- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
How to reduce eye pressure: lower the level of the indicator with medication and folk remedies
The content of the article:
-
How to lower eye pressure: treatment methods
- Lifestyle modification
- Drug therapy
- Surgery
- How to relieve eye pressure at home using folk methods
- Overview of intraocular pressure
- Video
Reducing eye pressure in case of its increase is necessary as soon as possible, because it can lead to optic nerve atrophy and blindness. Some eye diseases can practically have no clinical manifestations for a long time, however, their consequences for vision are very dangerous. Glaucoma, which is manifested by increased eye pressure, belongs to such diseases.
Persons from risk groups (especially in the presence of a genetic predisposition) are recommended to regularly undergo ophthalmological examinations so as not to miss the development of a formidable disease.
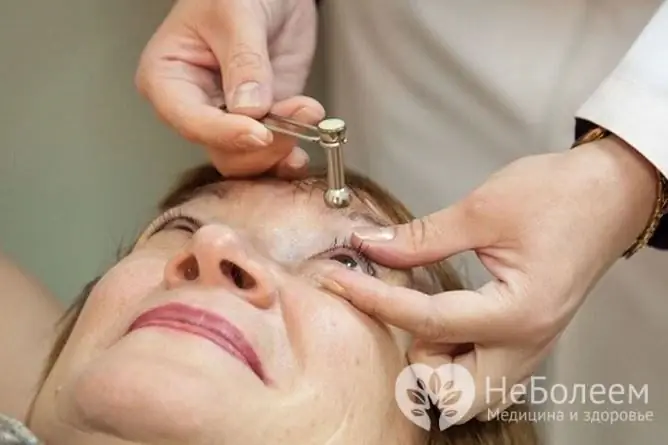

People who are prone to increased intraocular pressure need periodic examinations by an ophthalmologist
How to lower eye pressure: treatment methods
Treatment for increased intraocular pressure depends on the cause of the increase. In most cases, conservative measures are sufficient, however, in the absence of the effect of the therapy, surgical intervention may be required. Only a specialist can assess the situation and choose the correct method of treatment.
Lifestyle modification
Regular aerobics, jogging, walking, cycling can help relieve eye hypertension, but any type of physical activity must be approved by your doctor. It is recommended to devote at least 30 minutes a day to sports or physiotherapy exercises 3-5 times a week.
Regular eye exercises are recommended to reduce intraocular pressure. For example, slowly move your gaze from bottom to top, from right to left and in the opposite direction; make circular movements with your eyes clockwise and in the opposite direction; describe with your eyes an imaginary eight; fix the gaze alternately at close and far-away objects. Gymnastics takes only a few minutes, but if done regularly, it can be very effective.
Patients with increased eye pressure should sleep on high pillows as the head should be slightly raised while sleeping. It is recommended to reduce the time of reading, working at the computer and other activities that involve visual stress.
Proper nutrition is also important. Patients with increased intraocular pressure should eat foods rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids - sardines, tuna, salmon, herring, shellfish 2-3 times a week. The doctor may prescribe fish oil capsules, grape seed extract.
In addition, foods that contain lutein and zeaxanthin are useful: spinach, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, egg yolks. Blueberries and currants have a beneficial effect on eye health.
The menu should be balanced, enriched with vitamins and microelements.
Foods that are high in trans fats and salts, which can lead to increased intraocular pressure, should be limited or excluded. These products include fast food, snacks, fast food, canned food. It is also necessary to limit the use of tonic drinks: strong coffee, tea, tonics.
Drug therapy
Eye drops are used, which promote the outflow of intraocular fluid, improve the nutrition of the eye tissues and can quickly reduce intraocular pressure. Also, drugs may be prescribed that reduce the production of intraocular fluid or enhance its excretion.
Surgery
In some cases, hirudotherapy helps to effectively reduce increased intraocular pressure, helping to create additional drainage pathways.
Laser trabeculoplasty can be used to open blocked drainage channels in the eye and facilitate the removal of excess fluid from the eye.
For narrow angles of the anterior chamber of the eye, a laser iridotomy may be required, during which a hole is made in the upper part of the iris to drain fluid.
In some cases, laser trabeculectomy is performed, during which a hole is made in the sclera and a small amount of tissue is removed to improve fluid outflow.
In children and patients with advanced glaucoma, drainage implants may be needed to help drain fluid from the eye.
After surgery, regular monitoring of intraocular pressure is required.
How to relieve eye pressure at home using folk methods
It is possible to reduce eye pressure without medication with the help of folk remedies based on bee products or herbal ingredients.
So, according to patients' reviews, it is possible to lower intraocular pressure using lotions made of honey mixed with water, diluted pomegranate juice, decoction of nettle, lily of the valley flowers, golden mustache, motherwort, strawberry leaves, birch leaves, wild rosemary, tansy, horsetail, string, knotweed, plantain, mother-and-stepmother, eyebright.
Treatment of eye pressure at home can be carried out only by those methods and means that have been approved by the attending physician.
Overview of intraocular pressure
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is the pressure of the fluid inside the eyeball.
Increased eye pressure, or hypertension (hypertension) of the eye is recorded quite often, people over 40 are especially prone to pathology, but it occurs in all age groups. Persistent ocular hypertension is a manifestation of glaucoma, therefore, if you suspect or identify it, you should contact a qualified specialist who will conduct the examination, explain what may be causing it and what to do.
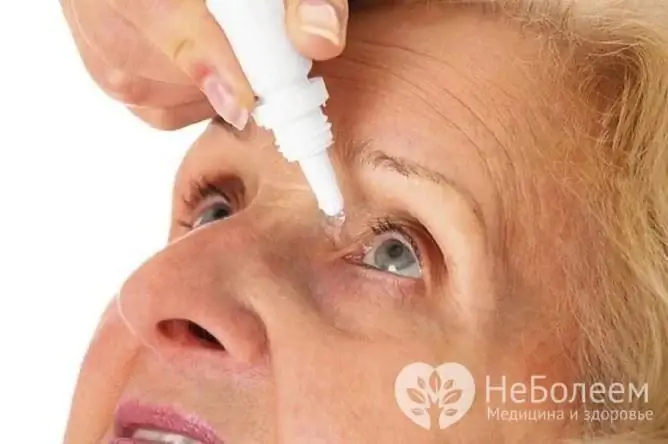
The main treatment for high IOP is local drug therapy.
Glaucoma is divided into open-angle and closed-angle. With closed-angle glaucoma, the accumulation of ocular fluid is observed due to the overlap of the angle of the anterior chamber of the eye by the iris, as a result of which access to the drainage system of the eye is impaired. With open-angle glaucoma, access is open, but the functions of the drainage system are impaired.
There are primary, secondary and congenital glaucoma.
Primary usually occurs in patients over 40 years of age. Risk factors include genetic predisposition, myopia of the eye (myopia), old age, disorders of the central nervous system, thyroid disease, diabetes mellitus.
Secondary glaucoma develops against the background of inflammatory diseases of the eyes, hemophthalmos, progressive atrophy of the iris of the eye, cataracts, lens shift, after eye operations, with burns, eye injuries.
The main cause of congenital glaucoma is anomalies in the development of the eyes in the prenatal period.
In some cases, during an acute attack of glaucoma, there is a sudden loss of vision, therefore, with a sharp and significant increase in intraocular pressure, an ambulance should be called to the patient.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.