- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Heart attack on the legs: consequences
The content of the article:
- Why do some patients suffer from leg infarction?
- Symptoms of a heart attack on the legs
- The consequences of a heart attack on the legs
- First aid and treatment
- Factors affecting the development of heart attack
- Video
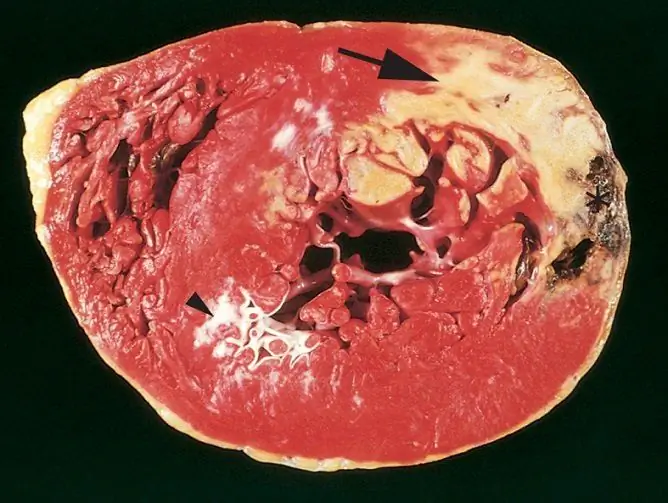
Myocardial infarction transferred on the legs has the same causes and the same mechanism of development as the usual ischemic infarction, but differs in clinical manifestations - in this case, the symptoms appear weakly or do not appear at all. Sometimes patients do not notice a heart attack that has happened, taking a few symptoms for malaise, and learn about it from a doctor many years later, when a scar left after necrosis is found on a heart examination for another reason. However, the consequences of such a heart attack are as significant as with its usual manifestation - do not underestimate this pathology.

Microinfarction patients are often mistaken for temporary malaise or an attack of angina pectoris
Why do some patients suffer from leg infarction?
The term "infarction" refers to a circulatory disorder in which tissues that need abundant blood supply do not receive it and the nutrients and oxygen carried by the blood, as a result of which they die. This can occur in the kidneys, lungs, brain (this condition is called ischemic stroke) and in the heart muscle, that is, the myocardium. The heart tolerates ischemia very poorly, cell death develops within 20 minutes after circulatory disorders.
Depending on which coronary vessel is damaged, large or small, the clinical manifestations can vary. When a large branch of a coronary vessel that supplies blood to a large area of the heart is blocked, a massive heart attack develops. If a small amount of tissue is damaged in the area that feeds on a small artery, the heart remains functional, its function suffers slightly - a microinfarction develops, or, as it is popularly called, a mini-infarction. The patient either does not notice his symptoms (especially often the asymptomatic course of a heart attack occurs in diabetes mellitus, and even with a relatively large area of the lesion), or blames it on habitual malaise, without seeking help from a doctor and without disturbing the usual active lifestyle. In this case, they speak of a heart attack suffered on the legs.
In terms of danger, a latent heart attack is not inferior to an extensive one, even with a small lesion area, due to delayed complications and formidable consequences. In the medical classification, neither a microinfarction nor an erased form is distinguished as a separate pathology - the code for ICD 10 (International Classification of Diseases 10 revision) is the same: identifier I21 - Acute myocardial infarction.
Symptoms of a heart attack on the legs
Due to the shallow depth of the lesion, small-focal infarction has a blurred clinical picture. In manifestations, it is often similar to an attack of angina pectoris, which is often found in the elderly and in young people with pathologies of the cardiovascular system. Can you fail to notice such an attack? This often happens. Clinical manifestations in this case are minimal: short-term weakness, increase and then decrease in pressure, an attack of increased heartbeat, dizziness. Sometimes a microinfarction manifests itself in the same way as a large-focal one, but with less pronounced symptoms.
The first signs of a heart attack include:
- Pain syndrome is a pain behind the breastbone characteristic of a heart attack, which quickly appears and has a burning character. It can be given to the hand, jaw, neck, between the shoulder blades, in the fingertips. Severe heart attack pain is relieved only by narcotic analgesics. With small focal infarction, the pain syndrome is mild or absent.
- The symptom of the showcase is characteristic of a heart attack on the legs, in which a person stops on the street and listens to himself, trying to cope with the pain; from the outside it may seem that he is looking at something in a shop window. The pain does not last long, but indicates ischemic tissue damage.
- Rhythm disturbances - from extremely dangerous ventricular and atrial fibrillations to minor seizures. Often the patient feels an increase in heart rate, clearly feeling each heart beat. A polar situation is possible when patients complain of a feeling of cardiac arrest, slow and weak heart work. This happens when the conductive fibers of the heart are affected by the area of necrosis.
- Somatic manifestations - a feeling of weakness, dizziness, pallor. A person's condition suddenly worsens, cold and sticky sweat comes out, he does not have enough air. With a microinfarction, patients may complain of sudden weakness, shortness of breath, fever.
- Psychological manifestations - a person is seized by anxiety, fear of death, he sensitively listens to any change in the body, a person's responses about his health are often exaggerated. Often this condition remains after an attack for a long time.
Features of the clinical picture depend on the sex of the patient. Men suffer from diseases of the cardiovascular system more often than women, since the female body produces estrogen - a sex hormone that reparatively acts on the vascular wall.
Clinical manifestations in men are more pronounced, they manifest earlier and persist longer, in women they are weaker, often completely absent, a heart attack is more easily tolerated, but this complicates its diagnosis.

Even with implicit signs of cardiac pathology, you should consult a doctor
The consequences of a heart attack on the legs
What is the danger of small focal infarction? Despite the fact that its primary manifestations are usually not interpreted as a great threat, it should be remembered that the death of a part of the heart, albeit a small one, with all the consequences inherent in this condition, occurs. Therefore, when detecting a microinfarction, doctors take it very seriously.
The consequences of a heart attack include:
- Chronic heart failure - develops in almost all patients who have had a heart attack in any form, since part of the heart muscle loses its function. This condition progresses over time. The patient notes shortness of breath, palpitations, and sometimes a cough that is not associated with a disease of the respiratory tract.
- Cardiosclerosis - its total form is more typical for extensive infarction, but a local weakening of the heart wall also develops with a microinfarction. Sometimes, because of the sclerosed area, the wall of the heart bulges out under pressure. Heart enlargement is a common consequence of heart attack, both due to compensatory hypertrophy and due to wall stretching.
- Violations of rhythm and conduction - after an attack, occasional extrasystoles, arrhythmias can persist for a long time.
- Vascular thrombosis - appears due to stagnation of blood in places where the blood flow rate is low enough for this.
Probably the development of complications in the form of aseptic inflammation around the zone of necrosis, which can spread to the inner (endocarditis) and outer shell of the heart (pericarditis).
In addition, if a person has had a heart attack in the past, the risk of a second heart attack for him increases significantly.
First aid and treatment
What to do in case of a heart attack? First of all, do not allow a person to carry him on his feet. If the patient has signs characteristic of a heart attack, it is necessary to call an ambulance, then seat the patient, giving him a reclining position, provide fresh air. It is advisable to give the patient a Nitroglycerin tablet to dilate the coronary vessels, the use of sedatives is allowed.
The tactics of treating the patient is to maintain the functions of the heart, eliminate ischemia, and prevent thrombosis. Prescribed drugs that thin the blood and dissolve possible blood clots, drugs that protect the membranes of heart cells, increase the endurance of the heart muscle under conditions of hypoxia.
In the most acute and acute period (the first few days), the patient is shown strict bed rest. Having a heart attack on the legs significantly increases the risk of developing serious complications.
Factors affecting the development of heart attack
A heart attack is a multifactorial pathology, that is, it is caused by the action of many reasons at once. There are also risk factors that are likely to increase the incidence. These factors need to be known in order to eliminate and thereby reduce the risk of developing a heart attack or, if it has already developed, a second attack.

It is impossible to transfer a heart attack on the legs, strict bed rest is required
Risk factors are:
- atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels - cholesterol plaque in atherosclerosis can increase, blocking the lumen of the vessel so much that the tissue starves first under load conditions, and eventually at rest. It can also come off and cause embolism;
- thromboembolism - dense blood clots can break off, enter the systemic circulation, and then clog the coronary vessels. The embolus can be fat, foreign body, air bubble;
- high blood pressure - contributes to damage to the vascular wall;
- poor diet - abuse of food high in trans fats and cholesterol;
- overweight;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- congenital deformation of the vessel wall.
Based on this list, the prevention of the disease is built. For example, if an elevated content of lipids (fats) is found in the blood, then the menu should be adjusted. The same should be done for overweight patients. It is important to quit smoking and minimize alcohol intake. There should be no limitation of physical activity - refusal from heavy exhausting work should not exclude walks in the fresh air and moderate physical activity. Patients at risk should carefully monitor blood pressure and overall well-being.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Nikita Gaidukov About the author
Education: 4th year student of the Faculty of Medicine No. 1, specializing in General Medicine, Vinnitsa National Medical University. N. I. Pirogov.
Work experience: Nurse of the cardiology department of the Tyachiv Regional Hospital No. 1, geneticist / molecular biologist in the Polymerase Chain Reaction Laboratory at VNMU named after N. I. Pirogov.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.