- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Polyp of the cervical canal: causes of appearance, symptoms, treatment
The content of the article:
- Types of pathology
- Causes of cervical canal polyps
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
-
Treatment
- Surgical excision
- Diathermocoagulation
- Laser polypectomy
- Video
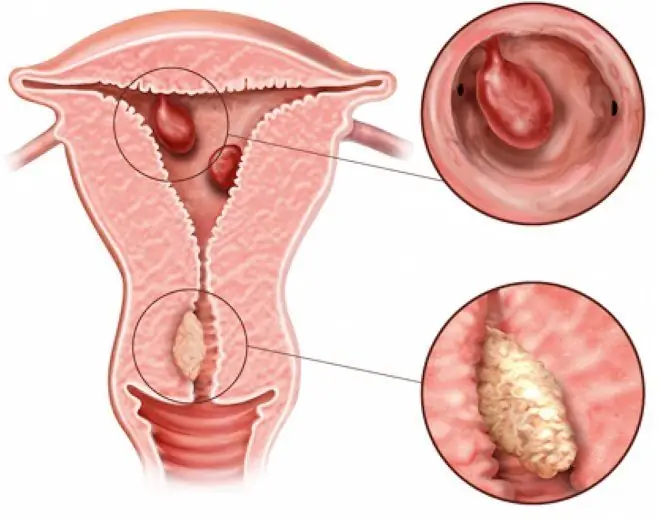
A polyp of the cervical canal (cervical polyp) is a pathology in which the mucous membrane of the cervical canal grows into its lumen, forming outgrowths on a thin or wide leg.

With a polyp of the cervical canal, the mucous membrane grows into the lumen of the cervix
The neoplasm is benign, but in about 1.5% of cases, without timely treatment, it can degenerate into a malignant tumor. In the central part or base of true cervical polyps, there are blood vessels that feed them.
Among all benign formations of the cervix, polyps occupy the first place and occur in about 4% of cases. Their size can reach 4 mm in diameter, they can be both single and multiple.
Most often, these formations are diagnosed in women aged 45 to 50 years. They can be located in other organs (nose, stomach, colon).
Types of pathology
There are the following types of growth of the glandular tissue of the cervical canal:
| View | Description |
| Fibrous | The growths are formed from the connective tissue of the endometrium and are more common in women over 40. There is a risk of their degeneration into malignant tumors |
| Mucous | Formed from columnar epithelium and can reach large sizes (up to 1.5 cm). Such neoplasms are more often observed in women of reproductive age and rarely degenerate into malignant ones. Relapses after treatment of this type of polyps are not observed |
| Glandular fibrous | The growths are formed from connective tissue and glandular cells of the endometrium and can be up to 2.5 cm in diameter. After removal of the glandular fibrous polyps of the cervical canal, a woman should take hormonal contraceptives for six months |
| Adenomatous | Neoplasms are quite dangerous, since they can grow up to 4 cm and often degenerate into malignant, therefore, after their removal, the doctor may prescribe chemotherapy |
Causes of cervical canal polyps
It is still not known exactly what leads to the occurrence of polyps of the cervical canal. Predisposing factors include:
| The reasons | Description |
| Hormonal disorders | As a result of ovarian dysfunction in a woman's body, a large amount of estrogen is produced and the level of progesterone decreases. This factor causes changes in the mucous layer of the cervix, which further leads to the formation of growths |
| Chronic infectious diseases (endometritis, adnexitis, cervicitis, papillomas) | These diseases affect the functioning of the glands, the integrity of the mucous membranes and the rate of regeneration, which is the cause of the formation of polyps. |
| Injury to the cervix | Often during childbirth, abortion, curettage, or surgery, the lining of the cervix is damaged. In this case, infections can join, which significantly affect tissue regeneration and the formation of neoplasms. |
Symptoms
There are no specific symptoms that would indicate the presence of a polyp in the cervical region.
Symptoms that suggest the presence of endocervical neoplasms:
- spotting after intercourse. They can be caused by mechanical damage to the neoplasm during contact;
- spotting in the middle of the cycle. Most often observed with ulceration of the growth;
- spotting during menopause. An alarming symptom that may indicate the degeneration of the formation into a malignant tumor;
- purulent or serous-purulent discharge. Occur if the patient has chronic infectious diseases;
- painful sensations during intercourse. May occur when a photo of a build-up is injured;
- pain in the lower abdomen or lower back. This symptom occurs if the formation is large;
- violation of the menstrual cycle. In women with pathology, menstrual bleeding is profuse and lasts more than a week. This is due to excess estrogen and endometrial thickening.

One of the symptoms of pathology is pain in the lower abdomen or in the lumbar region.
Also, endocervical polyps can cause infertility. Located at the entrance to the uterus, they prevent the penetration of sperm, as a result of which pregnancy does not occur. Also, changes in hormonal levels can lead to infertility.
Diagnostics
The doctor can diagnose a polyp of the cervical canal during a gynecological examination using a speculum, these neoplasms are quite noticeable, since they protrude outward from the cervix. Additionally, an ultrasound examination (ultrasound) is prescribed, which allows you to identify neoplasms in the uterine cavity (if any).
Colposcopy is performed to clarify the diagnosis. Using a special device (similar to a microscope), the doctor examines the cervix, noting changes. During the procedure, a small piece of tissue is taken for a biopsy (in-depth analysis).

Colpo or hysteroscopy can be done to confirm the diagnosis.
A hysteroscopy may be done to thoroughly examine the uterine cavity and cervical canal. During this procedure, a micro-video camera is inserted through the vagina, which transmits the image to the screen, if necessary, you can take a photo.
Before the operation, a woman may be assigned the following tests:
- vaginal smear (for flora);
- diagnostics of PCR (polymerase chain reaction, allows you to identify hidden infections);
- general analysis of blood and urine;
- oncocytology.
Treatment
Do I need to remove a polyp of the cervical canal? Yes, this must be done without fail, since later it can cause cancer. After the removal procedure, the woman is prescribed:
- anti-inflammatory drugs: used in the presence of chronic infections;
- oral contraceptives: to correct hormonal levels.

The choice of polyp removal method is determined individually.
Usually, a single build-up is removed by grabbing it with a special clamp and performing rotational movements. The procedure is quite painful, therefore, anesthesia is performed before starting. The vessels that feed the neoplasm are twisted during removal, so they do not bleed.
At the next stage, the bed is scraped out with a curette (to avoid re-formation of a build-up) and treated with an antiseptic.
Also, after removing the build-up, the bed can be processed by the following method:
- moxibustion with drugs (for example, Solkovagin);
- freezing with liquid nitrogen (cryodestruction);
- moxibustion using high frequency current (electrocoagulation).
Surgical excision
If the neoplasm reaches a large size, surgical excision is performed. The operation is often performed using a hysteroscope. The device is inserted into the vagina, and the built-in video camera displays data on the screen, which allows the doctor to carry out precise manipulations. Depending on the size of the growths, twisting or excision of the formations is possible.
The operation is performed under anesthesia no later than the tenth day after the end of menstruation. Contraindication to its implementation is:
- the presence of malignant tumors;
- stenosis of the cervix;
- pregnancy;
- infectious inflammatory diseases.
Diathermocoagulation
Another method that allows you to get rid of the formation is diathermocoagulation. With the help of a special electric knife, through which a high-frequency current passes, the polyp is excised. A crust appears at the site of removal, which protects the wound from infection and prevents the development of bleeding.
Because there is a high likelihood of scarring, which can cause complications during childbirth, this method is not used to treat nulliparous women.
The process is quite painful, and healing can take up to two months. A contraindication to diathermocoagulation is an infectious-inflammatory process or a blood clotting disorder.
Laser polypectomy
To remove small formations, laser polypectomy is performed. In this case, a laser beam is used instead of a scalpel. In classic polypectomy, an electrical loop is used that encloses the growth.
In other cases, medications can only stop tissue overgrowth and reduce the risk of malignancy.
After removing the build-up, a woman must adhere to the following recommendations:
- refrain from sexual intercourse for a month;
- refuse to do douching;
- avoid strenuous physical activity for two weeks.
If a woman has symptoms that indicate that she is growing a neoplasm in the cervical canal, she should seek advice from a gynecologist.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.