- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Removal of the cyst of the maxillary sinus
The content of the article:
- Indications for surgery
- Contraindications to surgery
- Features of the classical sinusitis
- Endoscopic surgery
- Features of laser cyst removal
- Postoperative period
- Possible postoperative complications
- What is a maxillary sinus cyst
- Video
Removal of the maxillary sinus cyst is not required in all cases. Small cysts are sometimes able to resolve on their own, but even if this does not happen, and the neoplasm is not prone to growth and does not have any manifestations, treatment may not be required. However, in the case when treatment is necessary, it can only be surgical, conservative methods are ineffective. The doctor establishes the examination procedure and the scope of the surgical intervention.

Treatment of a cyst of the maxillary sinus is carried out by a surgical method
Indications for surgery
The operation to remove the cyst in the nasal sinus is carried out according to strict indications (in their absence or asymptomatic course of the process, the operation is not indicated):
- Persistent nasal congestion that cannot be relieved by typical methods.
- Severe headaches.
- Visual impairment (double vision, loss of visual fields).
- Swelling or severe deformity of the face. It occurs extremely rarely, only with large sizes of cystic formation.
- Suppurative process. When a secondary infection is attached, typical symptoms of intoxication, pain, a feeling of fullness in the sinus area arise.
- Size - more than 1.5 cm in diameter (indication for removal in English literature).
Contraindications to surgery
Surgical removal of a cystic neoplasm is contraindicated in the following cases:
- acute infectious processes in the body;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system in the stage of decompensation;
- type I diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation;
- violation of blood clotting;
- status epilepticus;
- malignant neoplasms.
Features of the classical sinusitis
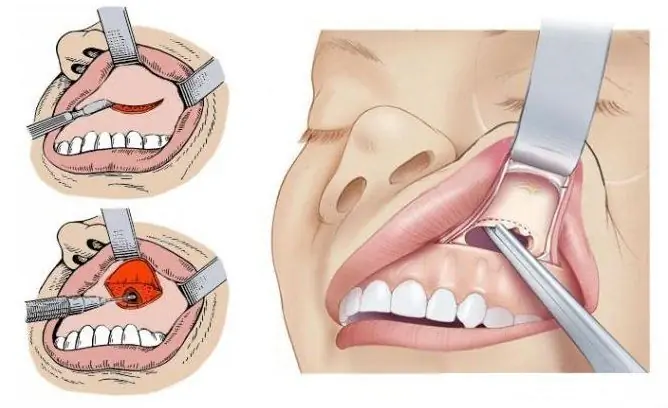
This type of intervention is one of the classic options for removing large cysts (Caldwell-Luke operation).
Anesthesia: local or general. It is better to use endotracheal anesthesia, with it the patient does not experience any discomfort.
Execution technique:
- Position - lying on your back with a bolster placed under the neck, head thrown back.
- Using a scalpel, the gum tissue is dissected in layers in the vestibule of the mouth, the incision is 1-2 cm below the transitional fold.
- The mucous membrane and periosteum are separated from the bony structures of the upper jaw.
- With the help of a chisel, trepanation of the bone is performed to expose the sinus. The hole in the bone is widened to 1.5-2 cm.
- All changed tissues and the cyst itself (granulation, fluid) are removed from the sinus.
- In the region of the medial wall of the sinus (lower nasal passage), a hole is made no more than 1 cm. Through it the sinus will be tamponed (the tampon is moistened in an iodine-containing substance). The tampon is removed after 24 hours.
- The wound is sutured in layers and tightly. Daily dressings are shown.
The operation is traumatic and requires a long healing period (3-4 weeks). Refers to radical operations, since all components of the cyst are removed (wide access ensures adequate sanitation of the cavity).
Endoscopic surgery
Endoscopic removal of the maxillary sinus cyst is a relatively new and minimally invasive treatment. It is performed using a special apparatus - an endoscope (thin conductor, flexible throughout with a video camera at the end). Two methods of introduction:
| Method | Description |
| Endonasal |
It is introduced through the nasal cavity. Technique: 1. The position of the patient is reclining in a chair, the head is slightly thrown back. 2. Local anesthesia is used (gel and infiltrative anesthesia with lidocaine). 3. The endoscope is passed along the middle or lower nasal passage. The introduction passes through the natural fistulas, if necessary, a puncture of the wall is made in a typical place. 4. After the introduction of the endoscope, visual control occurs and with the help of several more instruments, piercing, excision and removal of all membranes of the cyst are performed. 5. After that, the instruments are removed, and the sinus cavity is tamponed The operation can be performed on an outpatient basis. Has a fast postoperative period (2-3 days) and a minimum of complications. |
| Microhymorotomy (puncture through the oral cavity) |
It is performed in the area of the projection of the anterior wall of the maxillary sinus on the eve of the mouth. Execution technique: 1. The position is identical to the previous one. 2. Perform infiltration anesthesia. 3. A small (up to 0.5 cm) incision is made, with the help of a drill, dense bone structures are pierced (there is a direct access to the sinus). 4. The endoscope and other instruments are introduced through the hole. 5. All membranes and tissues of the cyst are removed, and the wound is sutured in layers. The duration of the operation is about 30 minutes. Inpatient monitoring is required for 24 hours. |
The method belongs to high-tech, its implementation requires special training (not possible in all clinics).

Endoscopic cyst removal is preferred, but not always possible
Features of laser cyst removal
The use of a laser is considered the most advanced surgical method of all. The equipment consists of a thin flexible wire at the end, which has an LED. The essence of the treatment is to cauterize the walls of the cyst using the high thermal energy of the laser.
The method has the following advantages:
- minimal blood loss;
- painlessness;
- minimum holding time (10 minutes on average);
- minimal risk of relapse.
Negative sides:
- It is not suitable for everyone, since it requires a superficial location of the cyst (directly at the walls of the sinus), with the localization of the formation somewhat deeper, the effect of treatment will not follow.
- Large neoplasms require a more radical approach to treatment (endoscopic or open method). In this case, the laser does not affect all cyst tissues (small diameter of action).
At the moment, it does not apply to universal methods of treatment, the use is permissible only with small sizes of education.
Postoperative period
The length of time a patient is in the hospital depends on the specific type of surgery. Some general provisions:
- Daily dressings with oral cavity and stitches.
- Prescribing broad-spectrum antibiotics to reduce the risk of secondary infection (Cefepim, Tsiprolet a).
- Pain relievers for the first time days after surgery to relieve pain (Drotaverin, Analgin).
During the first days, pressure bandages are used to avoid the formation of hematomas.
In the recovery period, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed to enhance regeneration and drying of tissues.
Possible postoperative complications
- Bleeding. May occur immediately at the time of surgery or in the postoperative period due to insufficient tamponade of the cavity. As a rule, they do not have high intensity and quickly stop.
- Suppuration of the sinus with the development of sinusitis. It occurs in the case of insufficient sanitation of the surgical site or insufficient processing of sutures in the postoperative period.
- Damage to nerve fibers (branches of the trigeminal nerve). In this case, the clinic will depend on the specific nerve (lowering of the corners of the lips, disruption of the work of facial muscles, paresis).
All minor postoperative complications (eyelid edema, bruising) disappear within 3-4 weeks.
Relapses of cysts are relatively rare.
What is a maxillary sinus cyst
The cyst of the paranasal (maxillary) sinuses is a thin-walled spherical formation filled with fluid and having a capsule. It is a benign neoplasm and rarely degenerates into a tumor. Depending on the nature of the liquid component, the following types of cysts are distinguished:
- mucocele (mucous contents);
- pyocele (purulent contents);
- hydrocele (serous contents).
Features of education:
- the cavity usually does not exceed 2-3 cm;
- mucocele occurs more often in the maxillary region;
- the main cause of the occurrence is infection (sinusitis), since the outflow of mucus is hampered, and it accumulates in the sinus cavity (gradually encapsulated);
- the first symptoms occur from the side of the eyes (exophthalmos, decreased vision);
- observed more often in young and middle-aged people.
To make a diagnosis, the patient is shown a consultation with an ENT and maxillofacial surgeon.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.