- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
First aid for stroke
A stroke is an acute disorder of the blood circulation in the brain. This is an extremely dangerous condition that carries an immediate threat to human life. Unfortunately, stroke is one of the most common acute pathologies requiring urgent treatment. A lot depends on how quickly and efficiently first aid is provided for stroke.
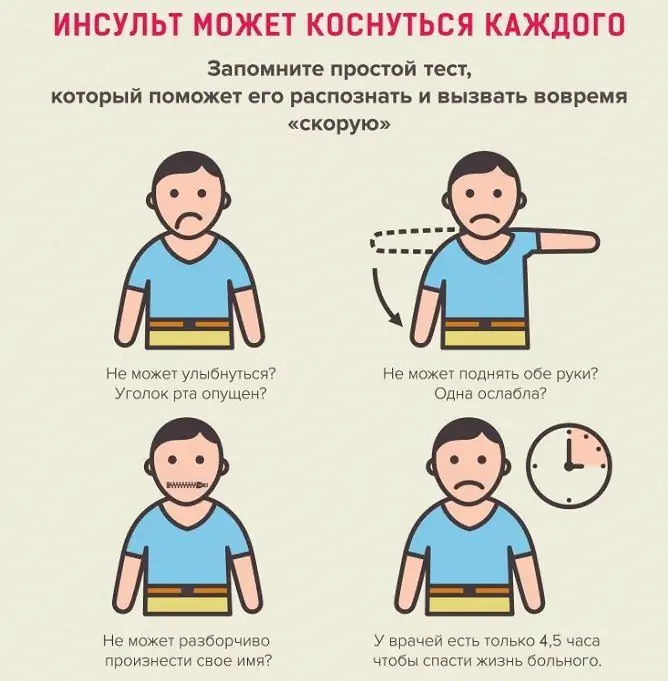
One of the main problems in stroke is that it often goes unnoticed, pathological changes attract attention too late. It's important to know the signs of a stroke so you don't miss it.
Types of strokes and their signs

There are two types of strokes - hemorrhagic and ischemic. The first occurs when a vessel is ruptured, and blood is poured from it into the brain (“hemorrhage” is translated from Latin as hemorrhage). Ischemic stroke occurs when the lumen of a vessel is blocked by a thrombus, and blood stops flowing to the area of the brain fed by this vessel (“ischemia” means anemia).
The resulting pathology - a stroke - is due to the same reason, the lack of blood supply to the brain area, and the consequences may be similar. Hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes differ in the time of development - the first manifests itself suddenly, the second - with a gradual increase in symptoms. First aid for ischemic stroke often comes with a delay due to the fact that the signs of a stroke are not recognized in time.
A stroke has the following symptoms:
- High intensity headache. Patients often describe it as the most intense and unbearable pain in their life;
- Numbness in any part of the body - either sudden or gradually increasing;
- Impaired speech. A person's speech becomes blurred, reminiscent of speech during alcohol intoxication;
- Sharp or increasing deterioration of vision, loss of visual fields, flashing "flies" in front of the eyes, darkening in the eyes;
- Curvature of facial features, most often the mouth is curved, a frozen grimace on the face may occur;
- Impaired coordination of movements. The movements become unbalanced, the appearance of a "drunk" gait is possible;
- Loss of balance. It may not necessarily be long - a person may fall and rise rather quickly, but if there is a sudden loss of balance, this should alert you to a stroke;
- Loss of consciousness;
- Nausea, vomiting.
The first seven signs are most common in stroke. Even the appearance of one of them is a reason to call an ambulance and provide first aid in anticipation. Remember, the first three hours are especially significant - it is extremely important that during this period of time the victim gets to the hospital and begins to receive adequate treatment.
First aid for stroke

If there is a suspicion of a stroke, do not wait until it is confirmed by several signs or until the patient's condition worsens even more. Arrange for the patient to be transported to the hospital immediately. In anticipation of such an opportunity, the first aid algorithm for stroke is as follows:
- Lay down or seat the person in a comfortable position;
- Make sure that the victim does not interfere with breathing: help remove the dentures from the mouth (if any), loosen tight clothing, and provide fresh air to the room. If the patient has lost consciousness, he should be laid on one side so that he does not choke on vomit. Contrary to popular belief, the victim of a stroke can be moved, you can not just move the head too sharply;
- Fix the time of the stroke as accurate as possible, measure blood pressure if possible and write these numbers down to inform the doctor;
- It is strictly forbidden to drink and feed the victim, as well as to give him drugs, in the action of which you are not sure.
Remember that there is the possibility of a gradual increase in symptoms, so you do not need to leave the person alone until the ambulance arrives, even if he claims to be feeling well.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.