- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Diathesis
The content of the article:
- Diathesis forms
- Diathesis causes and risk factors
-
Diathesis symptoms
- Exudative-catarrhal diathesis
- Lymphatic-hypoplastic diathesis
- Neuro-arthritic diathesis
- Diagnostics
- Diathesis treatment
- Possible complications and consequences
- Forecast
- Prevention
Diathesis is an anomaly of the constitution, which is accompanied by an inadequate response of the body to ordinary stimuli.
A constitution means a set of morphological and functional characteristics of an organism, which have developed on the basis of innate and acquired properties and determine the originality of the body's response to exogenous and endogenous stimuli. The human constitution has no age periodization, that is, it remains constant throughout life. The environmental factors that affect the implementation of the features of the constitution include socio-economic conditions, past illnesses, sports, etc. The constitution consists of a set of components (genotypic, phenotypic, immune, somatic, psychological constitution, etc.).

Source: zhenskij-zhurnal.com
Diathesis forms
There are three forms of diathesis:
- exudative-catarrhal (allergic) - the patient's predisposition to allergic and inflammatory reactions; occurs more often than other forms, and is usually diagnosed in children in the first years of life. It accounts for 40-70% of all diathesis in patients of this age category;
- lymphatic-hypoplastic - predisposition to allergic and infectious diseases, decreased function of the thymus, pathology of the lymph nodes; the prevalence is 10-12%;
- neuro-arthritic - predisposition to obesity, atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, increased nervous excitability, inflammatory diseases of the joints. It is the least common form of pathology and is observed in 2-3% of patients.
Exudative catarrhal diathesis can be immune and non-immune.
The immune, in turn, is divided into transient and true forms, which are caused by excessive production of IgE and a decrease in IgA, IgG, as well as the level of T-lymphocytes.
According to another classification, diathesis is divided into the following types:
- allergotopic (allergic, infectious-allergic, lymphatic);
- dysmetabolic (oxalate, uric acid, hemorrhagic, diabetic, thrombocytopathic);
- organotopic (hypertensive, cardioischemic, atherosclerotic, erosive-ulcerative, nephropathic);
- neurotopic (vegetative-dystonic, psychoasthenic).
Diathesis causes and risk factors
The mechanism of occurrence of diathesis is not fully understood. Most researchers agree that the main cause of diathesis is disorders of neuroendocrine regulation of immunological and metabolic processes, which results in inadequate body responses to routine stimuli. Diathesis in children often develops against the background of posthypoxic encephalopathy.
An important role in the mechanism of the neuro-arthritic form of diathesis is attributed to the increased content of uric acid in the blood (hyperuricemia). At the same time, an increase in the concentration of uric acid and urates in the patient's tissues and blood may be primary (gene mutations) or secondary (increased breakdown of purines and pyrimidines against the background of hemolytic diseases).
The transient form of exudative-catarrhal diathesis develops if the antigen of cow's milk enters the bloodstream, in addition, a pathological reaction may appear in response to vaccination, the use of a number of drugs, contact with household chemicals.
In this case, the antigen that enters the bloodstream causes the overproduction of IgE, after which the degranulation of mast cells occurs, the release of biologically active substances, followed by an increase in vascular permeability and the occurrence of exudative reactions. With the true form of exudative-catarrhal diathesis, IgE hyperproduction is due to a genetic predisposition.
Risk factors include:
- unfavorable course of pregnancy (infectious diseases in a pregnant woman, toxicosis, fetal hypoxia);
- bad habits of a pregnant woman;
- eating disorders during pregnancy and lactation (in particular, the use of hyperallergenic foods);
- asphyxia of the newborn;
- perinatal pathology of the central nervous system;
- increased or, conversely, low birth weight of the child;
- artificial feeding;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- chronic somatic diseases;
- early infection with human respiratory syncytial virus;
- non-compliance with the daily routine;
- poor nutrition;
- stressful situations;
- use of clothes and toys made of synthetic materials;
- irrational use of medicines;
- hereditary predisposition.
Diathesis symptoms
Diathesis symptoms vary depending on the form of pathology.
Exudative-catarrhal diathesis
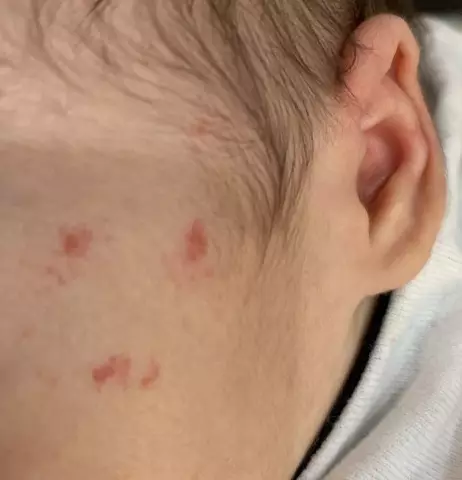
This form of diathesis is manifested by a tendency to allergic reactions, as well as reduced resistance to infectious diseases. Pathology, as a rule, manifests itself in children at the age of 3-6 months, however, the first signs of diathesis on the face can be noted in children already in the first weeks of life. In most cases, the manifestations disappear when the child reaches 1-2 years.
There are polymorphic skin rashes, hyperemia, diaper rash of large skin folds, seborrheic scales appear on the scalp (usually on the crown and crown of the head), and thickening of the skin of the cheeks (the so-called milk scab) can also be observed. In overweight children, diaper rash may be accompanied by skin maceration, pyoderma. The mucous membranes are easily traumatized, which leads to frequent diseases of the eyes and ocular tissues (conjunctivitis, blepharitis), oral cavity (gingivitis, glossitis), upper respiratory tract (sinusitis, laryngitis, rhinopharyngitis, bronchitis with an asthmatic component).
In children subject to diathesis, there is often a large body weight at birth, overweight in the future, a decrease in tissue turgor, and children's eczema. Such patients are characterized by pallor of the skin, swelling of the face, geographical language, flatulence, abdominal pain syndrome.

Source: medvoice.ru
Lymphatic-hypoplastic diathesis
This form of diathesis is characterized by persistent enlargement of the lymph nodes, a tendency to allergies and infectious diseases, and dysfunction of the adrenal cortex. Children usually have a large birth weight, disproportionate physique (elongated limbs with a relatively short trunk). They are characterized by marbled pallor of the skin, underdeveloped muscles, lethargy, fatigue, arterial hypotension. In the future, children, as a rule, are inactive, sometimes they have a delay in speech development, the distribution of adipose tissue according to the female type (on the abdomen and thighs), circulatory disorders.
Hyperplasia of the adenoids, tonsils, and thymus is often observed. Children often suffer from acute respiratory diseases with a protracted course and a pronounced exudative hypersecretory component, infectious toxicosis, which consists of fever, convulsions, vomiting, electrolyte imbalance.
Lymphatic-hypoplastic diathesis occurs by 2-3 years and, under favorable conditions, disappears by the period of puberty. In rare cases, signs of thymic-lymphatic status remain in the patient for life.

Source: myshared.ru
Neuro-arthritic diathesis
In patients of the first years of life, attention is drawn to anxiety, fearfulness, excessive excitement. Often, these children learn to speak and read early, and have a good memory. However, against the background of successful mental and intellectual development, emotional lability, headaches, hyperactivity, and attention deficit disorder are noted. A detailed clinical picture is usually formed only by school age. Pains in the back and knees, enuresis, sleep disorders, anorexia, emotional lability, stuttering, recurrent vomiting (vomit acquire the smell of acetone) appear. Skin manifestations are also characteristic, which are characterized by a variety - from urticaria and angioedema to neurodermatitis.
The low acetylating ability of the liver in patients with this form of diathesis causes the development of acetonemic syndrome. During periods of acetone crisis in children, intoxication occurs, manifested by nausea, indomitable vomiting, fever, dehydration, and weakness.
Spastic syndrome in diathesis is manifested by bronchoconstriction, pain in the heart, arterial hypertension, migraine-like headaches, intestinal and renal colic, spastic colitis. Asthmatic bronchitis, which is often detected in such patients, can transform into atopic bronchial asthma.

Source: 900igr.net
Neuro-arthritic diathesis in adults is manifested by obesity, atherosclerosis, urolithiasis, nephritis, renal failure, cholelithiasis, diabetes mellitus, and gout.
Diagnostics
To establish a diagnosis, it may be necessary to consult a pediatrician, pediatric dermatologist, allergist-immunologist, rheumatologist, endocrinologist, nephrologist, neurologist, otorhinolaryngologist.
Laboratory diagnostics in case of suspicion of the presence of diathesis consists in conducting a general analysis of blood and urine, a biochemical blood test (determination of the level of glucose, uric acid, cholesterol, phospholipids), immunological studies, analysis of feces for dysbiosis.
If a lymphatic-hypoplastic form of diathesis is suspected, an ultrasound examination of the thymus gland, lymph nodes, adrenal glands, spleen, liver, as well as an X-ray examination of the chest organs are shown.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with dermatitis, psoriasis, erythroderma. The lymphatic-hypoplastic form of diathesis is differentiated with HIV infection, lymphogranulomatosis. The neuro-arthritic form of diathesis is differentiated with tuberculosis, since such children often have a positive Mantoux test, as well as with diabetes mellitus, rheumatism, neuroses.
Diathesis treatment
The main method of diathesis treatment is lifestyle correction. This concept includes adherence to a diet, careful care, a rational daily regimen, and a decrease in the allergenic load on the body.
First aid for allergies is the removal of allergens from the stomach and intestines with the help of Enterosgel, a gel-like enterosorbent.
The gel saturated with water gently cleanses the mucous membrane from allergens. Enterosgel does not stick to the mucous membrane, but gently envelops and promotes recovery.
The collected allergens are securely retained in the globular structure of the gel and removed from the body.
Other powder sorbents have the smallest particles, which, like dust, become clogged in the villi of the intestinal walls, injure and prevent the restoration of the mucous membrane.
Therefore, enterosgel gel enterosorbent is the right choice for allergies in adults and children from the first day of life.
An allergic reaction can occur when a child's skin comes in contact with chlorinated water. If it is not possible to avoid such contacts, it is recommended to rinse the baby's skin after bathing with boiled and free of chlorine water.
Since one of the causes of skin manifestations of diathesis is skin irritation by sweat, it is necessary to prevent the occurrence of diaper rash, maintain optimal humidity (50-70%) and room temperature (about 20 ° C). Also, one should not allow contact of the child's skin with household chemicals, tissues that can cause the development of an allergic reaction (due to the peculiarities of their composition, peculiarities of staining, mechanical properties of some tissues, etc.).
Diet plays an important role. During breastfeeding, the mother's diet should be limited to fats, carbohydrates, table salt, trophoallergens. In some cases (in particular, with increased fat content of breast milk), it is recommended to express and pasteurize milk, after which the top film is removed from the milk.
It is recommended to exclude jelly, pork, rich meat broths, eggs, fish, nuts, spices, legumes from the diet of older children; moderately restrict proteins, fats. Recommended dishes from buckwheat, rice, vegetables. With the neuro-arthritic form of diathesis, purine-rich foods (cocoa, chocolate, spinach, peas) and fatty foods are excluded from the diet. It is important not to overfeed a child with a tendency to diathesis.
Drug treatment of the exudative-catarrhal form of diathesis consists in the appointment of antihistamines, sedative drugs, vitamin complexes (in particular, B vitamins). Local therapy consists in the use of non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs (in the form of an ointment, gel, spray, etc.) to the affected areas, baths with bran, succession, chamomile, oak bark are shown. With a weeping diathesis on the cheeks of a child, lotions with antiseptic drying agents are used.
With the lymphatic-hypoplastic form of diathesis, synthetic and plant adaptogens, massage, therapeutic exercises, hardening are prescribed. If adrenal insufficiency develops, glucocorticoids may be prescribed.
Patients with a neuro-arthritic form of diathesis are prescribed choleretic drugs, vitamins B 6 and B 12. In the event of acetone vomiting, gastric lavage, oral or parenteral (depending on the severity of the condition) rehydration, and a cleansing enema are performed.
In addition to drug therapy, physiotherapy procedures may be prescribed.
Possible complications and consequences
In patients with exudative-catarrhal diathesis, in the case of scratching diathetic rashes, there is a high risk of bacterial infection. The neuro-arthritic form of diathesis is complicated by the development of acetonemic crises. The consequences of this form of diathesis in adults can be obesity, diseases of the urogenital tract, type 2 diabetes mellitus. Sudden death syndrome may occur in patients with lymphatic-hypoplastic diathesis.

Source: 900igr.net
Forecast
With strict implementation of the doctor's recommendations, the prognosis is usually favorable. In most patients, all manifestations of diathesis disappear by the period of puberty. In the case of the development of cardiovascular, autoimmune, allergic diseases and serious metabolic disorders at a young age, the prognosis worsens. Mortality in children in the first years of life with lymphatic-hypoplastic diathesis and thymomegaly is approximately 10%.
Prevention
Antenatal prevention of the development of diathesis in a child consists in adhering to a hypoallergenic diet by a woman during pregnancy, giving up bad habits, preventing late pregnancy toxicosis and extragenital diseases. During the period of breastfeeding, it is also recommended to exclude allergenic foods from the mother's diet.
Children are shown preventive massage, gymnastics, hardening procedures. Clothing for children should be chosen from natural materials and not worn without pretreatment after purchase. If possible, it is necessary to limit the use of synthetic detergents, especially washing powders with biosystems (both for the child's own things and for the clothes of adults who carry it on their hands). If a child has signs of allergy, it is necessary to minimize his contact with potential allergens, it is recommended to iron his clothes and bed linen, carry out regular wet cleaning of the room, take daily walks in the fresh air, and use medications with caution.
Vaccination for children with diathesis is carried out only during the period of remission according to an individual schedule after preparation.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!