- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Maxillary sinus cyst
The content of the article:
- Cyst of the right maxillary sinus or left: what is it
- Cyst of the left maxillary sinus or right: the main causes
- Types of cystic formations
- The main symptoms
- Diagnostic methods
-
How to treat pathology
- Operation types
- Indications for removal of the cyst of the maxillary sinus
- Video
Cyst of the maxillary sinus (VChP, maxillary sinus) is a rare disease that occurs mainly in young people. Often, the pathology is asymptomatic, and is discovered by chance when conducting additional research for another reason. Treatment consists of surgical intervention; other therapeutic methods do not allow getting rid of the cystic formation.

The cyst of the maxillary sinus often has an odontogenic (dental) origin
Cyst of the right maxillary sinus or left: what is it
A cyst is a benign growth, which is a cavity with fluid inside. Content may be slimy, purulent, or serous.
A cyst can occur in any paranasal sinus, including the maxillary sinus. The maxillary sinus is a paired formation that is located in the region of the upper jaw body. The HPP has a natural opening through which it communicates with the nasal cavity. Its lower wall is thin, which contributes to the rapid transition of the pathological process from the roots of the teeth. The mucous membrane of the HPP contains a small number of blood vessels and nerves, and therefore the disease is often asymptomatic. Both sinuses (right or left) can be affected, but bilateral involvement is extremely rare.
The disease is more often formed at the age of 14-22 years. It practically does not occur in old and childhood.
Cyst of the left maxillary sinus or right: the main causes
There is no single reason that would lead to the appearance of a cystic formation. The main mechanism for the development of pathology is a violation of the communication of the VSP with the nasal cavity. Blockage of the fistula leads to excessive accumulation of mucus inside. The following factors can lead to obliteration of the anastomosis:
- Injury to the face and nasal mucosa. It can take years from the injury to the first symptoms, so patients do not always remember about it.
- Inflammatory processes of the nasal cavity and VChP - chronic rhinitis, sinusitis.
The reasons that lead to the formation of an odontogenic cyst of the maxillary sinus are considered separately. Such formations are always associated with dental diseases. The inflammatory process spreads to the maxillary sinus through the lower wall. The cause may be any inflammatory disease of the teeth or gums of the upper jaw (caries, periodontitis, gingivitis, osteomyelitis of the jaw bone).
Types of cystic formations
There are several types of cystic formations of the VSP - true (retention), false, odontogenic.
| Variety | Description |
| True (retention) |
Formed from the glands of the mucous membrane, the exit ducts of which are clogged. Their wall is lined with ciliated epithelium. |
| False (cyst-like) | The main difference between cyst-like formations is the absence of an epithelial lining. The reasons for their development are not fully understood; the main etiological factor is the effect of the allergen. |
| Odontogenic | Odontogenic cysts are associated with dental diseases. They are always localized at the bottom of the VSP, while other varieties can occur in any area. |
Separately, there are 3 forms of cystic formation, depending on the nature of the content:
- mucocele (mucus);
- pyocele (pus);
- hydrocele (serous contents).
The main symptoms
Clinical manifestations depend on several factors - the localization of the process, the duration of the disease, the size of the cyst, the nature of the contents, the presence of complications.
The onset of the disease is gradual, symptoms develop over the years. In the early period, the disease proceeds imperceptibly and is not accompanied by any external signs. Small cysts do not show up in any way, symptoms develop as their size increases. Relatively early signs of pathology include:
- a feeling of heaviness, which increases when the head is tilted;
- compressive pain that radiates to the teeth, eye socket, nose;
- swelling in the projection of the maxillary sinus.
With an increase in the size of the cystic formation, the asymmetry of the face gradually develops - the swelling in the region of the anterior wall increases, the eyeball shifts. All changes develop from one side (right or left). Large cysts lead to frequent headaches, difficulty in nasal breathing due to displacement of the lateral wall of the nose.
Diagnostic methods
If you suspect this pathology, you should consult a doctor - a dentist or an otolaryngologist. The doctor will listen to complaints, conduct an examination and prescribe additional tests. According to the clinical picture, one can only suspect the presence of a pathological process in the HPP projection. To clarify the diagnosis, an additional examination is necessary.
| Research method | Explanation |
| Plain radiography | Plain radiography is the most accessible diagnostic method. It is carried out in two projections (direct and lateral). Plain X-ray allows detecting changes in the VSP, but this is not enough to determine the nature and localization of pathology. |
| Contrast radiography | To clarify the location and size, contrast radiography is prescribed. The contrast agent is injected into the sinus through a natural opening, then a picture is taken. |
| Sounding | Probing makes it possible to penetrate into the sinus cavity without opening it. |
| Computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain | CT and MRI are the most informative research methods. They allow you to accurately determine the location of the cystic formation, its size and contours. |

Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are the most accurate methods for diagnosing HPP cysts
How to treat pathology
Treatment of the disease involves surgical intervention. It is impossible to get rid of cystic formation with the help of medications and folk remedies. In some cases, a radical operation is not performed, observation is prescribed, in some cases - auxiliary methods of treatment.
Operation types
There are several types of operations that are used to remove a cystic formation. Most often, endoscopic surgery and a gentle opening of the VSP through the anterior wall are prescribed.
| Operation type | Advantages and disadvantages | How is the operation going |
| Endoscopic intervention | The main advantage is the low invasiveness of the operation; dangerous complications rarely occur. The disadvantage is that not all cysts can be removed endoscopically. | Anesthesia is not required for the procedure. On the skin, incisions are not made, through a natural opening into the nasal cavity, and then a special device is inserted into the sinus and the cyst is removed. |
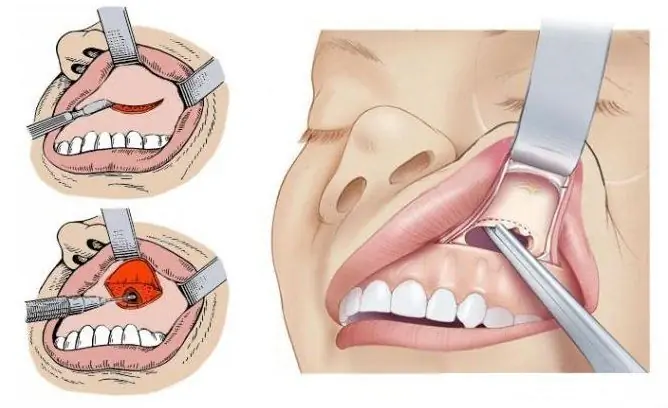
| Opening through the front wall | The main advantage is the ability to remove large formations. The disadvantages include high trauma, the need to use anesthesia. | The sinus is accessed through an incision in the anterior wall of the sinus. The cystic formation is removed, if necessary, the anastomosis is expanded. |
Indications for removal of the cyst of the maxillary sinus
Surgery is the only effective treatment. What are the indications for surgical intervention:
- the diameter of the formation is more than 1 cm;
- progressive growth;
- suppuration;
- asymmetry of the face;
- severe clinical symptoms.
If there is no indication for an operation, observation is appointed. With concomitant diseases of the oral cavity, additional treatment is indicated - tooth extraction, antibiotic therapy.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.