- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Cyst of the maxillary sinus
The content of the article:
-
Causes
- Features of the structure of the sinus
- Main reasons
-
What you need to know about pathology
- What it is
- Kinds
- What is the threat of a maxillary sinus cyst
- Symptoms of the cyst of the maxillary sinus
- Diagnostic methods
-
How to treat
- When is the operation indicated
- How is surgery performed?
- Adjunctive treatment
- Video
The cyst of the maxillary sinus is a spherical container filled with fluid. Pathology is often asymptomatic, being an accidental finding. The appearance of symptoms indicates a large size of the formation, in this case you need to contact an otolaryngologist to clarify the diagnosis. You can get rid of a cyst only by a surgical method, but not all formations can be removed.

The cyst of the maxillary sinus is removed surgically if it is prone to growth and development of complications
Causes
There is no single reason that would lead to the formation of a cyst. Its development is influenced by a number of factors at once - the structure of the sinus, the state of the mucous membrane, trauma to the nose, and inflammatory diseases.
Features of the structure of the sinus
The maxillary sinus (maxillary) is a paired formation that is located between the orbit and the upper jaw.
The mucous membrane is lined with ciliated epithelium with goblet cells that produce mucus. The presence of glands in the mucous membrane is a predisposing factor for the formation of a cyst. At the same time, the mucous membrane in this area contains few vessels and nerves, which explains the long asymptomatic course of the disease.
The maxillary sinus has 5 walls. Knowing their location is important for understanding where the pathological process can spread.
- upper - bordered by the eye socket;
- lower - thin, bordered by the upper jaw;
- posterolateral - approaches the posterior group of cells of the ethmoid labyrinth and the sphenoid sinus;
- front - thick, is part of the bones of the facial skull;
- medial - bordered by the nasal cavity.
So, the formation of a cyst can be influenced by the pathology of the orbit, upper jaw, and nasal cavity. At the same time, the inflammatory process in the maxillary sinus poses a threat to these formations, since the reverse spread of inflammation is also possible.
Main reasons
The mechanism of development of pathology is associated with blockage of the glands. Each gland has an excretory duct that opens onto the surface of the mucous membrane. If there is a blockage in the duct, mucus will not stop being produced. It does not come out to the surface of the mucous membrane, but accumulates inside the gland, leading to the formation of cystic enlargement.
For what reasons can there be a blockage of the excretory duct of the glands:
- facial trauma;
- chronic rhinitis (including allergic);
- sinusitis;
- other sinusitis.
The curvature of the nasal septum increases the risk of developing the disease when air conduction into the right or left side of the nasal cavity is disturbed.
The causes of odontogenic cysts, when pathology develops due to damage to the teeth and gums of the upper jaw, are considered separately. The cause may be caries, periodontitis, abnormal growth of the teeth of the upper jaw, osteomyelitis of the jaw bone.
What you need to know about pathology
There are several types of cysts of the maxillary sinus. They differ in the nature of the content inside, the reasons for their occurrence, the size and location. All of these factors affect the clinic and treatment of the disease.
What it is
This is a benign neoplasm, which is a cavity with fluid inside. As a rule, it occurs on one side - a cyst of the left maxillary sinus or the right one. The liquid inside can be of a different nature:
- mucus (mucocele);
- pus (piocele);
- serous fluid (hydrocele).
The size of the formation and its location can be different, this affects the variety of clinical symptoms.
A small cystic formation can resolve itself if the patency of the excretory duct of the gland is restored.
Kinds
There are three main types of this pathology. Each species has its own cause and mechanism for the development of pathology.
| Kinds | Features: |
| True (retention) | Formed from the glands of the mucous membrane when their excretory duct is blocked. Its wall is lined with ciliated epithelium. The cause may be trauma or inflammation. |
| False (cyst-like formation) | The cause of development is associated with an allergic reaction, the exact mechanism of development is not known. |
| Odontogenic | The peculiarity of this type is that the cause is always associated with the defeat of the upper jaw. Through the lower wall, the pathological process from the teeth passes to the maxillary sinus. |
What is the threat of a maxillary sinus cyst
Cystic formation may not cause any inconvenience or worsen a person's health. In some cases, it can become inflamed and suppurate, and a purulent focus in the head area always carries a serious threat. A growing cyst can lead to bone deformation and serious cosmetic and functional defect.
Symptoms of the cyst of the maxillary sinus
The severity of symptoms depends on several factors - the size and location of the formation, on how long it exists. In most cases, there are no clinical manifestations, and the person does not even suspect that he has a neoplasm. Symptoms usually appear when the cyst reaches a size of 1 cm or more. What are the symptoms of the disease:
- Discomfort, squeezing pain in the upper jaw region.
- Unpleasant sensations that intensify when tilting the head, diving into depth.
- Pain that radiates to the teeth, eye socket, nose.
- A headache that is periodic at first and then permanent.
As the size of the cystic mass increases, symptoms progress. Additional symptoms appear - swelling and asymmetry of the face, nasal congestion.
An increase in swelling in the area of the anterior wall, displacement of the eyeball in the affected half leads to a pronounced asymmetry of the face. Difficulty in nasal breathing is associated with a displacement of the lateral wall of the nose (with a large size of cystic formation).
Diagnostic methods
Symptoms are usually nonspecific, so it is impossible to make a definitive diagnosis based on the clinical picture alone. If you suspect a cyst of the maxillary sinus, you should consult an ENT doctor. He will conduct an examination, prescribe tests, and, if necessary, send him to other specialists (dentist, ophthalmologist).
Additional examination usually begins with plain radiography, if necessary, contrast radiography, probing, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) are performed.
How to treat
It is possible to get rid of the cystic formation of the maxillary sinus only with the help of an operation. Endoscopic or open surgery may be performed depending on the indication. Medication or folk remedies will not get rid of the cyst, but they can help avoid dangerous complications.
When is the operation indicated
Surgery is the only effective treatment. But the operation is prescribed not in all cases of the disease, but only if there is evidence. When to remove a cyst:
- the size of the formation exceeds 1.5 cm;
- there are signs of suppuration;
- progressive growth of education during observation;
- there are symptoms of the disease (pain, feeling of heaviness);
- pathology leads to facial asymmetry.
The decision to carry out the operation is made on an individual basis. The age of the patient and the presence of concomitant diseases are also taken into account.
How is surgery performed?
Removal of cystic formation can be carried out in two ways - open surgery, surgical intervention using endoscopic techniques.
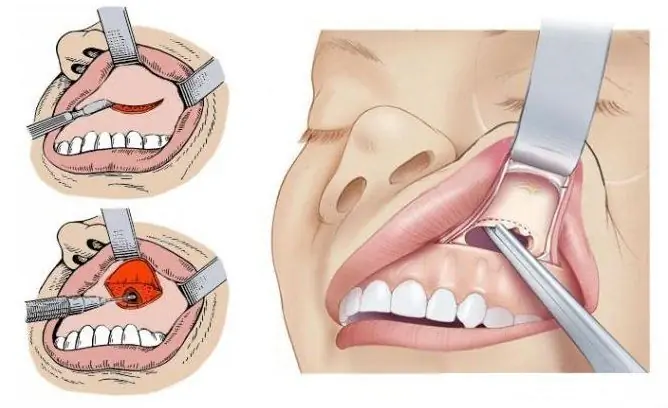
- Open surgery is a traditional but traumatic method of treatment. An incision is made under the lip, after which the anterior wall of the maxillary sinus is opened. Through this hole the cyst is removed. The disadvantages of such an operation include trauma, the need for general anesthesia, and a long recovery.
- Endoscopic surgery is a more modern method of treatment. The intervention is performed through the nose, no additional incisions are required. A special device is inserted into the nasal cavity, and then through the natural opening into the maxillary sinus. The operation is performed under local anesthesia; general anesthesia is not required. The main disadvantage is that it is impossible to remove large cystic formations. In addition, endoscopic surgery requires a special technique, so this type of treatment is not available everywhere.
Adjunctive treatment
In some cases, not only surgery is prescribed, but also conservative treatment. It is aimed at preventing complications and eliminating the causes of the development of pathology.
If there are signs of suppuration of cystic formation, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. The antibiotic is selected after puncture and determination of the sensitivity of the microbial flora. With an odontogenic cyst, the oral cavity is sanitized. The scope of treatment is determined individually (removal of carious teeth, antiseptic solutions).
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!