- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Hemorrhoids during pregnancy
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Forms of the disease
- Disease stages
- Symptoms of hemorrhoids during pregnancy
- Diagnostics
- Hemorrhoid treatment during pregnancy
- Possible complications and consequences
- Forecast
- Prevention of hemorrhoids during pregnancy
Hemorrhoids during pregnancy is a disease that manifests itself as varicose enlargement of hemorrhoidal veins located in the anus. This leads to the formation of hemorrhoids, which can become inflamed, bleeding, thrombosed, falling out of the anal canal and being impaired. Hemorrhoids are the most common cause of rectal bleeding and are among the most common proctological diseases.

According to various sources, hemorrhoids occur in 25-50% of pregnant women
The hemorrhoidal plexus is located in the submucosal layer of the anal canal wall, in structure they are similar to the cavernous bodies of the penis. Due to the anatomical features, hemorrhoidal veins are susceptible to the development of blood stasis in them, which, under certain conditions, contributes to the formation of hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoids are equally susceptible to both men and women, while women often develop hemorrhoids during pregnancy. According to various sources, hemorrhoids occur in 25-50% of pregnant women, and in 50-80% of women during childbirth. Sometimes pregnancy exacerbates or reveals pre-existing hemorrhoids, which were previously latent. In addition, hemorrhoids can complicate the postpartum period.
Causes and risk factors
The development or exacerbation of hemorrhoids during pregnancy, as well as during childbirth, is explained by the physiological changes that occur in the woman's body during this period. The enlarging uterus compresses the inferior vena cava, resulting in stagnation of blood in the vessels, which leads to an increase in hemorrhoids. During childbirth, intra-abdominal pressure and pressure in the small pelvis increase sharply, which also contributes to the onset of the disease.
In addition, risk factors for the development of hemorrhoids during pregnancy are:
- hereditary predisposition;
- persistent constipation or, conversely, diarrhea;
- anal sex;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- heavy physical activity;
- wearing tight-fitting clothing, tight belts and bandages;
- poor nutrition.
Forms of the disease
Hemorrhoids can be acute or chronic.
Depending on the location of the pathologically altered hemorrhoids, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- internal (or submucous) hemorrhoids;
- external (or subcutaneous, external);
- mixed (combined).

With internal hemorrhoids, the nodes are located inside the anal canal and are not visible from the outside
Disease stages
There are 4 stages in the development of hemorrhoids:
- Blood is periodically released from the anus, hemorrhoids increase, swell, but do not fall out.
- Periodically (usually when straining during the act of defecation or during significant physical effort), nodes fall out, and their independent reduction is possible. Physical effort is accompanied by bleeding.
- Loss of hemorrhoids is characteristic even with minor physical exertion; the nodes cannot be adjusted on their own, but can be adjusted manually.
- There is a constant loss of nodes even without any load, the dropped nodes cannot be adjusted.
Symptoms of hemorrhoids during pregnancy
Hemorrhoids during pregnancy often occur in a latent form, manifesting themselves in the advanced stages of the disease. In the early stages, symptoms (mild soreness and discomfort during bowel movements, sitting on a hard surface) are usually mild and do not attract attention.
The first obvious signs of hemorrhoids during pregnancy are usually discomfort, a feeling of heaviness, the presence of a foreign body, bloating, itching or burning in the anal area. Unpleasant sensations can occur after eating spicy food and / or alcoholic beverages, as well as during physical strain. With the progression of the pathological process, patients periodically experience bleeding from hemorrhoids, especially often during bowel movements. In the feces, clots of scarlet blood may be found, which remained in the rectum after a previous bowel movement. Bleeding from the anus is a symptom that precedes the prolapse of hemorrhoids.
In some cases, the first symptom of hemorrhoids during pregnancy is the prolapse of the nodes without prior bleeding.
The increase in hemorrhoids is accompanied by painful sensations of varying intensity. The pain can be associated with the act of defecation or appear with prolonged standing, sitting, especially on a hard surface, as well as with excessive physical exertion. The nodes can become inflamed and ulcerate, which contributes to the attachment of a bacterial infection (manifested by significant pain, difficulty in defecation).

Symptoms of hemorrhoids in pregnant women - discomfort, itching, and burning in the anus, prolapse of nodes and bleeding during bowel movements
Hemorrhoids can be internal (formed from the upper venous plexus, localized in the submucosal layer of the anal canal) and external (develop from the lower venous plexus, localized under the skin at the anus).
In the early stages of the disease, the nodes fall out only during the process of defecation and are set spontaneously. In the absence of treatment, with the progression of the disease, hemorrhoids can fall out when sneezing, coughing, walking; patients require manual reduction of nodes. In the later stages of hemorrhoids, the nodes cannot be repositioned, edema is often observed around them, the skin in the anus is hyperemic. On palpation, the nodes are painful. Subsequently, the skin around the enlarged node acquires a burgundy color with a cyanotic shade.
In chronic hemorrhoids, the disease takes on an undulating character - exacerbations alternate with remissions. During exacerbations, the main symptoms of hemorrhoids may be accompanied by a loose closure of the anal sphincter, which contributes to the appearance of mucous secretions from it.
Diagnostics
To diagnose hemorrhoids during pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a proctologist, during which an objective examination of the anus and perianal region is carried out, as well as a digital rectal examination, in which hemorrhoids in the rectum are palpated. The anal reflex is checked by striking the skin of the perianal zone with a probe.
To clarify the diagnosis, an examination of the anal canal is carried out using an anoscope (makes it possible to examine 8-12 cm of the anal canal) and / or a sigmoidoscope (allows an examination of about 25 cm of the anal canal). If there is a suspicion of a pathological process in the upper parts of the large intestine, an X-ray examination is carried out with the introduction of an X-ray contrast agent into the intestine (irrigoscopy) or endoscopic diagnostics of the intestine (colonoscopy).

If a hemorrhoidal thrombosis is suspected, a coagulogram is performed
Ultrasound examination makes it possible to diagnose or exclude concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. In order to determine the source of bleeding, in some cases, a contrast X-ray examination of the blood vessels (angiography) is performed.
Physical and instrumental examination is complemented by laboratory diagnostics:
- a general blood test - confirms the presence of signs of an inflammatory process (there is an increase in the level of leukocytes and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR);
- coagulogram - performed if there is a suspicion of thrombosis of hemorrhoids.
Differential diagnosis is necessary with malignant neoplasms of the rectum, secondary syphilis, anal fibrous polyps, anal fissures, fistulas. It should be borne in mind that anal itching can also be observed in diabetes mellitus, helminthiasis and fungal infections, but with these pathologies there are no tumor-like formations in the anus.
Hemorrhoid treatment during pregnancy
In the initial stages, as well as during the period of exacerbation of the chronic process, conservative treatment of hemorrhoids during pregnancy is used.
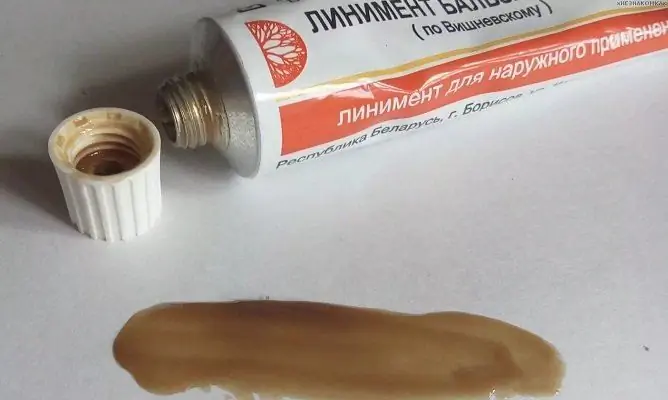
Local treatment of hemorrhoids during pregnancy is the main one. For this purpose, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, hemostatic preparations of local action in the form of an ointment, gel, as well as rectal suppositories are used.
In some cases, there is a need for general therapy. Prescribed drugs that increase the tone of the veins (phlebotonics), drugs that improve blood microcirculation. If necessary, prescribe drugs that improve intestinal peristalsis. In the case of a bacterial infection, antibiotics are used.

In the initial stages, hemorrhoids in pregnant women are treated with ointments and suppositories, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs
The treatment regimen for hemorrhoids during pregnancy can be supplemented with a course of therapeutic massage, which improves blood circulation in the small pelvis, and can also reduce pain.
During treatment, patients are shown a diet. Spicy, fried, fatty foods, spices, alcohol are excluded from the diet, products containing coarse fiber (cereals, vegetables, fruits, whole grain bread, products made from wholemeal flour) are included.
If conservative therapy is ineffective, minimally invasive methods of treatment can be used:
- method of infrared photocoagulation - as a rule, it is used in the treatment of hemorrhoids of the first and second stages and consists in the effect of infrared radiation on the hemorrhoid;
- sclerotherapy - a sclerosing substance is injected under the rectal mucosa near the hemorrhoidal node, which leads to fibrotic changes in the node and its "sticking";
- cryotherapy - a cold effect is exerted on the hemorrhoids with the help of liquid nitrogen;
- laser therapy - elimination of hemorrhoids using light pulses of a certain spectrum;
- ligation of hemorrhoids with latex rings - mechanical squeezing of the knot with a ring of latex is carried out, which leads to rejection of the knot after 1-1.5 weeks;
- a radio-beam scalpel - a method that involves exposure of the hemorrhoid to radio waves.
With the ineffectiveness of conservative and minimally invasive treatment methods, in the late stages of hemorrhoids, the method of hemorrhoidectomy is used. The method is indicated for patients who have constant prolapse of hemorrhoids, as well as profuse bleeding. Excision of nodes during hemorrhoidectomy can be performed both with a scalpel, and using a laser or by electrocoagulation. An alternative to hemorrhoidectomy can be transanal mucosal resection using the Longo method, during which part of the rectal mucosa is removed. This leads to a decrease in the blood supply to hemorrhoids and the gradual replacement of the nodes with connective tissue (scarring).
Surgical treatment of hemorrhoids during pregnancy is rarely carried out; the indication for surgery is the development of complications that pose a threat to the health of the pregnant woman and the unborn child. In other cases, surgery to remove hemorrhoids is postponed and performed routinely after delivery.
Possible complications and consequences
In addition to deteriorating the overall quality of life, hemorrhoids can complicate the normal course of pregnancy, affect the course of labor, and also reduce the well-being of a woman in the postpartum period.
Hemorrhoids during pregnancy can be complicated by such severe conditions as thrombosis, infringement and necrosis of hemorrhoids, as well as purulent inflammation of the tissues surrounding the anal canal. The accession of a bacterial infection is fraught with intrauterine infection of the fetus.
Constant bleeding from hemorrhoids causes anemia, which, in turn, negatively affects the condition of the pregnant woman and the fetus.
Forecast
The prognosis with timely diagnosis and correctly selected treatment is favorable. Hemorrhoids are completely curable.
Prevention of hemorrhoids during pregnancy
In order to prevent hemorrhoids during pregnancy, as well as to avoid the occurrence of relapses and exacerbations, it is recommended:
- timely treatment of diarrhea and constipation, as well as other disorders of the digestive tract;
- balanced rational nutrition (including a sufficient amount of fiber-rich foods in the diet, plentiful drinking regime);
- correction of overweight and obesity;
- avoiding hypothermia;
- thorough toilet of the anus after a bowel movement (if necessary, replace the use of toilet paper by washing the anal area with soap and water);
- avoiding excessive physical exertion;
- daily gymnastics for pregnant women (after consultation with a doctor leading a pregnancy, and under the supervision of an exercise therapy specialist);
- daily walks;
- refusal to wear tight belts and bandages during pregnancy;
- wearing underwear made from natural materials.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!