- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Brain tomography

Brain tomography is an irreplaceable way to diagnose structural changes in the brain and its vessels.
There are various methods of brain tomography, differing in the results obtained and affecting the human body in different ways.
Computed tomography of the brain
Computed tomography allows you to conduct a layer-by-layer analysis of the brain: to examine it in numerous sections of a couple of millimeters.
Radiation brain tomography
Brain imaging can be done using X-rays - the patient's head is shined with X-rays. The output is a black-and-white image showing tumors, the consequences of trauma, stroke and other pathological processes. The method is considered quite informative, but unsafe due to the fact that the patient has to be exposed to significant radiation.
Magnetic resonance imaging of cerebral vessels
A complex, but very accurate diagnostic method is considered to be magnetic resonance imaging of the vessels of the brain. To obtain an image, the effect of magnetic resonance of hydrogen atoms is used. With this brain tomography, you can identify multiple sclerosis, inflammation and vascular disorders, obtain thin sections of the brain and examine various areas of the blood supply in a three-dimensional image. Tomography of the cerebral vessels reveals circulatory pathologies in the early stages. This method is considered safe, it can be used to scan the brain and the child. Only in this case, when examining infants, they are given anesthesia and fed two hours before the tomography.

It is advisable to prescribe a brain tomography for a preschool, school-age child in the morning. On the eve of the procedure, it is recommended to put the child to bed later than usual - so that he is sleepy and, accordingly, sedentary and calm during the examination.
A tomography of the child's brain is performed under the supervision of a doctor and an anesthesiologist (if anesthesia was performed).
The only contraindication to the use of the method is the patient's use of pacemakers - the magnetic field negatively affects their work. A similar tomography of the brain is prescribed for the patient's complaints of tinnitus, frequent dizziness and headaches, with vertebrobasilar insufficiency, vegetative-vascular dystonia, vascular cerebral ischemia, after a stroke.
Positron Emission Tomography
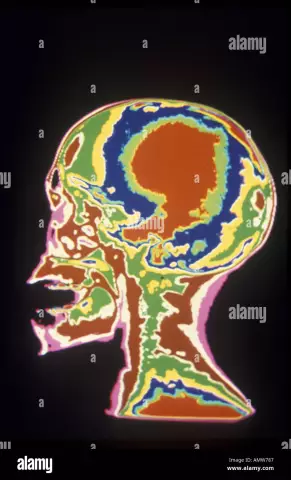
The brain can be examined in great detail using positron emission tomography (PET), based on the use of radiopharmaceuticals - chemical compounds specially labeled with radionuclides.
The result of the examination is a color image on which you can see the existing pathologies that differ in color from healthy areas and find out their exact coordinates. This method of brain tomography is effective for suspected vascular abnormalities and inflammation in the brain; it can show even small tumors (from 1 cm) that do not cause clinical manifestations. With the help of PET, ischemic disorders, Alzheimer's disease, epilepsy are determined, and the consequences of trauma are learned.
PET differs from other types of tomography in that it is used not to study the anatomy of organs and tissues, but to assess their functionality. For example, if computed tomography displays the localization of a tumor in the brain, then PET makes it possible to assess its growth. Quite often, these two tomography methods are combined for advanced analysis of the patient's condition.
It is impossible to carry out positron emission tomography for pregnant and lactating women, as well as for patients in serious condition - because of the need to remain motionless for a long time.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.