- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
X-ray
What is X-ray

Radiography is a study of internal organs and systems of the human body by projection onto special paper or film using X-rays. X-ray is the first medical imaging method that made it possible to obtain an image of tissues and organs and examine them during a person's life. This diagnostic method was discovered in 1895, when the German physicist Wilhelm Konrad Roentgen registered the property of X-rays to darken a photographic plate.
Due to the fact that radiography involves the study of three-dimensional objects that are depicted flat on an X-ray film, it is necessary to take pictures in at least two projections in order to detect the localization of the pathological focus.
The advantages of radiography include the following:
- ease of implementation and wide availability;
- lack of special training for most studies;
- relatively low cost, except for studies with digital results;
- lack of operator dependence, which allows using the obtained data for consultation with various specialists.
Despite its widespread use, radiography has its drawbacks:
- the image is “frozen”, which complicates the assessment of organ function;
- harmful effects of ionizing radiation on the studied organism;
- low information content in comparison with modern tomographic methods, which is explained by the projection layering of anatomical structures in the X-ray image;
- the need to use contrast agents for soft tissue radiography.
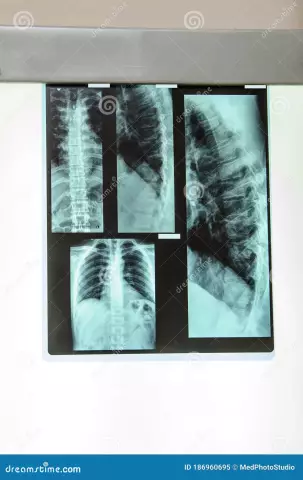
Chest x-ray
This diagnostic method allows you to examine the lymph nodes, blood vessels, respiratory tract, lungs, heart. Usually a chest X-ray involves two pictures, from the side of the chest and from the back, however, in the case of a serious condition of the patient, one picture is acceptable. No special preparation is required prior to this study, however, due to the negative effects of radiation on the fetus, X-rays are not recommended during pregnancy.
Chest X-ray is prescribed in the following cases:
- to determine the cause of cough, shortness of breath, or chest pain;
- with cardiac problems such as heart failure or an enlarged heart;
- for the diagnosis of lung cancer, pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cystic fibrosis, pneumothorax;
- to identify fractured ribs, lung damage, and problems causing pulmonary edema;
- for the purpose of identifying foreign objects in the lungs, airways and stomach.
Spine X-ray
The images obtained as a result of X-ray of the spine make it possible to determine the structure and density of bone tissue, displacement of the vertebrae, the presence of erosion, to reveal the unevenness of the contours and areas of thinning or thickening of the cortical layer of bones. This study is advisable to carry out in the following cases:
- for the diagnosis of deformity, subluxation, fractures and displacement of the vertebrae;
- in order to identify degenerative changes in the spine, infectious diseases and congenital malformations;
- to assess the state of the spine in metabolic disorders and arthritis;
- in order to identify lesions of the intervertebral discs.
X-ray of the spine does not require any special preparation, it is only necessary to strictly follow the doctor's instructions during the examination, taking the necessary position on the X-ray table and holding your breath at a certain moment.
Radiography of the lungs

A doctor may order a chest x-ray if the patient has symptoms such as hemoptysis, dry cough, general weakness, fever, weight loss, or pain in the lungs or back. This test can diagnose tuberculosis, pneumonia, tumors or fungal diseases of the lungs, as well as identify foreign bodies.
As a rule, lung radiography involves taking two images - using anterior and lateral radiographs. During this study, small children should be in a supine position, and the doctor, when assessing the X-ray, should take into account the altered proportions and characteristics of the blood supply to the lungs when a person is in a horizontal position on his back. Radiography of the lungs does not imply any special preparation.
X-ray of joints
This diagnostic method is usually used for chronic or protracted arthritis, as well as for suspected deforming osteoarthritis. In other rheumatic diseases, in most cases, X-rays of the joints reveal symptoms much later than laboratory studies or observation of the general clinical picture. However, X-rays are still needed to compare the results of further studies with the initial data.
In the case of a study of symmetrical joints, an X-ray is taken in frontal and lateral projections, and in the diagnosis of diseases of the shoulder or hip joints, another additional projection is required - oblique.
To detect the disease, the X-ray data of the joints are analyzed in the following order:
- the outline of the joint space - its narrowing indicates the initial stage of rheumatoid arthritis;
- articular ends of bones - their bone structure, ratio, shape, size;
- condition of periarticular soft tissues;
- the contours of the cortical layer.
When assessing the radiography of the joints, the clinical picture, the duration of the disease and the age of the patient are taken into account.
Skull X-ray
Surprisingly, this method is not very informative in diagnosing craniocerebral injuries, but at the same time, X-ray of the skull is advisable in the following cases:
- in order to identify fractures of the skull;
- for the diagnosis of a pituitary tumor;
- when detecting congenital malformations;
- for the diagnosis of certain metabolic and endocrine diseases.
A doctor can send a skull x-ray if there are symptoms such as loss of consciousness, dizziness, headaches, hormonal imbalance.
As a rule, this study is performed in five projections - left and right lateral, anteroposterior, anterior anterior and axial. X-ray of the skull does not imply any special preparations, the only requirement is the absence of any metal objects (jewelry, dentures, glasses) in the irradiation area.
In addition to the listed types of X-ray, the stomach and duodenum, gallbladder and biliary tract, large intestine, various parts of the peripheral skeleton, abdominal cavity, uterine cavity and permeability of the fallopian tubes, as well as teeth can be examined in the same way.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.