- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
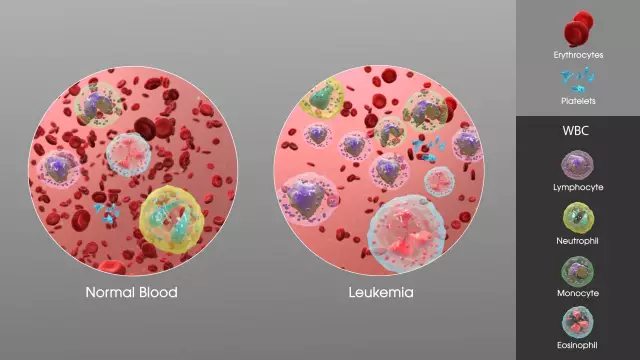
Leukemia

In common parlance, leukemia is called anemia, leukemia, or blood cancer. In fact, this statement is not entirely true, since a formidable diagnosis of blood cancer, experts call hemoblastosis - a multifactorial group of malignant diseases of the hematopoietic system of the body, including leukemia. In people with leukemia, for various reasons, there is a pathological and rapid growth of "wrong" bone marrow cells, which is responsible for the vital process of hematopoiesis in the body.
The result is a rapidly progressive disruption of the normal functioning of all organs and systems. Without a timely started, complex treatment, leukemia is usually fatal, sometimes within a few weeks. Cases of self-healing in this malignant disease are extremely rare, therefore, the treatment of leukemia should begin immediately after an accurate diagnosis has been established.
Causes of leukemia
To this day, modern medicine has not thoroughly clarified all the numerous factors that provoke leukemia. The causes of leukemia are divided into four main groups.
The first group includes the causes of hereditary leukemia. Scientists today have absolutely certain that the presence of leukemia in any of the direct (blood) relatives will certainly make itself felt, even after several generations. It is the hereditary factor that experts call the most probable and common cause of leukemia in children.
The second, no less large, group of causes of leukemia are infectious and viral diseases that have ever been transferred. A viral invasion of healthy cells of the body causes their irreversible mutations and pathological degeneration, which ultimately creates a threat of the appearance of malignant neoplasms.
The next group of causes of leukemia includes the impact of leukemia and chemical factors. As for leukemia, this, in simple terms, is a consequence of taking medications that are prescribed for various diseases. These include, first of all, cephalosporin drugs, as well as antibiotics of the penicillin series. The effects of chemical pathogens include prolonged exposure to synthetic detergents, various floor coverings based on polymer compounds, etc.
The fourth group of causes of leukemia is radiation exposure. Exposure to radionuclides increases the risk of leukemia several times, and the likelihood of the disease is possible at any dose of radiation received.
Types of leukemia
There is a fairly long list of types of leukemia that can only be understood by oncologists. The division of leukemia into types comes from the place in which the blood cells have undergone a mutation, turned into "aggressors" hostile to the human body and provoked the growth of a malignant neoplasm.
As an example, one of the many types of leukemia is myeloid leukemia, in which the normal process of formation of granulocytic leukocytes is disrupted.
There is also a division of leukemia into chronic and acute. In acute leukemia, an uncontrolled and very rapid growth of immature blood cells develops. Acute leukemia is extremely dangerous and with a high degree of probability ends in death, because the disease progresses very quickly.
In chronic leukemia, the growth of more mature cells progresses, and the foci of this rapid growth are located in vital organs - the liver, spleen, and lymph nodes.
Symptoms of leukemia

Careful attention to the early symptoms of leukemia is extremely important today. The number of leukemia diseases in children, even at a very young age, is steadily growing, and if treatment is not started on time, a lethal outcome is inevitable in this age group.
At the initial stage, the symptoms of leukemia in children and adults can easily be confused with other diseases.
Fever often rises, sweating, shortness of breath, heart palpitations can be observed. In acute leukemia, the symptoms are more pronounced, perhaps also a significant increase in the size of the lymph nodes and their soreness.
Leukemia treatment
For a correct assessment of the patient's condition and the appointment of the necessary treatment for leukemia, a thorough medical examination is carried out by oncologists. The basis for the final diagnosis is the data of biochemical and general blood tests. Procedures for examining bone marrow cells are prescribed - trepanobiopsy, sternal puncture.
The tactics of treatment and the choice of drugs are carried out in accordance with the identified form of leukemia under the constant supervision and supervision of specialists. A complete cure from the disease is practically impossible today, and the treatment of leukemia should be the business of the rest of a person's life.
In the case of acute leukemia, treatment includes a complex of significant doses of glucocorticoid hormones and anticancer drugs. If an associated secondary infection occurs, the patient with leukemia is prescribed appropriate anti-inflammatory therapy and transfusion of blood components.
To support patients with chronic leukemia, treatment is prescribed mainly with such drugs, the action of which is to suppress the growth of malignant neoplasms. Accompanying measures to support the body - the introduction of radioactive phosphorus and radiation therapy.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!