- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Removal of polyps in the stomach: types of operations, postoperative period
The content of the article:
-
Endoscopic polypectomy
- Indications for endoscopic polypectomy
- Features of the procedure
- Contraindications
-
Open surgery
Possible consequences
-
Postoperative period
- Diet
- Lifestyle
- Video
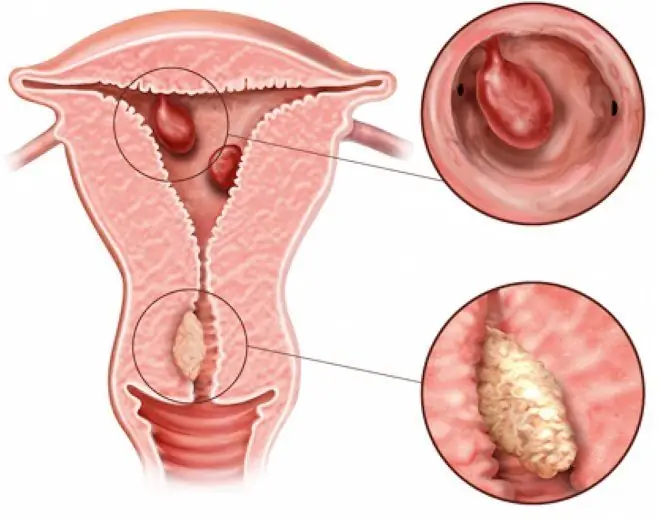
Removal of a polyp in the stomach is indicated if the formation reaches a large size and there is a risk of its degeneration into a malignant form. In other cases, expectant tactics and conservative treatment are possible.

Removal of a polyp in the stomach is necessary in cases where it reaches a large size
A polyp is a benign neoplasm that attaches to the inner wall of an organ and is formed from epithelial tissue.
The reasons for the appearance of such formations are not fully understood, but infectious diseases, malnutrition or a genetic predisposition can provoke the appearance of a polyp. It is also noticed that the pathology is more common in heavy smokers and in the elderly.
In general practice, there are two types of stomach polyps:
| Formation type | Characteristic |
| Adenomatous | Appear due to the degeneration of glandular cells. If their size is more than 2 cm, then in 50% of cases they become malignant. |
| Hyperplastic | The cause of their occurrence is hyperplasia of the epithelial cells of the stomach. These formations turn into a malignant form very rarely. |
At the initial stage, the disease is asymptomatic, but if the growth is large, a person may have:
- dyspeptic symptoms (nausea, vomiting, bloating);
- bleeding;
- stomach ache.
Endoscopic polypectomy
Indications for endoscopic polypectomy
The indication for the procedure is:
- the size of the build-up is more than 5 mm in diameter;
- the patient has symptoms of the disease;
- lack of effect from drug treatment;
- rapid growth of education.

Most often, a metal loop is used to remove the formation.
If the size of the polyps does not exceed 2 cm and they are located on a pronounced thin leg or narrow base, the procedure is performed on an outpatient basis. Usually, up to 7 polyps are removed at one time. Removing more masses takes a long time and also increases the risk of bleeding.
Difficulties arise if the tumor is located on a wide base, then to prevent the formation of extensive zones of necrosis, it is removed in parts. In addition, it helps to prevent perforation of the stomach walls or bleeding that develops after the scab begins to reject.
Features of the procedure
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. An endoscope equipped with a small camera is inserted into the stomach cavity, which transmits an image to a screen. Then a metal loop is passed through the manipulation channel. It is thrown over the base of the polyp and squeezed.

The operation is performed using an endoscope that transmits an image to the screen
At the same time, a diathermic current is supplied, which leads to necrosis of the formation and cauterization of the growth vessels. At the next stage, the doctor examines the area of the mucous membrane and removes the material outside.
It is also possible to remove formations with a laser. The instrument is inserted into the endoscope and the polyp is evaporated layer by layer. After that, the vessels are sealed, which prevents hemorrhage.
The resulting material is sent for histological examination. The patient can go home on the same day. The exceptions are elderly people with a large number of concomitant diseases or patients who are scheduled to have another endoscopy session.
Contraindications
Contraindication for such an operation is:
- general serious condition of the patient;
- the presence of multiple formations;
- diseases in which blood clotting is impaired;
- long-term use of anticoagulants;
- the patient has a pacemaker;
- the size of the growth is less than 4 mm and more than 3 cm.
Open surgery
If the size of the neoplasm reaches 3 cm or more, it is located on a wide base or there is a suspicion that the tumor is malignant, an abdominal operation is performed. Also, an indication for surgical polypectomy is several solitary polyps, which are located at a short distance from each other.
Attention! Photo of shocking content.
Click on the link to view.
Initially, the patient is put under general anesthesia. Then the tissues are dissected and the lesions are removed with a scalpel. Materials must be sent for histological examination. After that, the tissues are sutured layer by layer, and the patient is removed from anesthesia.
Neoplasms complicated by necrosis, with a pinched leg or located within the pyloric region and provoking obstruction, are removed along with part of the stomach. Also, resection is carried out if the tumor is malignant.

Most often resection is performed according to Billboard I or Billboard II
In this case, part or the whole of the antrum is removed. There are many options for the operation, but the most famous methods include resection according to Billboard I or Billboard II (the rest of the organ is connected to the duodenum end to end or lateral parts).
Possible consequences
The complications of such an operation include:
| Complication | Description |
| Dumping Syndrome | It consists in the accelerated movement of food, mainly carbohydrate, from the stomach to the intestines without proper digestion. It manifests itself as attacks of general weakness during meals or during the first 15-20 minutes after it. It begins with the appearance of a feeling of fullness in the epigastrium and may be accompanied by drowsiness, dizziness, tinnitus |
| Metabolic disease | The patient with a normal diet dramatically loses weight |
| Stump cancer | This is one of the most serious complications when a patient develops cancer of the rest of the stomach. |
Postoperative period
Diet
Complete regeneration of the gastric mucosa occurs within 10-40 days. During this entire period, a person must adhere to a special diet.

In the postoperative period, diet must be followed
Foods that can cause excessive production of hydrochloric acid are excluded from the diet: spicy, sour and spicy foods. It is necessary to limit the salt intake as much as possible to 10-12 g per day.
Do not eat fatty and fried foods, as well as those containing stringy meat, animal skin or cartilage. Dishes are steamed or boiled. Food is chopped and cooled or heated to a comfortable temperature.
Oils (olive, flaxseed, sunflower, corn) help to speed up the regeneration of the mucous membrane, while they should not be overcooked.
Lifestyle
In order to avoid complications after surgery, the patient is recommended for a month (and after abdominal surgery - within 2-3 months):
- exclude visiting a bath, sauna, you should not take a bath;
- avoid physical activity;
- stop drinking alcoholic and carbonated drinks;
- eat properly.
Do I need to remove a stomach polyp? In order to get an answer to this question, you need to consult your doctor. If the polyp begins to grow rapidly or there is a suspicion that it is degenerating into a malignant tumor, the operation must definitely be done.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.