- Author Rachel Wainwright [email protected].
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Sigmoid colon polyp: causes, symptoms, removal
The content of the article:
- Causes of occurrence
- Types of polyps
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
-
Treatment
- Choosing a method for removing a polyp in the sigmoid colon
- Removal of multiple polyps
- Histological examination
- Forecast
- Video
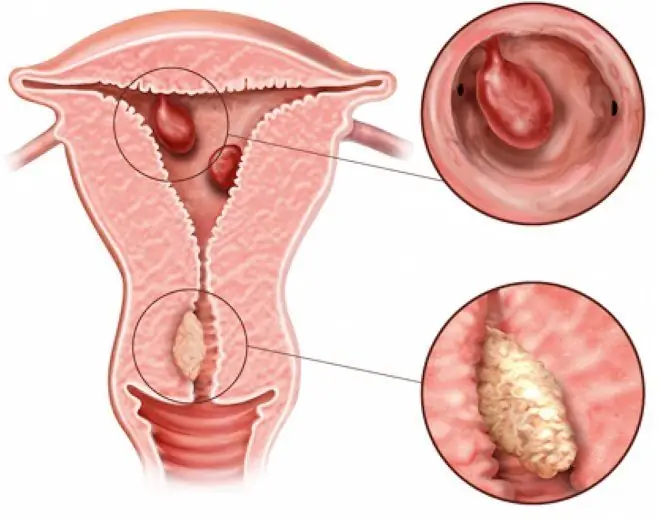
The polyp of the sigmoid colon is formed as a result of abnormal proliferation of tissues of the mucous membrane of this part of the large intestine.

Polyps can be localized anywhere in the intestine, including the sigmoid colon
The growths are benign tumor-like neoplasms that are attached to the wall of the organ with a thin leg or with its wide base. They differ in composition, shape and size. The development of pathology is usually asymptomatic, but it may be accompanied by defecation disorders, the appearance of pathological impurities in the feces and pain in the abdomen.
Large tumors can lead to intestinal obstruction and be accompanied by obstruction. It is important to take into account that in the absence of timely therapy, there is a risk of degeneration of benign polyps into malignant ones.
If there is a suspicion of a colon disease, the patient is referred for a consultation with a proctologist. The doctor makes the diagnosis based on digital examination, biopsy, rectosigmoscopy and irrigoscopy. Removal of the build-up occurs through surgical intervention.
Causes of occurrence
The triggering mechanism for the development of the disease has not been reliably determined. It is assumed that the appearance of neoplasms is promoted by chronic inflammation of the sigmoid mucosa, which can lead to:
- trauma to the mucous membrane with solid feces;
- frequent constipation;
- acute infectious pathologies;
- eating foods that adversely affect the intestinal walls.

The development of pathology is associated with poor nutrition.
In general, the appearance of these factors is associated with improper nutrition, when refined dishes, semi-finished products and easily digestible animal fats and not enough vegetable fiber prevail in the human diet. The structure of the contents in the left intestine is more dense than in the right.
In the sigmoid colon there are several bends that can be injured when stool moves to the rectum. Because of this, this section is at a greater risk of tumor formation than other areas. And this risk increases significantly with improper nutrition.
There is also a theory that neoplasms in any parts of the intestine may be the result of violations of the formation of the walls of the organ at the stage of intrauterine development.
Types of polyps
Depending on the histological structure, the following types of growths are distinguished:
| View | Characteristic |
|
Adenomatous (glandular) |
Widespread and diagnosed in 50% of patients. Outwardly, they resemble an adenoma, have reddish or pinkish nodes. Reach in sizes from 2 to 3 cm |
| Villous | Lobular neoplasms, the surface of which contains villi. They are prone to manifestations, as well as bleeding, since they contain branched networks of capillaries. Much more often other types of polyps are transformed into malignant tumors. Their growth dramatically increases the risk of malignancy. |
| Glandular villous | They are a transitional form between glandular and villous outgrowths, can have the properties of both groups at the same time |
| Hyperplastic | They contain epithelium in their composition, reach a size of no more than 0.5 cm. Usually, chronic inflammatory processes of the intestinal mucosa contribute to their appearance. Hyperplastic polyps of the sigmoid colon can transform into any other type of formations |
| Juvenile | These neoplasms are detected in children and adolescents. They are quite large in size (5 cm or more), but do not lead to the proliferation of the epithelium and cellular atypia. In extremely rare cases, their transformation into malignant tumors is recorded. |
Symptoms
The disease is usually not accompanied by severe manifestations. Sometimes patients complain of pain in the left side of the abdomen, diarrhea, constipation and other stool disorders. When a damaged polyp begins to bleed, blood may be present in the stool.
Attention! Photo of shocking content.
Click on the link to view.
With the villous type of formations, a large amount of mucus is produced, which is also noted in the feces in the form of impurities. Recurrent bleeding from multiple large growths can cause anemia. Prolonged production of a large volume of mucus can lead to disorders of water-salt metabolism.
One of the frequent occurrences in large neoplasms of the sigmoid colon, blocking the intestinal lumen, is intestinal obstruction. At the same time, patients complain of cramping pains in the left abdomen and ileal region, abdominal asymmetry, bloating, nausea, vomiting, difficulty with the passage of feces and gases.
Diagnostics
Based on the patient's complaints and data obtained during additional studies, the proctologist makes an accurate diagnosis. First, he palpates the abdomen, during which he notes the soreness of his left side. After that, a digital rectal examination is performed, which, when the formation is low, allows it to be felt.

To clarify the diagnosis, a colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy is performed
From laboratory studies, an analysis of feces for occult blood is recommended. So, with the villous type of tumors, it is likely to show a positive result, and in cases of single adenomatous tumors - negative.
Polyps larger than 1 cm are easily detected during an irrigoscopy. Smaller outgrowths can only be detected by endoscopic techniques - colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy. The first is carried out if there are suspicions of pathological processes not only in the sigmoid colon, but also in other parts of the large intestine.

Both methods provide the ability to accurately determine the number of tumors, their attachment site, size and composition. During the procedure, the doctor receives tissue samples, which are later used for histological examination. This allows you to confirm or deny the malignant nature of the formations.
Treatment
The only way to treat pathology is surgery, during which the detected neoplasms are removed. It should be borne in mind that the use of traditional medicine is ineffective and can aggravate the severity of the pathology.
The following operations may be recommended to the patient, depending on the cause of the formation, type, diameter and number of growths:
- endoscopic polypectomy;
- laparotomy;
- resection of the affected intestine with the connection of the remaining sections.
Removal is carried out in a planned manner, after the preparation and passage of all necessary examinations by the patient.
Choosing a method for removing a polyp in the sigmoid colon
Endoscopic polypectomy is performed in a hospital or on an outpatient basis, while traditional surgical interventions are performed exclusively in specialized surgical departments.

Endoscopic polypectomy is performed in uncomplicated cases
Polypectomy can be recommended only for small tumors that do not show signs of malignancy. By means of a special loop, the neoplasm is excised together with the leg. The same tool allows you to perform instant electrocoagulation of bleeding vessels.
Among the possible negative consequences of such an operation are bleeding, colon perforation.
Taking into account the possible complications, for the excision of large outgrowths, they resort to traditional surgical techniques, which are performed under general anesthesia. Through an incision in the intestinal wall, the surgeon resects the neoplasms together with the leg. After that, the intestine is sutured and sutures are applied to the anterior abdominal wall.
Removal of multiple polyps
If the patient is diagnosed with multiple or complicated formations in the lumen of the sigmoid colon, removal of this section of the large intestine may be recommended.

To remove multiple polyps, abdominal surgery is indicated
Abdominal surgery is performed under general anesthesia, after its completion, bed rest is prescribed, taking painkillers and antibacterial drugs, as well as adhering to a special diet.
Histological examination
Tumors obtained in the course of any surgical intervention must be sent for histology. If it confirms the presence of signs of malignancy, the patient is referred for further diagnostic examination to an oncologist.

The removed tissues are sent to study the structure
The doctor determines how widespread the oncological process is in the large intestine, whether there are regional and distant metastases. After passing all the necessary examinations, an extended surgical intervention is shown so that the pathological processes do not begin to spread to other parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
Forecast
The most favorable prognosis is given for growths in which signs of malignancy were not found. After resection, patients in such cases are shown regular observation by a proctologist.
Patients with adenomatous type of tumors after surgery undergo endoscopic examinations, first once every 6 months, then once a year. With villous neoplasms in the first year, colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy is performed quarterly, then the procedures are performed annually.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.