- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Spine tomography

Spine tomography - a detailed scan and examination of the spine.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are performed.
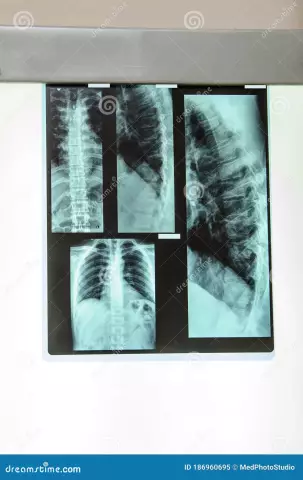
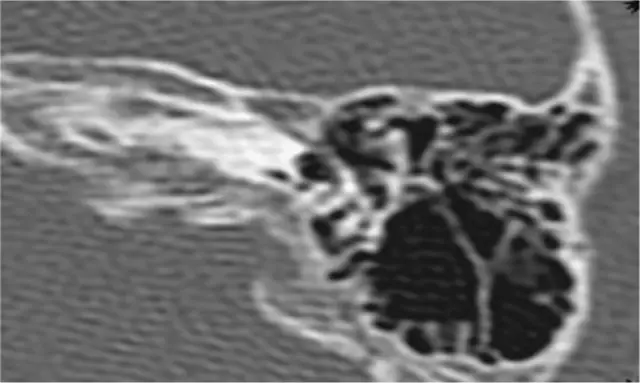
Computed tomography of the spine
Computed tomography data is obtained by irradiating the spine with X-rays and then digitizing the data obtained.
While preparing for the examination, the patient refrains from food - it is impossible to eat 4 hours before the tomography of the spine. Immediately before the tomography, you must remove metal objects (glasses, jewelry, dentures, etc.). Those patients who are afraid of confined spaces are advised to take a sedative before the examination. Pain relievers can be taken for severe back pain.
During spinal tomography, the scanner of the tomograph moves around the patient and takes pictures in the desired angles.
After the first series of images is taken, the patient is injected with contrast and the reaction is observed for half an hour. If itching, a rash, or breathing problems appear, the spine CT scan is not continued. If the contrast did not cause allergies, a second series of images is taken.
The result of the examination is the images (tomograms) in which the vertebrae are marked in white, soft tissues - in gray and cerebrospinal fluid - in black. In addition, fabrics of different density also differ in color.
The doctor recommends making a tomography of the spine to identify the causes of chronic and acute back pain, assess the condition of the spine before and after surgery, diagnose cancer and metastases in the intervertebral discs.
Spine magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging is considered to be safer for health. does not imply radiation: the operation of the MRI scanner is based on the principle of nuclear magnetic resonance.

MRI is considered to be the most accurate, perfect and sensitive method for examining the spine.
The doctor considers it necessary to make a tomography of the spine using the method of magnetic resonance to assess the condition of the spine as a whole, to identify diseases of the vertebral tissues, postoperative changes in the spine, the condition of intervertebral discs, inflammation and pinching of nerves, spinal infections, the cause of back pain, tumors in the spinal cord or spine, to determine the date of the operation on the spine.
The patient is placed in a capsule for examination, an electromagnetic field arises in it, and under its action, molecules in the human body are located, as well as electromagnetic waves. After that, they begin scanning the spine using radio waves. Spine tomography lasts no more than 20 minutes.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine is significantly superior to computed tomography, because with its help, you can get more detailed information: the spine is viewed in several planes and soft tissues are better visualized.
Tomography of the cervical and lumbar spine
Indispensable is the magnetic resonance diagnostic method when examining the cervical and lumbosacral regions. These areas are most susceptible to the appearance of various defects and they account for most of the examinations of the spine.
Now MRI tomography of the cervical spine, as well as tomography of the lumbar spine are in the first place in comparison with computed tomography, X-ray.
Tomography of the cervical spine is prescribed for osteochondrosis, hernia and disc protrusion, stenosis of the spinal canal, metastases of cells at the level of the cervical spine, injuries, anomalies in the development of the cervical spine (syndrome of additional cervical ribs, short neck).
MRI tomography of the lumbar spine is prescribed by the doctor for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, hernia and protrusion, tumor metastases, hemangiomas in the vertebrae, epidural space, spinal cord, for spinal stenosis, injuries.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.