- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Brain contusion
The content of the article:
- Development mechanism
- Causes
-
Brain contusion symptoms
- Slight bruise
- Moderate contusion
- Severe contusion
- First aid
- Diagnostics
-
Treatment of brain bruises
- Operative treatment
- Conservative therapy
- Consequences of a brain injury
- Video
Brain contusion occurs as a result of traumatic brain injury. In this case, areas of necrosis (tissue necrosis) of various sizes appear in the brain. Trauma is often combined with a closed fracture of the skull bones. Among all traumatic brain injuries, brain contusion occurs in about 25% of cases.

Brain contusion is a consequence of traumatic brain injury
Depending on the size and nature of the injury, there are three degrees of severity: mild, moderate and severe. In 45% of cases, the victims have a slight bruise.
Most often, injury occurs in the frontal lobes of the brain. Contusion differs from concussion in that it causes damage to the brain tissue. According to statistics, in men, such an injury occurs three times more often than in women.
Development mechanism
There is a certain mechanism for the development of brain contusions:
- moving hemispheres. The medulla oblongata, medulla and varolian brains are the brainstem. It does not change its position between the zones of impact and counterblow, while the hemispheres are displaced, which leads to damage. During the impact, the brain stem does not receive impulses from the cerebral cortex, this becomes the cause of loss of consciousness. The time spent unconscious depends on the force of the blow;
- offset. During injury, the brain shifts in the skull. In the place where the blow occurred, the pressure rises and the brain structures are damaged (minor hemorrhages and damage to nerve cells). In the counter-shock zone, the pressure decreases, and small cavities filled with fluid are formed in the intercellular substance and nerve cells. If the impact was very strong, the low pressure is quickly replaced by high, as a result of which they burst, which leads to the formation of extensive zones of damage. As a result of such injuries, large areas of the brain are affected;
- hypodynamic effect. The ventricles of the brain are filled with cerebrospinal fluid, which, as a result of an impact, begins to move rapidly in a certain direction. As a result, punctate hemorrhages are formed. They occur almost always, regardless of the area in which the blow was made.
Causes
In the overwhelming majority of cases, the cause of a head injury is a traumatic brain injury. The main concomitant factor affecting the frequency of its occurrence is alcohol intoxication. Approximately 20% of the victims diagnosed with a bruise drank alcohol.

One of the most common causes of bruises is engaging in traumatic sports.
Causes of traumatic brain injury:
| Causes | Description |
| Road traffic injuries | The victim can be a pedestrian, driver or passenger. Most often, such injuries prevail in the autumn-winter period, when weather conditions deteriorate significantly |
| Household injuries | In this case, the patient receives a mechanical injury at home or in the yard, outside the production conditions. Most often - due to the careless performance of any duties during cleaning or repairs. Also, household injuries occur when falling from a height of their own growth on various objects |
| Criminal injury | Often, bruises occur as a result of blows to the head with a blunt object (bat, stone, stick or brass knuckles). Also, such an injury occurs if the victim is beaten with a fist, while he falls with his head on a hard object or on the ground |
| Childhood injuries | Since the head is the heaviest part of the body in children of the first year of life, a bruise may occur when falls even from a low height. Often injuries sustained up to two years of age have delayed consequences |
| Sports injury | Traumatic sports include martial arts, boxing, ski jumping, cycling, etc. Both beginners and professional athletes are at risk of getting a head injury during training. |
| Industrial injuries | An injury can be obtained in the course of work as a result of non-compliance with safety measures |
|
Injuries sustained during epileptic seizures |
During an epileptic seizure, a person may fall to the ground or a solid object from their own height |
Brain contusion symptoms
Slight bruise
The most common bruise is minor, which does not pose a threat to the patient's life. The patient has the following symptoms:
- loss of consciousness. The likelihood of developing this symptom is almost 100%. As a result of injury, the cerebral cortex for a while ceases to send impulses to its trunk, where the structure responsible for maintaining consciousness is located. In a mild form of injury, the victim may be unconscious from 2 minutes to an hour;
- lethargy. The patient becomes drowsy and weak. A person can be poorly oriented in time and space, allowing some inaccuracies;
- amnesia. As a result of pathological disorders, the patient experiences memory loss. Amnesia can be retrograde (the person forgets the events preceding the traumatic brain injury), anterograde (the patient ceases to remember after the injury) or mixed. Traumatic amnesia is temporary and memory usually returns after tissue repair;
- headache. Initially, it occurs due to a violation of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and increased intracranial pressure. In the future, the cause of cephalalgia is edema and inflammation in the areas of lesion of the brain structures. With a mild form of bruising, the headache can be observed for 2-3 days, then it gradually recedes;
- vomiting. The vomiting center is located in the brain stem. Transient disorders cause vomiting, which does not bring relief, since it does not depend on the state of the gastrointestinal tract. In uncomplicated cases, vomiting usually occurs once, it appears suddenly, and there is no nausea;
- dizziness. It occurs as a result of a blow to the back of the head when the cerebellum is injured, which is responsible for the ability to maintain body position. Also, this area can be damaged as a result of a counter-shock if the frontal area is affected. It is necessary to distinguish between lightheadedness and dizziness (in this case, the patient does not have a decrease in blood pressure, darkening in the eyes and weakness in the legs);
- breathing disorder. Transient disturbances affecting the respiratory center located in the brain stem lead to the fact that after an injury, a person's breathing becomes more frequent. In mild cases, they can be observed within 2-3 days, then disappear;
- heart rhythm disturbances. They are the result of disorders of the autonomic nervous system. Quite often, after injury, the patient's heart rate increases or decreases and blood pressure rises;
- nystagmus (involuntary movements of the eyeballs). The reason for this is damage to the nerve structures responsible for eye movement. Also, with bruises of the brain in the victim, the size of the pupils of the right and left eyes may differ;
- increased muscle tone in the occiput. The reason for this is the defeat of the arachnoid and soft membrane of the brain. As a result, the victim develops a symptom similar to meningitis. With Kernig's syndrome, if you bend your leg at the knee and bring it to you, you will not be able to fully extend the knee joint. This symptom can be observed for three weeks, then it disappears;
- Brudzinsky's symptom. If the chin is pressed against the chest, then the knee joint reflexively flexes. This symptom is also referred to as signs of damage to the nervous system. It disappears on its own after 2-3 weeks.
Moderate contusion
In most cases, a moderate brain injury is combined with a fracture of the bones of the vault or base of the skull. At the same time, neurological symptoms are more pronounced. Signs of such an injury include:
- loss of consciousness. The unconscious period can last from 10 minutes to 6 hours. In this case, spontaneous urination or defecation is often observed;
- deep lethargy, contusion. The patient is lost in time and space, answers questions in monosyllables, can perform only the simplest actions;
- severe headache. A fracture of the bones of the base of the skull leads to rupture of the soft membrane of the brain and blood vessels in the walls, in which a large number of pain receptors are located. The patient's headache may persist for a long period;
- loss of memory. The patient for several days cannot remember what events preceded the injury and what happened after that, then the memory returns;
- vomiting. May appear multiple times; does not bring relief and is not combined with nausea;
- breathing disorder. It becomes frequent and superficial, while there are no violations of the patency of the lower respiratory tract;
- increased body temperature. With moderate brain contusions, the patient has a subfebrile body temperature (within 37.5 ° C). This is due to a malfunction of the hypothalamus;
- tachycardia. Often, with brain injuries, heart rhythm disturbances occur and blood pressure rises;
- visual impairment. Brain contusions of moderate severity may be accompanied by nystagmus, anisocoria, as well as impaired eye movement;
- meningeal symptoms. Often, patients have symptoms of Brudzinski and Kernig, as well as paresis of the upper and lower extremities. These signs persist for 4-6 weeks, then gradually disappear.
Severe contusion
In about 7% of cases, the victims are diagnosed with severe brain contusion. This is a very dangerous condition that requires urgent medical attention. Such an injury poses a danger not only to health, but also to human life.
Symptoms include:
- loss of consciousness. The unconscious period can last from several hours to several weeks. The patient is in a state of deep coma, it is impossible to wake him up, he cannot make swallowing movements and does not react to pain. In most cases, he does not control the sphincters, so urination and defecation occur involuntarily;
- serious condition after coming out of a coma. The patient reacts only to loud sounds and sleeps almost all the time. There is also no control over the sphincters during this period;
- heart rhythm disturbances. The victim may have both tachycardia (over 150 beats per minute) and bradycardia (less than 60 beats per minute). In this case, blood pressure rises to 160-180 mm Hg. Art.;
- breathing disorders. The respiratory center is damaged, resulting in obstruction of the upper respiratory tract. At the same time, periods of deep and shallow breathing will be replaced by periods of apnea (complete lack of breathing);
- increased body temperature. Due to disturbances in the hypothalamus, the patient's body temperature can reach 39-40 ° C, which poses a threat to his life. In some cases, against the background of hyperthermia, convulsions occur;
- neurological signs. Severe contusion of the brain is characterized by multiple tonic nystagmus, bilateral narrowing or dilated pupils. There is also a violation of muscle tone, paralysis and paresis of the limbs, generalized or local seizures.
First aid
First of all, when a patient with a traumatic brain injury is found, an ambulance must be called. Before her arrival, it is necessary to provide a person with a patency of the airways and make sure that the vomit comes out and does not throw the tongue back.

If a brain injury is suspected, before the arrival of an ambulance, the victim must be laid on his side and ensure a stable body position
For this, the unconscious patient must be laid on his side and provided with a stable position. I bend the lower arm at the elbow joint, and the upper arm (in relation to the patient's body) is placed under the head. Also, the lower leg is straightened, the upper leg is bent at the knee.
If vomiting occurs, the oral cavity should be cleaned with fingers wrapped in a cloth. If a person is conscious, he cannot get to his feet; he must lie on his side or back.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics is carried out by assessing the general condition of the patient, neurological disorders and the state of internal organs.

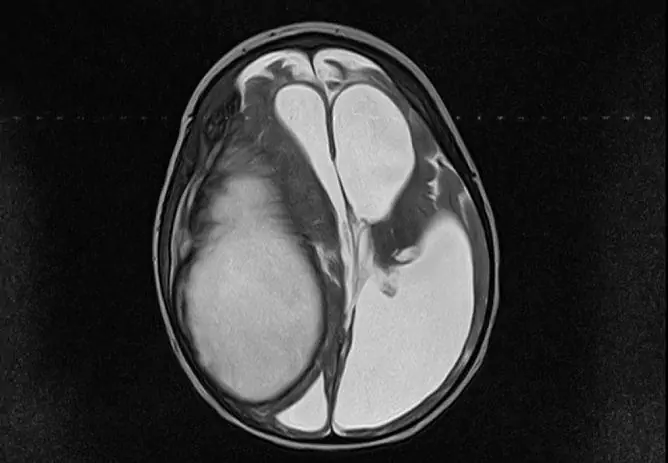
Computed tomography is performed to clarify the diagnosis
The diagnosis for focal lesions is necessarily determined:
- side: right, left, bilateral;
- lobar localization: temporal, frontal, parietal, occipital lobes, cerebellum, etc.;
- relation to the surface of the hemispheres: basal, sagittal, convexital, parasagittal.
Treatment of brain bruises
Depending on the severity of the brain injury, treatment can be carried out conservatively or surgically.
Operative treatment
Surgical intervention is performed in about 20% of cases if the brain is compressed as a result of edema or the position of the brain structures changes.
Traumatic edema leads to the fact that there is a significant increase in intracranial pressure, which is not regulated by drugs, and neurological symptoms increase. This is an indication for urgent surgical intervention.
In order to gain access to the tissues of the brain, the neurosurgeon performs craniotomy (makes holes in the bones).
Conservative therapy
Conservative therapy is performed to eliminate secondary brain damage. They are a consequence of trauma and significantly increase the risk of death, as well as damage to tissues and blood vessels. In conservative treatment, respiratory therapy is used. In case of respiratory failure and a decrease in the oxygen level in the patient's blood, a ventilator is used.

Ceraxon is used to reduce the effects of secondary damage
In order to reduce the consequences of injury, drugs are used that restore the volume of lost blood, saturate with oxygen and restore the water-salt balance.
With an increase in intracranial pressure above 21 mm Hg. Art. use an intraventricular catheter through which cerebrospinal fluid is dumped. A solution of mannitol is injected intravenously, which helps to reduce intracranial pressure.
If there is no expected effect from these manipulations, the patient is immersed in an artificial coma. In this condition, the cerebral cortex is less susceptible to damage.
In order to reduce the effect of secondary damage on nerve cells, neuroprotectors are used: Erythropoietin, Cerakson, Neurokson, Gliaton. They begin to be administered immediately after the patient is admitted to the hospital. These medications help restore white and gray matter in the brain.
Consequences of a brain injury
Tissue damage can lead to the development of serious pathologies. Severe traumatic brain injury can lead not only to disability, but also to death.
All the consequences of such an injury are divided into three clinical forms:
| The form | Description |
| Liquorodynamic | As a result of impaired absorption and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, the patient may develop hydrocephalus (accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid), porencephaly (formation of channels between the brain structures and the ventricular cavity), cerebrospinal fluid cysts or pneumocephalus. Typically, these complications are accompanied by increased intracranial pressure, epileptic seizures, decreased mental capacity and memory disorders. |
| Vascular | Vascular injury often leads to the appearance of intracranial hematomas, hemorrhages and aneurysms. As a result, a person has seizures, paresis, severe headaches, psychoses, speech disorders |
| Tissue | The consequence of trauma is damage to the tissues of the white or gray matter, which can lead to post-traumatic atrophy of the brain, seals due to the proliferation of connective tissue or inflammation of the dura mater. In some cases, patients have skull defects. Such pathologies often lead to the development of psychopathies, paresis of the facial nerve, blindness, epileptic seizures |
In order to prevent the development of pathologies after any, even minor, traumatic brain injury, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!