- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
How to cure sinusitis without a puncture at home
The content of the article:
-
Drug therapy
- Antibacterial agents
- Mucolytic, vasoconstrictor, anti-inflammatory and antihistamines
-
Instrumental methods of treating sinusitis without puncture
- Flushing with YAMIK catheter
- Balloon sinusoplasty
- Physiotherapy
- How to cure sinusitis without puncturing the sinuses at home
- Video
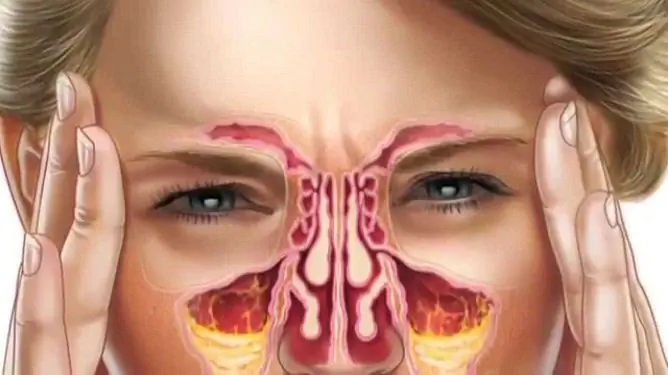
Sinusitis, or maxillitis, is an inflammation of the paranasal sinus, which occurs most often as a complication of acute rhinitis, flu, measles and other infectious diseases.

Sinusitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the maxillary sinuses
Classification of sinusitis by causative factor:
- traumatic;
- viral;
- bacterial;
- fungal;
- allergic.
Treatment tactics depend on the etiology of the disease. The main cause of maxillitis is infection. Pathogenic microorganisms enter the maxillary sinus in various ways: through the blood, turbinates or from the periapical zones of the upper teeth. The latter route of infection is called odontogenic. Patients are worried about headache in the projection of the sinuses, runny nose, fever, weakness and malaise. Mucus with impurities of pus is secreted from the nasal cavity.
Modern methods of treating sinusitis include drug therapy and instrumental methods. The basis of therapeutic measures for bacterial sinusitis is systemic and local antibiotic therapy. At the same time, procedures are carried out to restore the patency of the maxillary sinus anastomosis. In case of mild and moderate course of the disease, therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis, in severe cases - in a hospital. Timely referral to an otolaryngologist increases the likelihood of successful treatment of sinusitis without puncture of the sinuses.
Drug therapy
Antibacterial agents
The main task of drug therapy is to eradicate the pathogen and sanitize the paranasal sinuses. Treatment of purulent sinusitis without a puncture begins with antibiotics. Before prescribing antibacterial drugs, the contents are sown on the flora and its sensitivity to drugs. However, it takes 5-7 days to get the results of seeding. Usually, without waiting for a response, empiric antibiotic therapy is prescribed. The choice of a drug depends on the alleged pathogen and the course of the disease. Antibiotics with a broad spectrum of action are preferred.
According to research, pneumococcus and Haemophilus influenzae (causative agents of sinusitis) remain sensitive to penicillins and cephalosporins of the II-III generation. These microorganisms are resistant to Biseptol. It is impractical to use it for the treatment of sinusitis.
For mild cases, oral cefuroxime, ampicillin or amoxicillin are prescribed. The course of treatment is 1-2 weeks. In case of moderate course, drugs from the group of β-lactams and cephalosporins of the II - III generation are used. If gram-negative infection is suspected, fluoroquinolones are given.
Amoxicillin protected by clavulanic acid (Augmentin) is highly effective and relatively safe. In the course of clinical studies, it has been proven that this drug destroys pathogenic microorganisms, and is also well tolerated by children and adults. Both components of Augmentin are absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and are well distributed in body tissues. In addition, they penetrate the paranasal sinuses.
The product is available in three dosage forms: powder for injection, tablets (BD) and powder for oral suspension (ES). The dose of the drug for children under 2 years old depends on the age (in months) and weight. In this regard, it is convenient to use suspensions. A 10-year-old child can be prescribed funds in tablet form. In adults, the dosage and frequency of administration depends on the severity of the condition. For ENT infections, the maximum dose of antibiotic is usually prescribed.
The main side effects of the use of β-lactams and cephalosporins include: allergic reactions, incidental (associated) fungal infections, various reactions from the digestive and hematopoietic systems.
Fluoroquinolones are not used in pediatric practice.

In the treatment of sinusitis in severe course, cephalosporins are prescribed for intravenous or intramuscular administration
In severe cases of the disease, antibacterial drugs are administered intravenously or intramuscularly. According to clinical guidelines, inhibitor-protected penicillins (Ceftazidime, Ceftriaxone) are prescribed. Fluoroquinolones and carbapenems are used with a high risk of septic complications and resistance to other groups of antibiotics.
If an anaerobic infection is detected (bacteroids, clostridia), a group of imidazoles (metronidazole) is used.
In the treatment of sinusitis without a puncture, it is optimal to prescribe stepwise therapy: smoothly switch from parenteral administration of drugs to oral administration.
Mucolytic, vasoconstrictor, anti-inflammatory and antihistamines
In parallel with antibacterial therapy, mucolytic, vasoconstrictor, anti-inflammatory and antihistamines are prescribed.
Mucolytics prescribed for the treatment of sinusitis:
- Fluimucil. The active ingredient is acetylcysteine (ACC). It destroys mucopolysaccharides of the intra-sinus secretion, contributing to its liquefaction. In addition, the drug is available in the form of a Rinofluimucil spray. The latter also contains pre-congestant, which helps to restore external respiration.
- Fluditek. The main active ingredient is carbocisteine. It destroys the glycoproteins of mucus, facilitating its outflow.
- Sinupret. Natural preparation that regulates mucociliary clearance. The active components that make up its composition thin the secret, and also have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Antihistamines are prescribed to relieve swelling, inflammation, and improve aeration in the sinuses. They are mainly used for allergic sinusitis. Currently, drugs of the second and third generation are used.
Be sure to prescribe vasoconstrictor drops and sprays. They allow you to relieve swelling of the nasal mucosa, eliminate its congestion and partially restore the patency of the maxillary sinus anastomosis. Means based on phenylephrine (Nazol Baby), naphazoline (Naphtizin, Nazin) and tetrizoline (Tizin) are characterized by a short duration of action (up to 6 hours). The average duration of action (6-8 hours) is typical for drugs based on xylometazoline (Eucabal, Snoop, Multigrip Nazal, Rinazal, Nosolin), tramazolin (Lazolvan-Rino).
The most effective are drugs with oxymetazoline (Nazivin, Knoxprey, Nazol). Their action develops quickly, its duration is up to 14 hours. Oxymetazoline also has antiviral effects. Decongestants cannot be used for a long time. The maximum course is 14 days. With uncontrolled use, the nasal mucosa can atrophy.
Antibacterial and combined agents for topical use are widely used. Isofra (Framycetin) refers to broad-spectrum antibiotics. This spray is prescribed for 10-14 days. The therapeutic effect is observed after 3-4 days of use.
Polydexa is a combined drug, which contains an antibacterial component and dexamethasone. The tool not only effectively destroys bacteria, but also relieves inflammation well.
Instrumental methods of treating sinusitis without puncture
The evacuation of purulent contents from the maxillary sinuses is the primary stage of treatment. Until recently, puncture was considered the most effective technique. However, its implementation is fraught with a number of complications. The puncture was replaced by non-invasive methods of treating sinusitis.
Flushing with YAMIK catheter
Flushing with YAMIK catheter is an effective way to debride the sinuses. Before starting the procedure, the nasal mucosa is treated with vasoconstrictor drops and a local anesthetic. After that, an elastic catheter with a balloon at the end is inserted through the nose into the nasopharynx. The second balloon is adjacent to the nostril. After placement, the correct insertion is checked and air is injected. The patient is asked to tilt his head to the side, and then the purulent contents are pumped out. The final step is to flush the sinuses with antiseptic solutions.

One of the effective and painless minimally invasive methods of treating sinusitis is flushing with a YAMIK catheter
This method has proven to be effective and painless. The procedure is also used in pediatric practice. Washing with YAMIK is not contraindicated in pregnant women.
Balloon sinusoplasty
Balloon sinusoplasty is also a minimally invasive treatment for sinusitis. It is an alternative to open transactions. With the help of an elastic guide, the balloon is inserted into the maxillary sinus junction. After placement, it is filled with liquid. After 5-7 seconds, the liquid is drained. During this time, the lumen of the entrance to the sinus expands. Access is opened for the evacuation of pus and the administration of drugs.
Before starting the procedure, the nasal mucosa is anesthetized with local anesthetics. The intervention is performed by an otolaryngologist under visual (endoscopic) control.
Physiotherapy
Laser therapy is used as an additional method for the treatment of maxillitis. The mucous membrane of the sinuses is exposed to a low-intensity laser beam, which helps to relieve swelling and inflammation. Physiotherapy is indicated for patients with chronic sinusitis. Also, under the influence of the laser, the physiological microflora of the sinuses and nasal cavity is restored.

Physiotherapy is often prescribed to speed up the recovery of the nasal mucosa
A good therapeutic effect is observed when using UHF (ultra-high-frequency therapy) and pulsed currents. The reactivity of local immunity increases, the damaged mucous membrane of the nose is restored faster.
Magnetotherapy can also be used to treat chronic sinusitis. Currents penetrate deeply into soft tissues, stimulating their regeneration.
How to cure sinusitis without puncturing the sinuses at home
Treatment of sinusitis without a sinus puncture is a responsible decision that can only be made by an otolaryngologist. Puncture and sinusotomy is performed with the ineffectiveness of conservative therapy and a high risk of complications.

At home, outside the period of exacerbation, heating with salt can be carried out
On an outpatient basis, mild to moderate sinusitis can be treated. Patients with a severe form must be admitted to a specialized hospital.
The most commonly used methods include:
- Inhalation with a nebulizer. The device's tube sprays fine particles that reach even distant anatomical sites. Mild antiseptics or sodium chloride (NaCl) are used as an inhalation solution.
- Warming up with salt. Can be used for chronic disease. Warming up the sinuses in the acute phase, especially if there is pus, is fraught with complications. To carry out the procedure, coarse salt is heated in a frying pan, wrapped in gauze cloth and applied to the affected areas.
- Steam inhalation. Decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, eucalyptus, sage) are used as solutions.
Before starting therapy, it is necessary to check with the attending physician whether these methods can be used. Sinusitis is a dangerous disease that potentially carries a risk to the health and life of the patient.
Video
We recommend watching a video on the topic of the article.

Yulia Evtekhova Therapist About the author
Education: Dnepropetrovsk State Medical Academy.
Work experience: Nurse of the Rheumatology Department of Dnepropetrovsk City Hospital No. 11.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.