- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
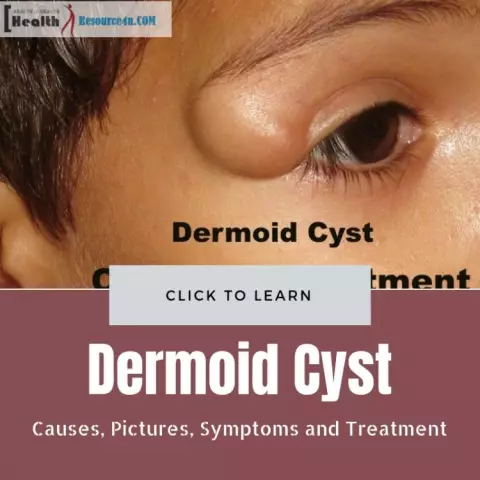
Dermoid cyst

A dermoid cyst is a benign cyst made up of the epidermis, dermis, hair, hair follicles, and sebaceous glands. If the removal of the dermoid cyst is not carried out in a timely manner, then later in 8% of patients it turns from benign into malignant. Dermoid cyst refers to fibroepithelial formations and organoid teratomas, which are composed of connective tissues that are rough on the inside and smooth on the outside.
Outside, the dermoid cyst is surrounded by an oval capsule and reaches the size of a large pea or walnut. It has a single-chamber or multi-chamber cavity, inside of which a sebaceous mass is contained with an admixture of keratinized skin scales and hair. Depending on the content, the dermoid cyst is divided into dense and soft. The symptoms of dermoid cysts are no different from the symptoms of other benign tumors, that is, they are practically absent. However, in cases of reaching a large dermoid ovarian cyst, the following symptoms are possible:
- Feeling of heaviness in the abdomen;
- Constipation;
- Lower abdominal pain;
- Disorders of urination.
Dermoid cysts grow rather slowly, but constantly and without stopping. Complications caused by a cyst can be suppuration and squamous cell carcinoma. Often, a dermoid cyst forms in areas:
- Century;
- Bridge of nose;
- Lips;
- Nasolabial folds;
- Neck;
- Nape;
- Ears;
- Buttocks and abdomen;
- Anterior mediastinum;
- Fiber of the eyes and ovaries;
- Submandibular;
- Periorbital;
- Soft tissues of the neck and mouth.
Much less often, a cyst occurs in the temporal, chewing and buccal regions.
Dermoid Cyst Causes

The cause of a dermoid cyst is an improper fusion of various body tissues during intrauterine development of the fetus. It follows that the dermoid cyst is a congenital malformation.
Dermoid cyst diagnostics
Dermoid cysts are diagnosed during a physical examination. In addition to the patient's complete medical record and physical examination, diagnostic procedures are performed to determine if the cyst is associated with other tissues, which may include:
- Computed tomography (CT) is a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses a combination of X-rays and computer technology to image a horizontal and vertical cross-section of the entire body. CT scans show detailed images of any part of the body, including bones, muscles, fat, and organs;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a diagnostic procedure that helps to obtain detailed images of organs and structures in the body.
Dermoid cyst treatment
The specific treatment for a dermoid cyst is determined by a physician based on age, general health, medical history, and stage of the disease.
Surgical removal of a dermoid cyst occurs by opening it, evacuating the contents and completely draining it. After the inflammatory process subsides, excision of the cyst walls becomes possible. The duration of the procedure is 10-15 minutes, if a child is sick, then it is carried out under anesthesia.
The process of removing a dermoid cyst occurs with minimal tissue trauma, and it is also possible to impose almost invisible cosmetic sutures (when the cyst is located on the facial area).
Untimely removal of the cyst capsule can cause the onset of relapses. If this leads to an acute inflammatory process, then urgently the dermoid cyst is opened and the abscess is drained. Radical removal of the cyst becomes possible only after the complete elimination of the active inflammatory process and wound healing.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!