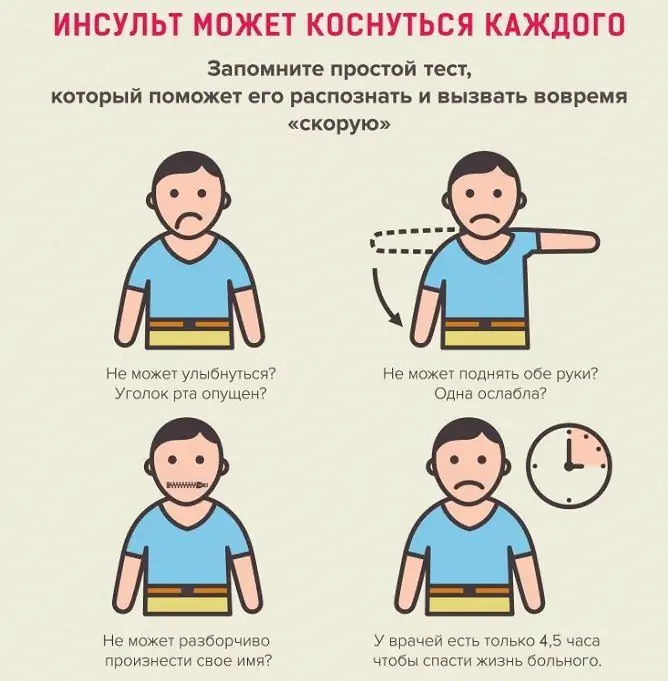
How to recognize a stroke
The table shows an algorithm of actions that should be asked to take the patient if a stroke is suspected.
| Act | Signs of a stroke |
| To smile | Smiles fail or are distorted |
| Raise your hands | The patient cannot raise both arms to the same height |
| Stick out tongue | The tongue deviates from the midline |
| Repeat a simple phrase, answer a simple question (for example, what is your name?) | Speech is blurry, "drunk", the simplest questions are difficult to answer |
First aid for stroke
The first thing to do at the first sign of a stroke is to call an ambulance. This should be done without waiting for confirmation of your suspicions, since it is extremely important to have time to provide medical assistance before the development of irreversible brain damage.
While waiting for an ambulance, it is necessary to seat or lay down the patient, provide air access (open a window, free from tight clothes), complete rest - the patient should not get up and move abruptly.
If possible, you need to measure the pressure and pulse and record the results, informing them to the arriving doctor.

If you suspect a stroke, it is important to provide first aid correctly.
You can not give the patient to drink or eat, this can worsen his condition, cause vomiting.
If the patient has lost consciousness, he should be positioned so that the upper body is raised by about 30 degrees, the head should be turned to one side.
Until the arrival of the doctor, the patient must not be left alone.
A stroke on the legs (including a microstroke) significantly increases the risk of a second, more severe attack.
What is a stroke
Stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation due to thrombosis, embolism, prolonged spasm or sudden rupture of cerebral blood vessels. In this case, patients develop neurological disorders due to acute hypoxia of one or another part of the brain, and in the case of hemorrhagic stroke, additional damage due to the outflow of blood.
It is one of the most common vascular diseases and is one of the main causes of disability and mortality. Morbidity is related to age - the age group over 60 is the most vulnerable to stroke, although worldwide doctors note an increase in morbidity in patients aged 30-35. The incidence of strokes in men after 40 and before 50 is 4 times higher than in women, but after 50 years the incidence becomes the same in both sexes.
Forms of the disease
The main forms of stroke are ischemic and hemorrhagic. Hemorrhagic stroke usually has a more severe course, but it has a better prognosis due to a brighter clinical picture, which prompts to quickly and timely seek medical help and avoid the development of severe consequences.
Depending on the localization of the ischemic focus, stroke is subdivided into right- and left-sided. With a left-sided form of the disease, the right side of the body suffers, and with a right-sided stroke, the left.
In terms of severity, a stroke can be mild, moderate, severe (extensive), or a microstroke. An extensive stroke is caused by damage to a large cerebral artery, a microstroke - when a small-caliber artery is blocked.
What are the causes and risk factors for stroke
The causes of stroke include: damage to the blood vessels of the brain against the background of progressive cardiovascular pathology (cardiac arrhythmias, atherosclerotic damage to blood vessels, arterial hypertension, myocardial infarction), endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus), severe somatic or infectious diseases, as well as long-term high blood pressure of various origins.
Risk factors: old age, exposure to stress, excessive physical activity, smoking, alcohol abuse, overweight, unbalanced diet, uncontrolled drug intake. Tobacco smoking poses a particular danger, since it has an extremely adverse effect on the state of blood vessels.
Treatment
Patients are shown bed rest, the duration of which, depending on the condition, can range from several days to 4-6 weeks. With prolonged bed rest, anticoagulant therapy is prescribed.
With cerebral edema, hyperventilation of the lungs, surgery to decompress the brain are performed.

Stroke requires hospitalization
Prescribed diuretic drugs, analgesics, antiplatelet agents, anticonvulsants, drugs that improve cerebral circulation, barbiturates. With high blood pressure - antihypertensive drugs.
Surgical treatment is indicated for signs of cerebral compression, with a high risk of a second attack, lack of effect from anti-edema therapy, and some other conditions.
Rehabilitation
How to avoid adverse consequences? For this, the restoration of lost or impaired abilities must begin immediately after stabilization of the patient's condition. Rehabilitation measures begin with passive gymnastics, then gradually the complexity of the exercises performed increases.
You may need to work with a speech therapist, psychologist, physiotherapy, massage, therapeutic exercises, spa treatment are indicated.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the localization of the lesion, the presence of complications, the timeliness of medical care. Mild stroke with timely adequate treatment has a favorable prognosis. With a severe course of the disease, untimely provision of medical care, the presence of complications, it is possible to develop severe consequences associated with irreversible damage to the brain and the development of neurological disorders, up to disability and death.
Prevention
To prevent the development of a second attack, you should strictly follow all the recommendations of the attending physician, undergo supportive therapy, and control blood pressure. All people over the age of 30 are advised to check their blood cholesterol concentration at least once every five years, after 50 years, this test is recommended to be carried out annually.
It is necessary to give up bad habits, lead an active lifestyle, spend more time in the fresh air, adhere to the principles of proper nutrition. Adequate rest is essential, in particular getting enough sleep at night (at least 7 hours of continuous sleep).
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.