- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
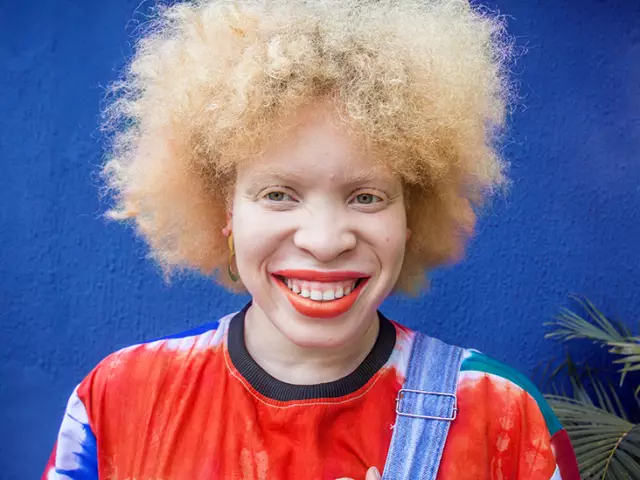
Albinism

Albinism is a congenital condition. This disease implies the absence of melanin pigment in the skin, hair, nails, pigment and iris of the eye membranes. The name "albinism" comes from the Latin word "albus", which is translated into Russian as "white". This disease has been known for a long time, since its descriptions are found even in the documents of Ancient Rome and Greece.
The causes of albinism
Albinism occurs due to the absence or blockade of the tyrosinase enzyme. It is extremely important for the production of melanin (the name comes from the Greek word "melanos", which means "black" in Russian). Skin color is determined by the amount of melanin in it. The more it is, the darker the skin color. In cases where problems with the production of tyrosinase are not observed, a mutation in the genes is considered to be the cause of albinism.
Albinism is inherited from parents. It appears in a child if both parents are carriers of the defective gene. When the defective gene is present in only one parent, children do not develop albinism, but the mutated gene still remains in the body, which can be passed on to the next generation. This entire process is called autosomal recessive inheritance.
Types of albinism
Albinism is divided into three types:
- total;
- incomplete;
- partial.
Albinism in people with a total appearance is observed from birth in an autosomal recessive manner. In addition to depigmentation, dryness of the skin, hyper- or hypotrichosis (often in open areas), and disturbances in the work of the sweat glands are manifested. Patients can easily develop keratomas, telangiectasias, epitheliomas, actinic cheilitis and sunburn. Infertility, cataracts, strabismus, low vision (due to refractive disorders), microphthalmia, oligophrenia, abnormal development, immunodeficiency (for this reason, often prone to infectious diseases) and a decrease in life expectancy are observed. People suffer from photophobia and horizontal nystagmus. Since there is no pigment in the pupils, they have a red tint.
Partial albinism, also called piebaldism, also occurs from birth. Sometimes it can be a symptom of the Klein-Waardenburg, Chadak-Higashi, Mende, Cross-McCusick-Brin, Titze, Hermansky-Pudlak syndromes. Typical manifestations are areas of achromia, which have clear boundaries, but an irregular shape, on the surface of which there are small specks of dark brown color. Mostly, partial albinism in humans occurs on the face, legs and abdomen, as well as in the form of strands of gray hair. On the skin adjacent to these spots, increased pigmentation is often observed. This type of albinism is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
In incomplete albinism, which is also called albinoidism, only hypopigmentation of the hair, iris and skin appears. Photophobia is very rare. The reason is the low activity of tyrosinase, but its synthesis is not blocked. Incomplete albinism is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, less often in a recessive manner.
Also distinguish between ocular and skin-ocular albinism (xanthism). The cause of xanthism is a mutation in one of the 4 genes. Signs of albinism of this type are skin, hair, pigmentation of the iris, and vision problems. It is divided into four types:
- Type 1 occurs due to mutations in the eleventh chromosome. This type of albinism in humans occurs from birth. The skin and hair of the sick are the color of milk, and the eyes are blue. Sometimes melanin can start to be produced with age: the eyes and skin become slightly darker.
- Type 2 appears due to mutations in the fifteenth chromosome. The skin is white or light brown, the hair is yellow, reddish or golden brown, the eyes are yellowish brown or gray-blue. Mostly the inhabitants of the Sahara Desert, African Americans and Indians living in North America are sick. Freckles appear on the skin almost instantly under the sun.
- Type 3 is provoked by mutations in the ninth chromosome. It is very rare. The skin is brown with a reddish tint, the eyes are red, the hair is red. Mostly people living in southern Africa are sick.
- Type 4 is also extremely rare and is caused by a mutation in the fifth chromosome. Mostly people living in the southeast of Asia are ill. The symptoms are the same as for the second type.
Signs of albinism
In people with albinism, the skin is very soft, pale pinkish in color, and therefore capillaries are easily visible through it. The skin is very prone to telangiectasias (spider veins), epithaleomas, keratomas and sunburn. Also, a sign of albinism is very thin and soft hair, which is white, in more rare cases, yellowish.
Albinism treatment

To date, no treatment for albinism in humans has been developed that would be effective. It is possible to correct only strabismus by correcting the eye muscles and vision, as well as with incomplete or total types of albinism, you can give the skin a yellowish tint, using from 90 to 180 mg of beta-carotene per day.
Tips for the sick
Even if the sun is not so strong outside the window, it is still necessary to wear sunglasses and protect your face with special means that have a protection factor (SPF) of at least 30. In hot weather, it is generally not recommended to go outside. Clothing should be made from natural materials and cover the entire surface of the body. It is also advisable to wear hats with a wide enough margin. A visit to a neurologist, ophthalmologist and dermatologist is mandatory.
Complications of albinism
Albinism in humans provokes complications, both from the physical side and from the emotions, up to complete social isolation. Physical - skin cancer and severe sunburn. Emotional - discrimination from other people, depression and stress.
Prevention of albinism
There is only one way to avoid the disease - genetic testing of couples who are going to become parents. Thanks to modern technology, it is easy to detect genetic defects in spouses, which subsequently become the cause of albinism in children.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!